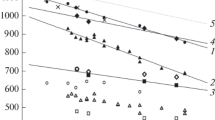
Abstract
Molecular dynamics simulation is used to comparatively investigate the structure stability, lattice variation, and surface energy of Ag nanoparticles. It is revealed that the most stable structure of shapes transformed from an octahedron to a cuboctahedron with the cluster size increasing, and the energetically larger lattice contraction of particles should have higher surface energy. Simulation also shows that the cubic shapes have contributed highly to the lattice contractions of particles, and the lattice constants of octahedral shapes are the nearest to bulk Ag. In addition, a systematic work on the melting behavior of polyhedral shapes is carried out by shape factor, and the surface energy-dependent shape evolution of Ag particles is revealed. The present results agree well with experimental observations in the literature, and provide a deep understanding of the different physical and chemical properties of Ag nanoparticles.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Myasnichenko VS, Neyts EC (2016) Size-dependent strain and surface energies of gold nanoclusters. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:792–800
Baletto F, Mottet C, Ferrando R (2002) Freezing of silver nanodroplets. Chem Phys Lett 354:82–87
Barber CB, Dobkin DP, Huhdanpaa H (1996) The quickhull algorithm for convex hulls. ACM T Math Software 22:469–483
Binkowski I, Shrivastav GP, Horbach J, Divinski SV, Wilde G (2016) Shear band relaxation in a deformed bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater 109:330–340
Chen L, Fan JL, Gong HR (2017) Phase transition and mechanical properties of tungsten nanomaterials from molecular dynamic simulation. J Nanopart Res 19:118
Darbha GK, Ray A, Ray PC (2007) Gold nanoparticle-based miniaturized nanomaterial surface energy transfer probe for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of mercury in soil, water, and fish. ACS Nano 1:208–214
Feng D, Feng Y, Yuan S, Zhang X, Wang G (2017) Melting behavior of Ag nanoparticles and their clusters. Appl Therm Eng 111:1457–1463
Häkkinen H, Abbet S, Sanchez A, Heiz U, Landman U (2003) Structural, electronic, and impurity-doping effects in nanoscale chemistry: supported gold nanoclusters. Angew Chem 42:1297–1300
Huang R, Wen YH, Zhu ZZ, Sun SG (2012) Pt−Pd bimetallic catalysts: structural and thermal stabilities of core−shell and alloyed nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 116:8664–8671
Jiang Q, Liang LH, Zhao DS (2001) Lattice contraction and surface stress of fcc nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 105:6275–6277
Jiang Q, Li JC, Chi BQ (2002) Size-dependent cohesive energy of nanocrystals. Chem Phys Lett 366:551–554
Lewis LN (1993) Chemical catalysis by colloids and clusters. Chem Rev 93:2693–2730
Li ZY, Young NP, Vece MD, Palomba S, Palmer RE, Bleloch AL, Curley BC, Johnston RL, Jiang J, Yuan J (2008) Three-dimensional atomic-scale structure of size-selected gold nanoclusters. Nature 451:46–49
Lim HS, Ong CK (1992) Stability of face-centered cubic and icosahedral lead clusters. Surf Sci 269(270):1109–1115
Liu Y, Wang C, Wei Y, Zhu L, Li D, Jiang JS, Markovic NM, Stamenkovic VR, Sun S (2011) Surfactant-induced postsynthetic modulation of Pd nanoparticle crystallinity. Nano Lett 11:1614–1617
Lu HM, Jiang Q (2004) Size-dependent surface energies of nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 108:5617–5619
Medasani B, Vasiliev I (2009) Computational study of the surface properties of aluminum nanoparticles. Surf Sci 603:2042–2046
Medasani B, Park YH, Vasiliev I (2007) Theoretical study of the surface energy, stress, and lattice contraction of silver nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 75:235436
Neyts EC, Bogaerts A (2009) Numerical study of the size-dependent melting mechanisms of nickel nanoclusters. J Phys Chem C 113:2771–2776
Ouyang G, Wang CX, Yang GW (2009) Surface energy of nanostructural materials with negative curvature and related size effects. Chem Rev 109:4221–4247
Pavan L, Baletto F, Novakovic R (2015) Multiscale approach for studying melting transitions in CuPt nanoparticles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:28364–28371
Plimpton S (1995) Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J Comp Phys 117:1–19
Preston-Thomas H (1990) The International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90). Metrologia 27:3–10
Qi WH, Huang BY, Wang MP, Yin ZM, Li JJ (2009) Molecular dynamic simulation of the size-and shape-dependent lattice parameter of small platinum nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 11:575–580
Rapallo A, Olmos-Asar JA, Oviedo OA, Ludueña M, Ferrando R, Mariscal MM (2012) Thermal properties of Co/Au nanoalloys and comparison of different computer simulation techniques. J Phys Chem C 116:17210–17218
Ruda M, Crespo EA, Debiaggic SR (2010) Atomistic modeling of H absorption in Pd nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 495:471–475
Stich I, Car R, Parrinello M, Baroni S (1989) Conjugate gradient minimization of the energy functional: a new method for electronic structure calculation. Phys Rev B 39:4997–5004
Stukowski A (2010) Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO–the open visualization tool. Model Simul Mater Sc 18:015012
Sun J, He L, Lo YC, Xu T, Bi H, Sun L, Zhang Z, Mao SX, Li J (2014) Liquid-like pseudoelasticity of sub-10-nm crystalline silver particles. Nature Mater 13:1007–1012
Tao A, Sinsermsuksakul P, Yang P (2006) Polyhedral silver nanocrystals with distinct scattering signatures. Angew Chem 45:4597–4601
Wang Y, Teitel S, Dellago C (2004) Melting and equilibrium shape of icosahedral gold nanoparticles. Chem Phys Lett 394:257–261
Wang ZL, Zhong YQ, Wang SY (2012) A new shape factor measure for characterizing the cross-section of profiled fiber. Tex Res J 82:454
Wang Y, Wan D, Xie S, Xia X, Huang CZ, Xia Y (2013) Synthesis of silver octahedra with controlled sizes and optical properties via seed-mediated growth. ACS Nano 7:4586–4594
Wang Q, Chen L, Xiong L, Gong HR (2017) Mechanical and thermodynamic properties of cubic boron nitride from ab initio calculation. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 104:276–280
Wasserman HJ, Vermaak JS (1970) On the determination of a lattice contraction in very small silver particles. Surf Sci 22:164–172
Wu YN, Huang R, Zhang XM, Wen YH (2016) Octadecahedral and dodecahedral iron nanoparticles: an atomistic simulation on stability and shape evolutions. Phys Lett A 380:739–744
Zhou XW, Johnson RA, Wadley HNG (2004) Misfit-energy-increasing dislocations in vapor-deposited CoFe/NiFe multilayers. Phys Rev B 69:144113
Funding
This research work was supported by the Youth Project of Science and Technology of Jiangxi Provincial Education Development (Grant No. GJJ160714), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20171BBB216002), Science Foundation of Aeronautics of China (Grant No. 2016ZF56022), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51463017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Wang, Q. & Xiong, L. Molecular dynamics study on structure stability, lattice variation, and melting behavior of silver nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 19, 300 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4003-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4003-7