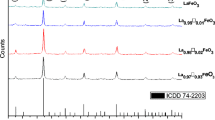
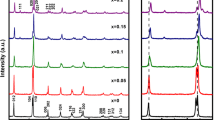
Abstract
Exchange bias (EB) of multiferroics presents many potential opportunities for magnetic devices. However, instead of using low-temperature field cooling in the hysteresis loop measurement, which usually shows an effective approach to obtain obvious EB phenomenon, there are few room temperature EB. In this article, extensive studies on room temperature EB without field cooling were observed in BiFeO3 nano- and microcrystals. Moreover, with increasing size the hysteresis loops shift from horizontal negative exchange bias (NEB) to positive exchange bias (PEB). In order to explain the tunable EB behaviors with size dependence, a phenomenological qualitative model based on the framework of antiferromagnetic (AFM) core-two-dimensional diluted antiferromagnet in a field (2D-DAFF) shell structure was proposed. The training effect (TE) ascertained the validity of model and the presence of unstable magnetic structure using Binek’s model. Experimental results show that the tunable EB effect can be explained by the competition of ferromagnetic (FM) exchange coupling and AFM exchange coupling interaction between AFM core and 2D-DAFF shell. Additionally, the local distortion of lattice fringes was observed in hexagonal-shaped BiFeO3 nanocrystals with well-dispersed behavior. The electrical conduction properties agreed well with the space charge-limited conduction mechanism.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadvand H, Safdari SR, Golikand AN, Dasgupta P, Poddar A, Salamati H (2015) Exchange bias in Co/CoO/Co3O4 nanostructures. J Magn Magn Mater 377:19–23. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.10.021
Belik AA (2013) Origin of magnetization reversal and exchange bias phenomena in solid solutions of BiFeO3-BiMnO3: intrinsic or extrinsic? Inorg Chem 52:2015–2021. doi:10.1021/ic302384j
Bink C (2004) Training of the exchange-bias effect: a simple analytic approach. Phys Rev B 70:014421. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.70.014421
Chakrabarti K, Dalal B, Ashok VD, Das K, Chaudhuri SS, De SK (2014b) Large magnetic exchange anisotropy at a heterointerface composed of nanostructured BiFeO3 and NiO. J Phys D Appl Phys 47:325002. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/47/32/325002
Chakrabarti K, Sarkar B, Ashok VD, Das K, Chanclhuri SS, De SK (2013) Interfacial magnetism and exchange coupling in BiFeO3-CuO nanocomposite. Nanotechnology 24:505711. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/24/50/505711
Chaturvedi S, Shirolkar MM, Rajendra R, Singh S, Ballav N, Kulkarni S (2014b) Coercivity and exchange bias of bismuth ferrite nanoparticles isolated by polymer coating. J Appl Phys 115:123906. doi:10.1063/1.4869657
Chen XZ, Qiu ZC, Zhou JP, Zhu GQ, Bian XB, Liu P (2011) Large-scale growth and shape evolution of bismuth ferrite particles with a hydrothermal method. Mater Chem Phys 126:560–567. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.01.027
Chen P, Günaydln-Sen Ö, Ren WJ, Qin Z, Brinzari TV, McGill S, Cheong SW, Musfeldt JL (2012) Spin cycloid quenching in Nd3+-substituted BiFeO3. Phys Rev B 86:014407. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.86.014407
Chuturvedi S, Das R, Poddar P, Kulkarni S (2015) Tunable band gap and coercivity of bismuth ferrite-polyaniline core-shell nanoparticles: the role of shell thickness. RSC Adv 5:23563–23568. doi:10.1039/C5RA00933B
Ceylan A, Baker CC, Hasanain SK, Shah SI (2006) Effect of particle size on the magnetic properties of core-shell structure nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 100:034301. doi:10.1063/1.2219691
Chaturvedi S, Sarkar I, Shirolkar MM, Jeng US, Yeh YQ, Rajendra R, Ballav N, Kulkarni S (2014a) Probing bismuth ferrite nanoparticles by hard x-ray photoemission: anomalous occurrence of metallic bismuth. Appl Phys Lett 105:102910. doi:10.1063/1.4895672
Chakrabarti K, Sarkar B, Ashok VD, Das K, Chaudhuri SS, Mitra A, De SK (2014a) Exchange bias effect in BiFeO3-NiO nanocomposite. J Appl Phys 115:013906. doi:10.1063/1.4861140
Chen ZW, Wu YP, Hu JQ (2013) Ethanol-assisted hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of BiFeO3 nanopowders. J Am Ceram Soc 96:1345. doi:10.1111/jace.12296
Dieny B (1994) Giant magnetoresistance in spin-value multilayers. J Magn Magn Mater 136:335–359. doi:10.1016/0304-8853(94)00356-4
Dong SN, Yao YP, Hou Y, Liu YK, Tang Y, Li XG (2011) Dynamic properties of spin cluster glass and exchange bias effect in BiFeO3 nanocrystals. Nanotechnology 22:385701. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/22/38/385701
Dho J, Qi XD, Kim H, MacManus-Driscoll JL, Blamire MG (2006) Large electric polarization and exchange bias in multiferroic BiFeO3. Adv Mater 18:1445–1448. doi:10.1002/adma.200502622
Dai HY, Chen J, Li T, Liu DW, Xue RZ, Xiang HW, Chen ZP (2015) Effect of BaTiO3 doping on the structural, electrical and magnetic properties of BiFeO3 ceramics. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 26:3717–3721. doi:10.1007/s10854-015-2890-x
Huang FZ, Wang ZJ, Lu XM, Zhang JT, Min KL, Lin WW, Ti RX, Xu TT, He J, Yue C, Zhu JS (2014) Peculiar magnetism of BiFeO3 nanoparticles with size approaching the period of the spiral spin structure. Sci Rep 3:2907. doi:10.1038/srep02907
Huang XH, Ding JF, Zhang GQ, Hou Y, Yao YP, Li XG (2008) Size-dependent exchange bias in La0.25Ca0.75MnO3 nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 78:224408. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.78.224408
Lebeugle D, Colson D, Forget A, Viret M, Bonville P, Marucco JF, Fusil S (2007) Room-temperature coexistence of large electric polarization and magnetic order in BiFeO3 single crystals. Phys Rev B 76:024116. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.76.024116
Lu SZ, Qi XD (2014) Magnetic and dielectric properties of nanostructured BiFeO3 prepared by sol-gel method. J Am Ceram Soc 97:2185–2194. doi:10.1111/jace.12960
Meiklejohn WH, Bean CP (1957) New magnetic anisotropy. Phys Rev 105:904–913. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.102.1413
Moran TJ, Gallego JM, Schuller IK (1995) Increased exchange anisotropy due to disorder at permalloy/CoO interfaces. J Appl Phys 78:1887–1891. doi:10.1063/1.360225
Manna PK, Yusuf SM, Shukla R, Tyagi AK (2011) Exchange bias in BiFe0.8Mn0.2O3 nanoparticles with an antiferromagnetic core and a diluted antiferromagnetic shell. Phys Rev B 83:184412. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.83.184412
Mocherla RSV, Karthik C, Ubic R, Rao MSR, Sudakar C (2013) Tunable bandgap in BiFeO3 nanoparticles: the role of microstrain and oxygen defects. Appl Phys Lett 103:022910. doi:10.1063/1.4813539
Mocherla PSV, Karthik C, Ubic R, Rao MSR, Sudakar C (2014) Effect of microstrain on the magnetic properties of BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 105:132409. doi:10.1063/1.4897143
Mao ZQ, Zhan XZ, Chen X (2015) Exchange bias in diluted-antiferromagnet/antiferromagnet bilayers. J Phys D Appl Phys 48:025002. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/48/2/025002
Mishra SK, Radu F, Dürr HA, Eberhardt W (2009a) Training-induced positive exchange bias in NiFe/IrMn bilayers. Phys Rev Lett 102:177208. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.177208
Nogués J, Lederman D, Moran TJ, Schuller IK (1996) Positive exchange bias in FeF2-Fe bilayers. Phys Rev Lett 76:4624–4627. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.76.4624
Parkin S, Jiang X, Kasier C, Panchula A, Roche K, Samant M (2003) Magnetically engineered spintronic sensors and memory. Rroc IEEE 91:661–680. doi:10.1109/JPROC.2003.811807
Park TJ, Papaefthymiou GC, Viescas AJ, Moodenbaugh AR, Wong SS (2007) Size-dependent magnetic properties of single-crystalline multiferroic BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Nano Lett 7:766–772. doi:10.1021/nl063039w
Palewicz A, Przenioslo R, Sosnowska I, Hewat AW (2007) Atomic displacements in BiFeO3 as a function of temperature: neutron diffraction study. Acta Cryst B63:537–544. doi:10.1107/S0108768107023956
Passamani EC, Larica C, Marques C, Takeuchi AY, Proveti JR, Favre-Nicolin E (2007) Large vertical loop shifts in mechanically synthesized (Mn, Fe)2O3-tnanograins. J Magn Magn Mater 314:21–29. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2007.02.008
Pradhan DK, Choudhary RNP, Rinaldi C, Katiyar RS (2009) Effect of Mn substitution on electrical and magnetic properties of Bi0.9La0.1FeO3. J Appl Phys 106:024102. doi:10.1063/1.3158121
Quan Z, Hu H, Xu S, Liu W, Fang GJ, Li MY, Zhao XZ (2008) Surface chemical bonding states and ferroelectricity of Ce-doped BiFeO3 thin films prepared by sol-gel process. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 48:261–266. doi:10.1007/s10971-008-1825-x
Reddy KR, Park W, Sin BC, Noh J, Lee Y (2009) Synthesis of electrically conductive and superparamagnetic monodispersed iron oxide-conjugated polymer composite nanoparticles by in situ chemical. J Colloid and Interface Sci 335:34–39. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2009.02.068
Reddy KR, Lee KP, Gopalan AI, Kim MS, Showkat AM, Nho YC (2006) Synthesis of metal (Fe orPd)/alloy (Fe-Pd)-nanoparticles-embedded multiwall carbon nanotube/sulfonated polyaniline composites by γ-irradiation. J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem 44:3355–3364. doi:10.1002/pola.21451
Reddy KR, Sin BC, Yoo CH, Park W, Ryu KS, Lee JS, Sohn D, Lee Y (2008) A new one-step synthesis method for coating multi-walled carbon nanotubes with cuprous oxide nanoparticles. Scr Mater 58:1010–1013. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.01.047
Reddy KR, Lee KP, Gopalan AI (2007) Novel electrically conductive and ferromagnetic composites of poly(aniline-co-aminonaphthalenesulfonic acid) with iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and characterization. J Appl Polym Sci 106:1181–1191. doi:10.1002/app.26601
Ramachandran B, Dixit A, Naik R, Lawes G, Rao MSR (2010) Charge transfer and electronic transitions in polycrystalline BiFeO3. Phys Rev B 82:012102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.82.012102
Su YC, Hu JG (2012) Exchange bias training effect under different energy dissipation pattern. J Appl Phys 112:043906. doi:10.1063/1.4748266
Tamilsevan A, Balakumar S, Sakar M, Nayek C, Murugavel P, Kumarc KS (2014) Role of oxygen vacancy and Fe-O-Fe bond angle in compositional, magnetic, and dielectric relaxation on Eu-substituted BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Dalton Trans 43:5731. doi:10.1039/C3DT52260A@@@10.1039/C3DT52260A
Wang J, Neaton JB, Zheng H, Nagarajan V, Ogale SB, Liu B, Viehland D, Vaithyanathan V, Schlom DG, Waghmare UV et al (2003) Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures. Science 299:1719–1722. doi:10.1126/science.1080615
Wang BM, Liu Y, Ren P, Xia B, Ruan KB, Yi JB, Ding J, Li XG, Wang L (2011) Large exchange bias after zero-field cooling from an unmagnetized state. Phys Rev Lett 106:077203. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.077203
Xue XB, Yuan XY, Rui WB, Xu QY, You B, Zhang W, Zhou S, Du J (2013) Temperature dependent exchange bias effect in polycrystalline BiFeO3/FM (FM=NiFe, Co) bilayers. Eur Phys J B 86:121. doi:10.1140/epjb/e2013-31003-y
Xu XL, Liu WF, Zhang H, Guo MC, Wu P, Wang SY, Gao J, Rao GH (2015) The abnormal electrical and optical properties in Na and Ni codoped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 117:174106. doi:10.1063/1.4919822
Yang YC, Liu Y, Wei JH, Pan CX, Xiong R, Shi J (2014) Electrospun nanofibers of p-type BiFeO3/n-type TiO2 hetero-junctions with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv 4:31941. doi:10.1039/C4RA04258A
Zhang WR, Chen AP, Jian J, Zhu YY, Chen L, Lu P, Jia QX, MacManus-Driscoll JL, Zhang XH, Wang HY (2015) Strong perpendicular exchange bias in epitaxial La0.7Sr0.3MnO3:BiFeO3 nanocomposite films through vertical interfacial coupling. Nanoscale 7:13808. doi:10.1039/C5NR03231H
Zhang H, Liu WF, Wu P, Hai X, Guo MC, Xi XJ, Gao J, Wang X, Guo F, Xu XL et al (2014) Novel behaviors of multiferroic properties in Na-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Nano 6:10831. doi:10.1039/C4NR02557A@@@10.1039/C4NR02557A
Zhou JP, Yang RL, Xiao RJ, Chen XM, Dong CY (2012) Structure and phase transition of BiFeO3 cubic micro-particles prepared by hydrothermal method. Mater Res Bull 47:3630–3636. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.06.050
Zhu XH, Hang QM, Xing ZB, Yang Y, Zhu JM, Liu ZG, Ming NB, Zhou P, Song Y, Li ZS et al (2011) Microwave hydrothermal synthesis, structural characterization, and visible-light photocatalytic activities of single-crystalline bismuth ferric nanocrystals. J Am Ceram Soc 94:2688–2693. doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2011.04430.x
Zhang BS, Quan ZC, Zhang TJ, Guo T, Mo SB (2007) Effect of oxygen gas and annealing treatment for magnetically enhanced reactive ion etched (Ba0.65, Sr0.35) TiO3 thin films. J Appl Phys 101:014107. doi:10.1063/1.2402100
Zhou JP, Xiao RJ, Zhang YX, Shi ZH, Zhu GQ (2015) Novel behaviors of single-crystalline BiFeO3nanorods hydrothermally synthesized under magnetic field. J Mater Chem C 3:6924–6931. doi:10.1039/C5TC00747J@@@10.1039/C5TC00747J
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 11104202 and 51572193) and the Research Grant Council of Hong Kong (Project No. HKU 702112P and RGC 701813).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 6572 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Wang, S.Y., Liu, W.F. et al. Room temperature exchange bias in multiferroic BiFeO3 nano- and microcrystals with antiferromagnetic core and two-dimensional diluted antiferromagnetic shell. J Nanopart Res 19, 182 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3880-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3880-0