Abstract
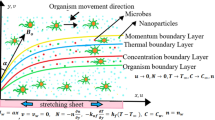
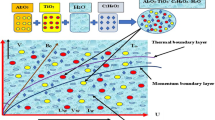
The main aim of this work is to study the thermal conductivity of base fluid with mild inclusion of nanoparticles. We perform numerical study for transportation of Maxwell nanofluids with activation energy and Cattaneo–Christov flux over an extending sheet along with mass transpiration. Further, bioconvection of microorganisms may support avoiding the possible settling of nanoentities. We formulate the theoretical study as a nonlinear coupled boundary value problem involving partial derivatives. Then ordinary differential equations are obtained from the leading partial differential equations with the help of appropriate similarity transformations. We obtain numerical results by using the Runge–Kutta fourth-order method with shooting technique. The effects of various physical parameters such as mixed convection, buoyancy ratio, Raleigh number, Lewis number, Prandtl number, magnetic parameter, mass transpiration on bulk flow, temperature, concentration, and distributions of microorganisms are presented in graphical form. Also, the skin friction coefficient, Nusselt number, Sherwood number, and motile density number are calculated and presented in the form of tables. The validation of numerical procedure is confirmed through its comparison with the existing results. The computation is carried out for suitable inputs of the controlling parameters.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All date generated or analyzed during this study are included in this paper.
Abbreviations
- \(u_{1}, u_{2}\) :
-
velocity components (m/s)
- \(x,y\) :
-
Cartesian coordinates (m)
- \(U_{w}\) :
-
stretching velocity of plate (m/s)
- \(B_{0}\) :
-
magnetic field strength (T)
- \(C\) :
-
concentration of nanoparticles
- \(T\) :
-
temperature of nanoparticles (K)
- \(N\) :
-
Microorganism distribution
- \(g\) :
-
gravity (m/s2)
- \(k_{1}\) :
-
vortex viscosity
- \(\rho _{p}\) :
-
liquid density
- \(C_{p}\) :
-
volume friction constant
- \(\rho _{m}\) :
-
motile microorganism density
- \(D_{B}\) :
-
Brownian motion coefficient (m2/s)
- \(D_{T}\) :
-
thermophoresis constant (m2/s)
- \(D_{n}\) :
-
diffusion constant of microorganisms (m2/s)
- \(T_{\infty }\) :
-
ambient temperature (K)
- \(C_{\infty }\) :
-
ambient concentration of nanoparticles
- \(N_{\infty }\) :
-
ambient motile microorganisms
- \(\tau _{1}\) :
-
relaxation time of heat flux
- \(m\) :
-
fitted rate parameter
- \(E_{a}\) :
-
activation energy (J/mol)
- \(b_{1}\) :
-
chemotaxis constant (m)
- \(b\) :
-
thermal relaxation constant
- \(W_{c}\) :
-
maximum swimming cell speed (m/s)
- \(n\) :
-
rotation of microorganisms (1/s)
- \(q_{w}\) :
-
heat transfer rate (W/m2)
- \(M\) :
-
magnetic parameter
- \(Kp\) :
-
porosity parameter
- \(Nr\) :
-
buoyancy ratio parameter
- \(Rb\) :
-
Rayleigh number
- \(Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(Nbt\) :
-
diffusivity ratio
- \(Nc\) :
-
ratio of heat capacities
- \(Le\) :
-
Lewis number
- \(Sc\) :
-
Schmidt number
- \(E\) :
-
activation energy coefficient
- \(Lb\) :
-
bioconvection Lewis number
- \(Pe\) :
-
Peclet number
- \(H\) :
-
suction/injection parameter
- \(A\) :
-
chemical reaction rate
- \(\alpha \) :
-
thermal diffusivity (m2/s)
- \(\beta \) :
-
Deborah number
- \(\nu _{nf}\) :
-
kinematic viscosity (m2/s)
- \(\lambda \) :
-
fluid relaxation time
- \(\sigma \) :
-
electrical conductivity (S/m)
- \(\rho \) :
-
density (kg/m3)
- \(\gamma \) :
-
average volume of microorganisms
- \(\omega \) :
-
mixed convection
- \(\eta \) :
-
similarity variable
- \(\theta \) :
-
similarity temperature
- \(\phi \) :
-
similarity concentration of nanoparticles
- \(\chi \) :
-
similarity density of micro-organisms
- \(\delta \) :
-
temperature difference
- \(\Omega \) :
-
microorganism concentration difference
- \(p\) :
-
nanoparticles
- \(w\) :
-
on the sheet surface
- \(\infty \) :
-
Ambient
References
Abbas, Z., Abdal, S., Hussain, N., Hussain, F., Adnan, M., Ali, B., Zulqarnain, R.M., Ali, L., Younas, S.: MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer of nanofluid over a vertical stretching sheet in the presence of a heat source. Sci. Inq. Rev. 3(4), 60–73 (2019)
Abdal, S., Hussain, S., Ahmad, F., Ali, B.: Hydromagnetic stagnation point flow of micropolar fluids due to a porous stretching surface with radiation and viscous dissipation effects. Sci. Int. 27, 3965–3971 (2015)
Abdal, S., Ali, B., Younas, S., Ali, L., Mariam, A.: Thermo-diffusion and multislip effects on MHD mixed convection unsteady flow of micropolar nanofluid over a shrinking/stretching sheet with radiation in the presence of heat source. Symmetry 12(1), 49 (2020)
Abdal, S., Alhumade, H., Siddique, I., Alam, M.M., Ahmad, I., Hussain, S.: Radiation and multiple slip effects on magnetohydrodynamic bioconvection flow of micropolar based nanofluid over a stretching surface. Appl. Sci. 11(11), 5136 (2021a)
Abdal, S., Hussain, S., Siddique, I., Ahmadian, A., Ferrara, M.: On solution existence of MHD Casson nanofluid transportation across an extending cylinder through porous media and evaluation of priori bounds. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–16 (2021b)
Abdal, S., Mariam, A., Ali, B., Younas, S., Ali, L., Habib, D.: Implications of bioconvection and activation energy on Reiner–Rivlin nanofluid transportation over a disk in rotation with partial slip. Chin. J. Phys. 73, 672–683 (2021c)
Abid, N., Ramzan, M., Chung, J.D., Kadry, S., Chu, Y.-M.: Comparative analysis of magnetized partially ionized copper, copper oxide–water and kerosene oil nanofluid flow with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–14 (2020)
Ahmad, F., Abdal, S., Ayed, H., Hussain, S., Salim, S., Almatroud, A.: The improved thermal efficiency of Maxwell hybrid nanofluid comprising of graphene oxide plus silver/kerosene oil over stretching sheet. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 27, 101257 (2021)
Ahmed, A., Khan, M., Hafeez, A., Ahmed, J.: Thermal analysis in unsteady radiative Maxwell nanofluid flow subject to heat source/sink. Appl. Nanosci. 10, 5489–5497 (2020)
Ali, L., Liu, X., Ali, B., Mujeed, S., Abdal, S.: Finite element simulation of multi-slip effects on unsteady mhd bioconvective micropolar nanofluid flow over a sheet with solutal and thermal convective boundary conditions. Coatings 9(12), 842 (2019a)
Ali, L., Liu, X., Ali, B., Mujeed, S., Abdal, S.: Finite element analysis of thermo-diffusion and multi-slip effects on MHD unsteady flow of Casson nano-fluid over a shrinking/stretching sheet with radiation and heat source. Appl. Sci. 9(23), 5217 (2019b)
Ali, B., Hussain, S., Nie, Y., Khan, S.A., Naqvi, S.I.R.: Finite element simulation of bioconvection Falkner–Skan flow of a Maxwell nanofluid fluid along with activation energy over a wedge. Phys. Scr. 95(9), 095214 (2020a)
Ali, L., Liu, X., Ali, B., Mujeed, S., Abdal, S., Khan, S.A.: Analysis of magnetic properties of nano-particles due to a magnetic dipole in micropolar fluid flow over a stretching sheet. Coatings 10(2), 170 (2020b)
Ali, L., Liu, X., Ali, B., Mujeed, S., Abdal, S., Mutahir, A.: The impact of nanoparticles due to applied magnetic dipole in micropolar fluid flow using the finite element method. Symmetry 12(4), 520 (2020c)
Ali, B., Naqvi, R.A., Nie, Y., Khan, S.A., Sadiq, M.T., Rehman, A.U., Abdal, S.: Variable viscosity effects on unsteady MHD an axisymmetric nanofluid flow over a stretching surface with thermo-diffusion: FEM approach. Symmetry 12(2), 234 (2020d)
Ali, B., Ali, L., Abdal, S., Asjad, M.I.: Significance of Brownian motion and thermophoresis influence on dynamics of Reiner–Rivlin fluid over a disk with non-Fourier heat flux theory and gyrotactic microorganisms: a numerical approach. Phys. Scr. 96(9), 094001 (2021a)
Ali, B., Naqvi, R.A., Ali, L., Abdal, S., Hussain, S.: A comparative description on time-dependent rotating magnetic transport of a water base liquid \(\mathrm{H_{2}O}\) with hybrid nano-materials \(\mathrm{Al_{2}O_{3}\text{-}Cu}\) and \(\mathrm{Al_{2}O_{3}\text{-}TiO_{2}}\) over an extending sheet using Buongiorno model: finite element approach. Chin. J. Phys. 70, 125–139 (2021b)
Ali, B., Nie, Y., Hussain, S., Habib, D., Abdal, S.: Insight into the dynamics of fluid conveying tiny particles over a rotating surface subject to Cattaneo–Christov heat transfer, Coriolis force, and Arrhenius activation energy. Comput. Math. Appl. 93, 130–143 (2021c)
Dawar, A., Shah, Z., Islam, S.: Mathematical modeling and study of MHD flow of Williamson nanofluid over a nonlinear stretching plate with activation energy. Heat Transf. 50(3), 2558–2570 (2021)
Devi, S.S.U., Mabood, F.: Entropy anatomization on Marangoni Maxwell fluid over a rotating disk with nonlinear radiative flux and Arrhenius activation energy. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 118, 104857 (2020)
Ferdows, M., Zaimi, K., Rashad, A.M., Nabwey, H.A.: MHD bioconvection flow and heat transfer of nanofluid through an exponentially stretchable sheet. Symmetry 12(5), 692 (2020)
Goyal, M., Bhargava, R.: Boundary layer flow and heat transfer of viscoelastic nanofluids past a stretching sheet with partial slip conditions. Appl. Nanosci. 4(6), 761–767 (2014)
Habib, D., Abdal, S., Ali, R., Baleanu, D., Siddique, I.: On bioconvection and mass transpiration of micropolar nanofluid dynamics due to an extending surface in existence of thermal radiations. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 27, 101239 (2021)
Habib, D., Salamat, N., Abdal, S., Siddique, I., Ang, M.C., Ahmadian, A.: On the role of bioconvection and activation energy for time dependent nanofluid slip transpiration due to extending domain in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. Ain Shams Eng. J. 13(1), 101519 (2022)
Hosseinzadeh, K., Salehi, S., Mardani, M., Mahmoudi, F., Waqas, M., Ganji, D.: Investigation of nano-bioconvective fluid motile microorganism and nanoparticle flow by considering mhd and thermal radiation. Inform. Med. Unlocked 21, 100462 (2020)
Hussain, F., Abdal, S., Abbas, Z., Hussain, N., Adnan, M., Ali, B., Zulqarnain, R.M., Ali, L., Younas, S.: Buoyancy effect on MHD slip flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid flow over a vertical porous plate. Sci. Inq. Rev. 4(1), 01 (2020a)
Hussain, S.M., Sharma, R., Mishra, M.R., Alrashidy, S.S.: Hydromagnetic dissipative and radiative graphene Maxwell nanofluid flow past a stretched sheet-numerical and statistical analysis. Mathematics 8(11), 19–29 (2020b)
Irfan, M., Khan, M., Khan, W.: Heat sink/source and chemical reaction in stagnation point flow of Maxwell nanofluid. Appl. Phys. A 126(11), 1–8 (2020)
Jabeen, K., Mushtaq, M., Akram Muntazir, R.: Analysis of MHD fluids around a linearly stretching sheet in porous media with thermophoresis, radiation, and chemical reaction. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 9685482 (2020)
Jafar, A.B., Shafie, S., Ullah, I.: Mhd radiative nanofluid flow induced by a nonlinear stretching sheet in a porous medium. Heliyon 6(6), e04201 (2020)
Khan, M.I., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Ali, Z.: Modeling of Cattaneo–Christov double diffusions (CCDD) in Williamson nanomaterial slip flow subject to porous medium. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9(3), 6172–6177 (2020)
Mondal, S.K., Pal, D.: Gyrotactic mixed bioconvection flow of a nanofluid over a stretching wedge embedded in a porous media in the presence of binary chemical reaction and activation energy. Int. J. Ambient Energy (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2020.1814860
Nadeem, S., Hussain, S.: Flow and heat transfer analysis of Williamson nanofluid. Appl. Nanosci. 4(8), 1005–1012 (2014)
Narender, G., Govardhan, K., Sarma, G.S.: Magnetohydrodynamic stagnation point on a Casson nanofluid flow over a radially stretching sheet. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 11(1), 1303–1315 (2020)
Panigrahi, L., Panda, J., Swain, K., Dash, G.C.: Heat and mass transfer of MHD Casson nanofluid flow through a porous medium past a stretching sheet with Newtonian heating and chemical reaction. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Math. Sci. 6(3), 11 (2020)
Ramesh, K., Khan, S.U., Jameel, M., Khan, M.I., Chu, Y.-M., Kadry, S.: Bioconvection assessment in Maxwell nanofluid configured by a Riga surface with nonlinear thermal radiation and activation energy. Surf. Interfaces 21, 100749 (2020)
Rashid, U., Baleanu, D., Iqbal, A., Abbas, M.: Shape effect of nanosize particles on magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a stretching sheet with entropy generation. Entropy 22(10), 1171 (2020)
Sha, Z., Dawar, A., Alzahrani, E.O., Kumam, P., Khan, A.J., Islam, S.: Hall effect on couple stress 3D nanofluid flow over an exponentially stretched surface with Cattaneo Christov heat flux model. IEEE Access 7, 64844–64855 (2019)
Shafiq, A., Sindhu, T.N., Khalique, C.M.: Numerical investigation and sensitivity analysis on bioconvective tangent hyperbolic nanofluid flow towards stretching surface by response surface methodology. Alex. Eng. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2020.08.007
Shah, Z., Dawar, A., Khan, I., Islam, S., Ching, D.L.C., Khan, A.Z.: Cattaneo–Christov model for electrical magnetite micropoler Casson ferrofluid over a stretching/shrinking sheet using effective thermal conductivity model. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 13, 100352 (2019)
Shahid, A.: The effectiveness of mass transfer in the MHD upper-convected Maxwell fluid flow on a stretched porous sheet near stagnation point: a numerical investigation. Inventions 5(4), 64 (2020)
Shahid, A., Huang, H., Bhatti, M.M., Zhang, L., Ellahi, R.: Numerical investigation on the swimming of gyrotactic microorganisms in nanofluids through porous medium over a stretched surface. Mathematics 8(3), 380 (2020)
Shahid, A., Huang, H., Khalique, C., Bhatti, M.: Numerical analysis of activation energy on MHD nanofluid flow with exponential temperature-dependent viscosity past a porous plate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143(3), 2585–2596 (2021)
Sharanappa, D.S., Tawade, J.V., Veena, M., Pallavi, S.: MHD boundary layer flow of a Casson nano liquid over a penetrable linearly stretching sheet with frictional heating effects in Brinkmann–Forcheiemerr porous medium. Mater. Today Proc. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.125
Yahya, A.U., Salamat, N., Habib, D., Ali, B., Hussain, S., Abdal, S.: Implication of bio-convection and Cattaneo–Christov heat flux on Williamson Sutterby nanofluid transportation caused by a stretching surface with convective boundary. Chin. J. Phys. 73, 706–718 (2021a)
Yahya, A.U., Salamat, N., Huang, W.-H., Siddique, I., Abdal, S., Hussain, S.: Thermal characteristics for the flow of Williamson hybrid nanofluid (\(\mathrm{MoS_{2}+ZnO}\)) based with engine oil over a stretched sheet. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 26, 101196 (2021b)
Funding
N/A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each of the authors contributed equally to each part of this work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdal, S., Siddique, I., Ahmadian, A. et al. Enhanced heat transportation for bioconvective motion of Maxwell nanofluids over a stretching sheet with Cattaneo–Christov flux. Mech Time-Depend Mater 27, 1257–1272 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-022-09551-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-022-09551-2