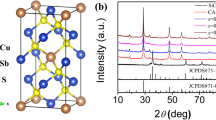
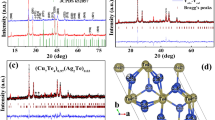
Abstract
In this study, large-scale synthesis of Cu3SbSe4 and Cu3Sb0.98Sn0.02Se4 nanoparticles with a narrow size distribution was achieved through a rapid-injection route. These nanoparticles showed a monodisperse and quasi-spherical morphology. The Cu3SbSe4 and Cu3Sb0.98Sn0.02Se4 nanoparticle-based bulk materials were then prepared by hot-pressed sinter of the nanoparticles, and their thermoelectric performances were systematically studied. Due to the reduced lattice thermal conductivity from enhanced phonon scattering at the grain interfaces of the bulk materials, the maximum ZT value of the Cu3Sb0.98Sn0.02Se4 bulk materials reached 0.50 at 575 K.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biswas K, He J, Blum ID, Wu CI, Hogan TP, Seidman DN, Dravid VP, Kanatzidis MG (2012) High-performance bulk thermoelectrics with all-scale hierarchical architectures. Nature 489:414–418. doi:10.1038/nature11439
de Mello Donega C, Liljeroth P, Vanmaekelbergh D (2005) Physicochemical evaluation of the hot-injection method, a synthesis route for monodisperse nanocrystals. Small 1:1152–1162. doi:10.1002/smll.200500239
Do D, Ozolins V, Mahanti SD, Lee MS, Zhang Y, Wolverton C (2012) Physics of bandgap formation in Cu-Sb-Se based novel thermoelectrics: the role of Sb valency and Cu d levels. J Phys Condens Matter 24:415502. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/24/41/415502
Fan J, Liu HL, Shi XY, Bai SQ, Shi X, Chen LD (2013) Investigation of thermoelectric properties of Cu2GaxSn(1−x)Se3 diamond-like compounds by hot pressing and spark plasma sintering. Acta Mater 61:4297–4304. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2013.04.003
Godart C (2009) Materiaux a Effets Thermoelectriques. Éditions techniques de l’ingénieur
Hicks LD, Dresselhaus MS (1993) Thermoelectric figure of merit of a one-dimensional conductor. Phys Rev B 47:16631–16634. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.47.16631
Lenoir B, Michenaud J-P and Dauscher A (2010) Thermoelectricite: des Principes aux Applications. Éditions techniques de l’ingénieur
Li D, Li R, Qin X-Y, Zhang J, Song C-J, Wang L, Xin H-X (2013a) Co-precipitation synthesis of Sn and/or S doped nanostructured Cu3Sb1−xSnxSe4−ySy with a high thermoelectric performance. CrystEngComm 15:7166. doi:10.1039/c3ce40956b
Li W, Zamani R, Ibanez M, Cadavid D, Shavel A, Morante JR, Arbiol J, Cabot A (2013b) Metal ions to control the morphology of semiconductor nanoparticles: copper selenide nanocubes. J Am Chem Soc 135:4664–4667. doi:10.1021/ja400472m
Li XY, Li D, Xin HX, Zhang J, Song CJ, Qin XY (2013c) Effects of bismuth doping on the thermoelectric properties of Cu3SbSe4 at moderate temperatures. J Alloys Compd 561:105–108. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.01.131
Li D, Li R, Qin XY, Song CJ, Xin HX, Wang L, Zhang J, Guo GL, Zou TH, Liu YF, Zhu XG (2014) Co-precipitation synthesis of nanostructured Cu3SbSe4 and its Sn-doped sample with high thermoelectric performance. Dalton Trans 43:1888–1896. doi:10.1039/c3dt52447g
Liu ML, Chen IW, Huang FQ, Chen LD (2009) Improved thermoelectric properties of Cu-doped quaternary chalcogenides of Cu2CdSnSe4. Adv Mater 21:3808–3812
Madras G, McCoy BJ (2001) Distribution kinetics theory of Ostwald ripening. J Chem Phys 115:6699–6706. doi:10.1063/1.1403687
Mateeva N, Niculescu H, Schlenoff J, Testardi L (1998) Correlation of Seebeck coefficient and electric conductivity in polyaniline and polypyrrole. J Appl Phys 83:3111–3117
Nolas GS, Takizawa H, Endo T, Sellinschegg H, Johnson DC (2000) Thermoelectric properties of Sn-filled skutterudites. Appl Phys Lett 77:52. doi:10.1063/1.126874
O’Dwyer MF, Humphrey TE, Linke H (2006) Concept study for a high-efficiency nanowire based thermoelectric. Nanotechnology 17:S338–S343. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/17/11/s18
Pei Y, Shi X, LaLonde A, Wang H, Chen L, Snyder GJ (2011) Convergence of electronic bands for high performance bulk thermoelectrics. Nature 473:66–69. doi:10.1038/nature09996
Poudel B, Hao Q, Ma Y, Lan YC, Minnich A, Yu B, Yan XA, Wang DZ, Muto A, Vashaee D, Chen XY, Liu JM, Dresselhaus MS, Chen G, Ren ZF (2008) High-thermoelectric performance of nanostructured bismuth antimony telluride bulk alloys. Science 320:634–638. doi:10.1126/science.1156446
Shakouri A (2011) Recent developments in semiconductor thermoelectric physics and materials. In: Clarke DR, Fratzl P (eds) Annual review of materials research, vol 41. Annual Reviews, Palo Alto, pp 399–431
Shi XY, Huang FQ, Liu ML, Chen LD (2009) Thermoelectric properties of tetrahedrally bonded wide-gap stannite compounds Cu2ZnSn1−xInxSe4. Appl Phys Lett 94:122103. doi:10.1063/1.3103604
Shi X, Xi L, Fan J, Zhang W, Chen L (2010) Cu–Se bond network and thermoelectric compounds with complex diamondlike structure. Chem Mater 22:6029–6031. doi:10.1021/cm101589c
Skoug EJ, Cain JD, Morelli DT (2011) High thermoelectric figure of merit in the Cu3SbSe4-Cu3SbS4 solid solution. Appl Phys Lett. doi:10.1063/1.3605246
Skoug EJ, Cain JD, Morelli DT (2012) Improved thermoelectric performance in Cu-based ternary chalcogenides using S for Se substitution. J Electron Mater 41:1232–1236. doi:10.1007/s11664-012-1969-x
Wei T-R, Wang H, Gibbs ZM, Wu C-F, Snyder GJ, Li J-F (2014) Thermoelectric properties of Sn-doped p-type Cu3SbSe4: a compound with large effective mass and small band gap. J Mater Chem A 2:13527–13533
Yang SH, Zhu TJ, Sun T, He J, Zhang SN, Zhao XB (2008) Nanostructures in high-performance (GeTe)x(AgSbTe2)100−x thermoelectric materials. Nanotechnology 19:245707. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/19/24/245707
Yang CY, Huang FQ, Wu LM, Xu K (2011) New stannite-like p-type thermoelectric material Cu3SbSe4. J Phys D. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/44/29/295404
Zhu P, Imai Y, Isoda Y, Shinohara Y, Jia X, Ren G, Zou G (2004) Electrical transport and thermoelectric properties of PbTe prepared by HPHT. Mater Trans 45:3102–3105
Zou TH, Qin XY, Li D, Li LL, Sun GL, Wang QQ, Zhang J, Xin HX, Liu YF, Song CJ (2014) Enhanced thermoelectric performance of β-Zn4Sb3 based composites incorporated with large proportion of nanophase Cu3SbSe4. J Alloys Compd 588:568–572. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.049
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge support for this research received from the Program for Innovative Research Team in University of Ministry of Education of China (IRT13R54).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Qiao, X., Fan, X. et al. Facile synthesis of monodisperse Cu3SbSe4 nanoparticles and thermoelectric performance of Cu3SbSe4 nanoparticle-based materials. J Nanopart Res 17, 285 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3094-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3094-2