Abstract
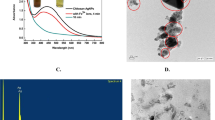
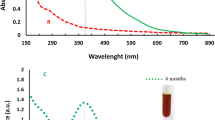
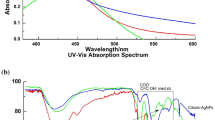
Size uniformity and defined surface coating are important parameters for the biological properties of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). Green synthesis uses biomolecules either in pure form or plant extracts as both reductants and stabilizers yielding a wide size range and capping composed of oxidation products and biomolecules present in the reaction mixture. Herein, we used an established methodology, silver nitrate as the metal precursor, and sodium citrate and tannic acid for reduction and stabilization to produce weakly passivated citrate capped AgNPs (CtAgNPs). Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry was used to determine the total concentration of silver in the purified nanoparticles colloidal dispersion and results correlated with absorbance at localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) peak for quick estimation of silver concentration. The CtAgNPs were functionalized with chitosan oligosaccharide (mean Mn 5000) and betanin to yield chitosan and betanin capped AgNPs. Their biocidal properties were tested against Staphylococcus aureus American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) 12,600. Citrate-stabilized AgNPs had a LSPR peak at 432 nm, mean core diameter of 37.9 ± 8.6 nm, and a monomodal distribution, and were roughly spherical. A slight red shift in LSPR peak was observed upon capping change. The minimum inhibitory concentration against S. aureus was 12.5 ppm Ag for all the nanoparticles. Our study advances the path of exploiting size reproducible techniques in AgNP synthesis, post-synthesis biomolecule functionalization for defined surface, and a clear procedure for estimating the concentration of Ag in assays. This is envisaged to encourage investigations with distinct sizes and capping for cross-comparison.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoli BM, Gumfekar S, Hu A, Zhou YN, Zhao B (2012) Thiocarboxylate functionalization of silver nanoparticles: effect of chain length on the electrical conductivity of nanoparticles and their polymer composites. J Mater Chem 22:20048–20056. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM33280A
Baalousha M, Afshinnia K, Guo L (2018) Natural organic matter composition determines the molecular nature of silver nanomaterial-NOM corona. Environ Sci Nano 5:868–881. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EN00018B
Barbalinardo M, Caicci F, Cavallini M, Gentili D (2018) Protein corona mediated uptake and cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in mouse embryonic fibroblast. Small 14:1801219. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201801219
Barbosa JAC, Abdelsadig MSE, Conway BR, Merchant HA (2019) Using zeta potential to study the ionisation behaviour of polymers employed in modified-release dosage forms and estimating their pKa. Int J Pharm 1:100024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpx.2019.100024
Barillo DJ, Marx DE (2014) Silver in medicine: a brief history BC 335 to present. Burns 40:S3–S8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2014.09.009
Bastús NG, Merkoçi F, Piella J, Puntes V (2014) Synthesis of highly monodisperse citrate-stabilized silver nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: kinetic control and catalytic properties. Chem Mater 26:2836–2846. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm500316k
Bastús NG, Piella J, Puntes V (2016) Quantifying the sensitivity of multipolar (dipolar, quadrupolar, and qctapolar) surface plasmon resonances in silver nanoparticles: the effect of size, composition, and surface coating. Langmuir 32:290–300. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03859
Bell RA, Kramer JR (1999) Structural chemistry and geochemistry of silver-sulfur compounds: critical review. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620180103
Bhattacharjee S (2016) DLS and zeta potential – what they are and what they are not? J Control Release 235:337–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.06.017
Carapeto AP, Ferraria AM, do Rego AMB (2017) Unraveling the reaction mechanism of silver ions reduction by chitosan from so far neglected spectroscopic features. Carbohydr Polym 174:601–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.100
Cavassin ED, de Figueiredo LFP, Otoch JP, Seckler MM, de Oliveira RA, Franco FF, Marangoni VS, Zucolotto V, Levin ASS, Costa SF (2015) Comparison of methods to detect the in vitro activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNP) against multidrug resistant bacteria. J Nanobiotechnol 13:64. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-015-0120-6
Chernousova S, Epple M (2013) Silver as antibacterial agent: ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:1636–1653. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201205923
Chopra I (2007) The increasing use of silver-based products as antimicrobial agents: a useful development or a cause for concern? J Antimicrob Chemother 59:587–590. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkm006
Clogston JD, Patri AK (2011) Zeta potential measurement. In: McNeil SE (ed) Characterization of nanoparticles intended for drug delivery. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 63–70
CLSI (2018) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically CLSI standard M07, 11th edn. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne
Dadosh T (2009) Synthesis of uniform silver nanoparticles with a controllable size. Mater Lett 63:2236–2238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.07.042
De Leersnyder I, De Gelder L, Van Driessche I, Vermeir P (2018) Influence of growth media components on the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Bacillus subtilis in a liquid growth medium. Sci Rep 8:9325. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27540-9
Desireddy A, Conn BE, Guo J, Yoon B, Barnett RN, Monahan BM, Kirschbaum K, Griffith WP, Whetten RL, Landman U, Bigioni TP (2013) Ultrastable silver nanoparticles. Nature 501:399–402. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12523
Durán N, Silveira CP, Durán M, Martinez DST (2015) Silver nanoparticle protein corona and toxicity: a mini-review. J Nanobiotechnol 13:55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-015-0114-4
Edington JW (1975) Electron diffraction in the electron microscope, monographs in practical electron microscopy in materials science, vol 2. philips technical library. Macmillan Press, London
Esteves LC, Pinheiro AC, Pioli RM, Penna TC, Baader WJ, Correra TC, Bastos EL (2018) Revisiting the mechanism of hydrolysis of betanin. Photochem Photobiol 94:853–864. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12897
Fernandes DLA, Paun C, Pavliuk MV, Fernandes AB, Bastos EL, Sá J (2016) Green microfluidic synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles via genetic algorithm optimization. RSC Adv 6:95693–95697. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA20877K
Frank T, Stintzing FC, Carle R, Bitsch I, Quaas D, Straß G, Bitsch R, Netzel M (2005) Urinary pharmacokinetics of betalains following consumption of red beet juice in healthy humans. Pharmacol Res 52:290–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2005.04.005
Gliszczyńska-Świgło A, Szymusiak H, Malinowska P (2006) Betanin, the main pigment of red beet: molecular origin of its exceptionally high free radical-scavenging activity. Food Addit Contam 23:1079–1087. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652030600986032
Gonçalves LCP, Trassi MA d S, Lopes NB et al (2012) A comparative study of the purification of betanin. Food Chem 131:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.08.067
Greulich C, Braun D, Peetsch A, Diendorf J, Siebers B, Epple M, Köller M (2012) The toxic effect of silver ions and silver nanoparticles towards bacteria and human cells occurs in the same concentration range. RSC Adv 2:6981. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra20684f
Griggs JP, Jacob JP (2005) Alternatives to antibiotics for organic poultry production. J Appl Poult Res 14:750–756. https://doi.org/10.1093/japr/14.4.750
Helmlinger J, Sengstock C, Groß-Heitfeld C, Mayer C, Schildhauer TA, Köller M, Epple M (2016) Silver nanoparticles with different size and shape: equal cytotoxicity, but different antibacterial effects. RSC Adv 6:18490–18501. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA27836H
Hühn J, Carrillo-Carrion C, Soliman MG, Pfeiffer C, Valdeperez D, Masood A, Chakraborty I, Zhu L, Gallego M, Yue Z, Carril M, Feliu N, Escudero A, Alkilany AM, Pelaz B, del Pino P, Parak WJ (2017) Selected standard protocols for the synthesis, phase transfer, and characterization of inorganic colloidal nanoparticles. Chem Mater 29:399–461. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b04738
Johnston KA, Smith AM, Marbella LE, Millstone JE (2016) Impact of as-synthesized ligands and low-oxygen conditions on silver nanoparticle surface functionalization. Langmuir 32:3820–3826. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b00232
Johnston KA, Stabryla LM, Smith AM, Gan XY, Gilbertson LM, Millstone JE (2018) Impacts of broth chemistry on silver ion release, surface chemistry composition, and bacterial cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Environ Sci Nano 5:304–312. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EN00974G
Kang H, Buchman JT, Rodriguez RS, Ring HL, He J, Bantz KC, Haynes CL (2019) Stabilization of silver and gold nanoparticles: preservation and improvement of plasmonic functionalities. Chem Rev 119:664–699. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00341
Khan M, Shaik MR, Adil SF, Khan ST, al-Warthan A, Siddiqui MRH, Tahir MN, Tremel W (2018) Plant extracts as green reductants for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles: lessons from chemical synthesis. Dalton Trans 47:11988–12010. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8DT01152D
Le Ouay B, Stellacci F (2015) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: a surface science insight. Nano Today 10:339–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2015.04.002
Lee K-S, El-Sayed MA (2006) Gold and silver nanoparticles in sensing and imaging: sensitivity of plasmon response to size, shape, and metal composition. J Phys Chem B 110:19220–19225. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp062536y
Louie SM, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2016) Critical review: impacts of macromolecular coatings on critical physicochemical processes controlling environmental fate of nanomaterials. Environ Sci Nano 3:283–310. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EN00104H
Manukumar HM, Chandrasekhar B, Rakesh KP, Ananda AP, Nandhini M, Lalitha P, Sumathi S, Qin HL, Umesha S (2017a) Novel T-C@AgNPs mediated biocidal mechanism against biofilm associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (Bap-MRSA) 090, cytotoxicity and its molecular docking studies. MedChemComm 8:2181–2194. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MD00486A
Manukumar HM, Umesha S, Kumar HNN (2017b) Promising biocidal activity of thymol loaded chitosan silver nanoparticles (T-C@AgNPs) as anti-infective agents against perilous pathogens. Int J Biol Macromol 102:1257–1265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.030
Manukumar HM, Yashwanth B, Umesha S, Venkateswara Rao J (2017c) Biocidal mechanism of green synthesized thyme loaded silver nanoparticles (GTAgNPs) against immune evading tricky methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus 090 (MRSA090) at a homeostatic environment. Arab J Chem:S1878535217301880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.09.017
Marpu S, Benton E (2018) Shining light on chitosan: a review on the usage of chitosan for photonics and nanomaterials research. Int J Mol Sci 19:1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061795
Mcmahon MD, Lopez R, Meyer HM et al (2005) Rapid tarnishing of silver nanoparticles in ambient laboratory air. Appl Phys B Lasers Opt 80:915–921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-005-1793-6
Mittal AK, Chisti Y, Banerjee UC (2013) Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol Adv 31:346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.01.003
Nanocomposix (2012) Guidelines for nanotoxicology researchers using nanocomposix materials. https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0257/8237/files/nanoComposix_Guidelines_for_Nanotox_Researchers.pdf?13692. Accessed 6 Mar 2020
Padmos JD, Boudreau RTM, Weaver DF, Zhang P (2015) Impact of protecting ligands on surface structure and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Langmuir 31:3745–3752. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b00049
Paramelle D, Sadovoy A, Gorelik S, Free P, Hobley J, Fernig DG (2014) A rapid method to estimate the concentration of citrate capped silver nanoparticles from UV-visible light spectra. Analyst 139:4855–4861. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AN00978A
Pavliuk MV, Fernandes AB, Abdellah M, Fernandes DLA, Machado CO, Rocha I, Hattori Y, Paun C, Bastos EL, Sá J (2017) Nano-hybrid plasmonic photocatalyst for hydrogen production at 20% efficiency. Sci Rep 7:8670. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09261-7
Pestov A, Nazirov A, Modin E, Mironenko A, Bratskaya S (2015) Mechanism of Au(III) reduction by chitosan: comprehensive study with 13C and 1H NMR analysis of chitosan degradation products. Carbohydr Polym 117:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.09.030
Petersen EJ, Henry TB, Zhao J, MacCuspie RI, Kirschling TL, Dobrovolskaia MA, Hackley V, Xing B, White JC (2014) Identification and avoidance of potential artifacts and misinterpretations in nanomaterial ecotoxicity measurements. Environ Sci Technol 48:4226–4246. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4052999
Phan HT, Haes AJ (2019) What does nanoparticle stability mean? J Phys Chem C 123:16495–16507. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b00913
Rainville L, Dorais M-C, Boudreau D (2013) Controlled synthesis of low polydispersity Ag@SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles for use in plasmonic applications. RSC Adv 3:13953. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra41677a
Ranoszek-Soliwoda K, Tomaszewska E, Małek K, Celichowski G, Orlowski P, Krzyzowska M, Grobelny J (2019) The synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles with plant extracts. Colloids Surf B 177:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.01.037
Ranoszek-Soliwoda K, Tomaszewska E, Socha E, Krzyczmonik P, Ignaczak A, Orlowski P, Krzyzowska M, Celichowski G, Grobelny J (2017) The role of tannic acid and sodium citrate in the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 19:273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3973-9
Rodrigues TS, Zhao M, Yang T et al (2018) Synthesis of colloidal metal nanocrystals: a comprehensive review on the reductants. Chem Eur J 24:16944–16963. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201802194
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Shen H, Lu G, Zhang T, Liu J, Gu Y, Perriat P, Martini M, Tillement O, Gong Q (2013) Shape effect on a single-nanoparticle-based plasmonic nanosensor. Nanotechnology 24:285502. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/28/285502
Stabryla LM, Johnston KA, Millstone JE, Gilbertson LM (2018) Emerging investigator series: it’s not all about the ion: support for particle-specific contributions to silver nanoparticle antimicrobial activity. Environ Sci Nano 5:2047–2068. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EN00429C
Stamplecoskie K (2015) Silver nanoparticles: from bulk material to colloidal nanoparticles. In: Alarcon EI, Griffith M, Udekwu KI (eds) Silver nanoparticle applications: in the fabrication and design of medical and biosensing devices. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 1–12
Tran QH, Nguyen VQ, Le A-T (2013) Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, properties, toxicology, applications and perspectives. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 4:033001. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/4/3/033001
Treichel JL (2004) Antioxidants and ocular cell type differences in cytoprotection from formic acid toxicity in vitro. Toxicol Sci 82:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfh256
Tulve NS, Stefaniak AB, Vance ME, Rogers K, Mwilu S, LeBouf RF, Schwegler-Berry D, Willis R, Thomas TA, Marr LC (2015) Characterization of silver nanoparticles in selected consumer products and its relevance for predicting children’s potential exposures. Int J Hyg Environ Health 218:345–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2015.02.002
Yang T-H, Gilroy DK, Xia Y (2017) Reduction rate as a quantitative knob for achieving deterministic synthesis of colloidal metal nanocrystals. Chem Sci 8:6730–6749. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC02833D
Zook JM, Long SE, Cleveland D, Geronimo CLA, MacCuspie RI (2011) Measuring silver nanoparticle dissolution in complex biological and environmental matrices using UV–visible absorbance. Anal Bioanal Chem 401:1993–2002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5266-y
Acknowledgments
The authors extend gratitude to the Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility (SAIF), Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, for TEM, SAED, EDS, and HR-ICP-MS facilities. We also thank the Institute of Excellence (IOE) at the University of Mysore for providing DLS and zeta potential analysis equipment.
Funding
Mbae, K.M had financial support from the Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India, through the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) to pursue a Ph.D. under the Scholarship Scheme for students from African Countries.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mbae, K.M., Umesha, S. Physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of post-synthesis betanin and chitosan oligosaccharide functionalized silver nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 22, 346 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05070-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05070-8