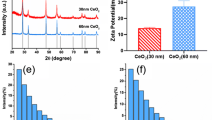
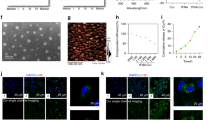
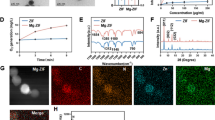
Abstract
Cerium oxide nanoparticles (nanoceria) have been widely used in industries and biomedical fields due to its unique properties. Previous biodistribution studies of nanoceria in vivo have shown that they are accumulated in the bone of mice after intravenous administration, about 20 % of the total intake, however, the potential effect and the mechanism of nanoceria on bone metabolism are not well-understood. Our results showed that both 25 and 50 nm nanceria decreased the damage of cell viability induced by H2O2 in a dose-dependent manner. The apoptosis ratio of pre-incubated group with nanoceria was lower than the H2O2 group. The cellular uptake studies indicated that there was a dose-dependent accumulation of both two size nanoparticles in bone marrow stromal cells. Nanoceria could be uptaken by cells due to the synergistic effect of multiple endocytosis mechanisms, and then evenly distributed in the cytoplasm without entering the nucleus. Our results suggest that nanoceria could reduce intracellular ROS level induced by H2O2 in a dose-dependent manner, moreover, maintain the normal function of mitochondria, suggesting nanoceria may have potent applications for preventing or treating osteoporosis.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin KA, Hassan MS, Awad el ST, Hashemel KS (2011) The protective effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles against hepatic oxidative damage induced by monocrotaline. Int J Nanomed 6:143–149
Bai XC, Lu D, Bai J, Zheng H, Ke ZY, Li XM, Luo SQ (2004) Oxidative stress inhibits osteoblastic differentiation of bone cells by ERK and NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314:197–207
Chen Q, Takeyama N, Brady G, Watson AJ, Dive C (1998) Blood cells with reduced mitochondrial membrane potential and cytosolic cytochrome c can survive and maintain clonogenity given appropriate signals to suppress apoptosis. Blood 92:4545–4553
Chen J, Patil S, Seal S, McGinnis JF (2006) Rare earth nanoparticles prevent retinal degeneration induced by intracellular peroxides. Nat Nanotechnol 1:142–150
Colon J, Herrera L, Smith J, Patil S, Komanski C, Kupelian P, Seal S, Jenkins DW, Baker CH (2009) Protection from radiation-induced pneumonitis using cerium oxide nanoparticles. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 5:225–231
Corma A, Atienzar P, García H, Chane-Ching JY (2004) Hierarchically mesostructured doped cerium oxide with potential for solar-cell use. Nat Mater 3:394–397
Das M, Patil S, Bhargava N, Kang JF, Riedel LM, Seal S, Hickman JJ (2007) Auto-catalytic ceria nanoparticles offer neuroprotection to adult rat spinal cord neurons. Biomaterials 28:1918–1925
Dong XT, Hong GY, Yu DC, Yu DS (1997) Synthesis and properties of cerium oxide nanometer powder by pyrolysis of amorphous citrate. J Mater Sci Technol 13:113–116
Estevez AY, Pritchard S, Harper K, Aston JW, Lynch A, Lucky JJ, Ludington JS, Chatani P, Mosenthal WP, Leiter JC, Andreescu S, Erlichman JS (2011) Neuroprotective mechanisms of cerium oxide nanoparticles in a mouse hippocampal brain slice model of ischemia. Free Radic Biol Med 51:1155–1163
Greulich C, Diendorf J, Simon T, Eggeler G, Epple M, Köller M (2011) Uptake and intracellular distribution of silver nanoparticles in human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater 7:347–354
Heckert EG, Karakoti AS, Seal S, Self WT (2008) The role of cerium redox state in the SOD mimetic activity of nanoceria. Biomaterials 29:2705–2709
Hirst SM, Karakoti AS, Tyler RD, Sriranganathan N, Seal S, Reilly CM (2009) Anti-inflammatory properties of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Small 5:2848–2856
Horie M, Nishio K, Fujita K, Endoh S, Miyauchi A, Saito Y, Iwahashi H, Yamamoto K, Murayama H, Nakano H, Nanashima N, Niki E, Yoshida Y (2009) Protein adsorption of ultrafine metal oxide and its influence on cytotoxicity toward cultured cells. Chem Res Toxicol 22:543–553
Karakoti A, Hench LL, Seal S (2006) The potential toxicity of nanomaterials-The role of surfaces. JOM 58:77–82
Karakoti A, Singh S, Dowding JM, Seal S, Self WT (2010) Redox-active radical scavenging nanomaterials. Chem Soc Rev 39:4422–4432
Korsvik C, Patil S, Seal S, Self WT (2007) Superoxide dismutase mimetic properties exhibited by vacancy engineered ceria nanoparticles. Chem Commun 14:1056–1058
Li XD, Wang JS, Chang B, Chen B, Guo C, Hou GQ, Huang DY, Du SX (2011) Contents lists available at sciencedirect journal of ethnopharmacology panax notoginseng saponins promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells. J Ethnopharmacol 134:268–274
Lin W, Huang YW, Zhou XD, Ma Y (2006) Toxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles in human lung cancer cells. Int J Toxicol 25:451–457
Liu AL, Zhang ZM, Zhu BF, Liao ZH, Liu Z (2004) Metallothionein protects bone marrow stromal cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced inhibition of osteoblastic differentiation. Cell Biol Int 28:905–911
Liu Y, Jiao F, Qiu Y, Li W, Lao F, Zhou G, Sun B, Xing G, Dong J, Zhao Y, Chai Z, Chen C (2009) The effect of Gd@C82(OH)22 nanoparticles on the release of Th1/Th2cytokines and induction of TNF-a mediated cellular immunity. Biomaterials 30:3934–3945
Lord MS, Jung M, Teoh WY, Gunawan C, Vassie JA, Amal R, Whitelock JM (2012) Cellular uptake and reactive oxygen species modulation of cerium oxide nanoparticles in human monocyte cell line U937. Biomaterials 33:7915–7924
Mancini M, Anderson BO, Caldwell E, Sedghinasab M, Paty PB, Hockenbery DM (1997) Mitochondrial proliferation and paradoxical membrane depolarization during terminal differentiation and apoptosis in a human colon carcinoma cell line. J Cell Biol 138:449–469
Martinou I, Desagher S, Eskes R, Antonsson B, André E, Fakan S, Martinou JC (1999) The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria during apoptosis of NGF-deprived sympathetic neurons is a reversible event. J Cell Biol 144:883–889
Matés JM, Sánchez-Jiménez FM (2000) Role of reactive oxygen species in apoptosis: implications for cancer therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32:157–170
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Ozgocmen S, Kaya H, Fadillioglu E, Aydogan R, Yilmaz Z (2007) Role of antioxidant systems, lipid peroxidation and nitric oxide in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Mol Cell Biochem 295:45–52
Pagliari F, Mandoli C, Forte G, Magnani E, Pagliari S, Nardone G, Licoccia S, Minieri M, Di Nardo P, Traversa E (2012) Cerium oxide nanoparticles protect cardiac progenitor cells from oxidative stress francesca pagliari. ACS Nano 6:3767–3775
Ray G, Husain SA (2002) Oxidants, antioxidants and carcinogenesis. Indian J Exp Bio 40:1213–1232
Robert AY, Tu CA, Robert MP (2012) Distribution, elimination, and biopersistence to 90 days of a systemically introduced 30 nm ceria-engineered nanomaterial in rats. Toxicol Sci 127:256–268
Sánchez-Rodríguez MA, Ruiz-Ramos M, Correa-Muñoz E, Mendoza-Núñez VM (2007) Oxidative stress as a risk factor for osteoporosis in elderly Mexicans as characterised by antioxidant enzymes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 8:124–130
Schubert D, Dargusch R, Raitano J, Chan SW (2006) Cerium and yttrium oxide nanoparticles are neuroprotective. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342:86–91
Singh S, Kumar A, Karakoti A, Seal S, Self WT (2010) Unveiling the mechanism of uptake and sub-cellular distribution of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Mol BioSyst 6:1813–1820
Tarnuzzer RW, Colon J, Patil S, Seal S (2005) Vacancy engineered ceria nanostructures for protection from radiation-induced cellular damage. Nano Lett 5:2573–2577
van Engeland M, Nieland LJ, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B, Reutelingsperger CP (1998) Annexin V-affinity assay: a review on an apoptosis detection system based on phosphatidylserine exposure. Cytometry 31:1–9
Vander Heiden MG, Chandel NS, Williamson EK, Schumacker PT, Thompson CB (1997) Bcl-xL regulates the membrane potential and volume homeostasis of mitochondria. Cell 91:627–637
Verma S, Rajaratnam JH, Denton J, Hoyland JA, Byers RJ (2002) Adipoctyic proportion of bone marrow is inversely related to bone formation in osteoporosis. J Clin Pathol 55:693–698
Wauquier F, Leotoing L, Coxam V, Guicheux J, Wittrant Y (2009) Oxidative stress in bone remodelling and disease. Trends Mol Med 15:468–477
Xia T, Kovochich M, Liong M, Mädler L, Gilbert B, Shi H, Yeh JI, Zink JI, Nel AE (2008) Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano 2:2121–2134
Yalin S, Bagis S, Polat G, Dogruer N, Cenk Aksit S, Hatungil R, Erdogan C (2005) Is there a role of free oxygen radicals in primary male osteoporosis? Clin Exp Rheumatol 23:689–692
Zhai YQ, Zhang SY, Pang H (2007) Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of cerium oxide nanocrystalline using ammonium bicarbonate as precipitan. Mater Lett 61:1863–1866
Zhao WH, Gou BD, Zhang TL, Wang K (2012) Lanthanum chloride bidirectionally influences calcification in bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biochem 113:1776–1786
Zhuang J, Dinsdale D, Cohen GM (1998) Apoptosis, in human monocytic THP.1 cells, results in the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria prior to their ultracondensation, formation of outer membrane discontinuities and reduction in inner membrane potential. Cell Death Differ 5:953–962
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Chinese Natural Science Foundation project (No. 21271059) and Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20111301110004), Hebei Province “Hundred Talents Program” (BR2–202), Training Program for Innovative Research Team, and Leading Talent in Hebei Province University (LJRC024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qun Zhang, Kun Ge contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Ge, K., Duan, J. et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles protect primary mouse bone marrow stromal cells from apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. J Nanopart Res 16, 2697 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2697-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2697-3