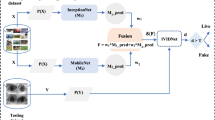
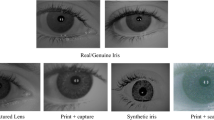
Abstract
In the modern era of computing, the iris-based biometric systems are gaining significant attention for secured and automatic human authentication. However, past decades have witnessed numerous spoofing assaults on these iris-based recognition systems where an attacker impersonates an exact replica of biometrical information of the genuine user. Particularly, these direct attacks are targeted on the iris sensor module of the biometric system by presenting the fake artefacts of a bonafide iris trait. With the emergence of data-driven paradigm (i.e. handcrafted feature learners such as support vector machine (SVM), decision tree (DT), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), ensembles, etc. or automatic image features extraction-based classifiers such as convolutional neural networks (CNN), generative adversial networks (GAN)), mitigating these iris spoof attacks has become comparatively an easier and accurate task of computer vision. An iris spoof detector (ISD) is a mechanism through which the vitality of a presented iris trait is measured intelligently by classifying it as genuine or counterfeit. In this study, we explicate a taxonomy-based comparative analysis of state-of-the-art (SOTA) ISDs that employ machine learning or deep learning-based approaches. We expound a novel taxonomy for classifying ISDs based on underlying criterion such as feature type, learning algorithm, pre-trained models, data augmentation, hybrid, etc. Furthermore, we investigate and analyze various benchmark datasets employed in the various data-driven iris spoof detectors (D2ISD). We also illustrate prominent performance evaluation protocols that are widely adopted in the SOTA approaches. Though, pioneer contributions related to D2ISD is reported in the literature, but several potential open research problems still exist, that requisite a futuristic attention of the investigators in this active field of research.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used/generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdellatef E, Ismail NA, Abd Elrahman SESE, Ismail KN, Rihan M, Abd el-Samie FE (2019) Cancelable multi - biometric recognition system based on deep learning. Vis Comput 36(0123456789):1097–1109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01715-5
Agarwal R and Jalal AS (2021) “Presentation attack detection system for fake Iris: a review,” Multimed. Tools Appl, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10378-7.
Agarwal R, Jalal AS, Arya KV (2020) Enhanced binary hexagonal Extrema pattern (EBHXEP) descriptor for Iris liveness detection. Wirel Pers Commun 115(3):2627–2643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07700-9
Agarwal R, Jalal AS, Arya KV (2021) Local binary hexagonal Extrema pattern (LBHXEP): a new feature descriptor for fake iris detection. Vis Comput 37(6):1357–1368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01870-0
Ahmadi N, Nilashi M, Samad S, Rashid TA, Ahmadi H (2019) An intelligent method for iris recognition using supervised machine learning techniques. Opt Laser Technol 120(December 2018):105701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105701
Alaslni MG, Elrefaei LA (2019) Transfer learning with convolutional neural networks for IRIS recognition. Int J Artif Intell Appl 10(5):49–66. https://doi.org/10.5121/ijaia.2019.10505
Bakkouri I, Afdel K (2020) Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system based on multi-layer feature fusion network for skin lesion recognition in dermoscopy images. Multimed Tools Appl 79(29–30):20483–20518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-07988-1
Bakkouri I, Afdel K, Benois-Pineau J, Catheline G, For the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiativ (2022) BG-3DM2F: Bidirectional gated 3D multi-scale feature fusion for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis, vol. 81, no. 8
Bhatti UA, Huang M, Wang H, Zhang Y, Mehmood A, Di W (2018) Recommendation system for immunization coverage and monitoring. Hum Vaccines Immunother 14(1):165–171. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2017.1379639
Bhatti UA, Huang M, Wu D, Zhang Y, Mehmood A, Han H (2019) Recommendation system using feature extraction and pattern recognition in clinical care systems. Enterp Inf Syst 13(3):329–351. https://doi.org/10.1080/17517575.2018.1557256
Bhatti UA, Yu Z, Li J, Nawaz SA, Mehmood A, Zhang K, Yuan L (2020) Hybrid watermarking algorithm using Clifford algebra with Arnold scrambling and chaotic encryption. IEEE Access 8:76386–76398. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988298
Bhatti UA, Zeeshan Z, Nizamani MM, Bazai S, Yu Z, Yuan L (2022) Assessing the change of ambient air quality patterns in Jiangsu Province of China pre-to post-COVID-19. Chemosphere 288(2):132569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132569
Bhatti UA et al (2022) Local Similarity-Based Spatial–Spectral Fusion Hyperspectral Image Classification With Deep CNN and Gabor Filtering. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3090410
Bhogal APS, Sollinger D, Trung P, Uhl A (2017) Non-reference image quality assessment for biometric presentation attack detection. Proc - 2017 5th Int Work Biometrics Forensics, IWBF 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWBF.2017.7935080
Boulkenafet Z, Komulainen J, Hadid A (2018) On the generalization of color texture-based face anti-spoofing. Image Vis Comput 77:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2018.04.007
Busch C (2017) “The ISO/IEC standards for testing of Presentation Attack Detection,”, [Online]. Available: https://christoph-busch.de/files/Busch-PAD-standards-170329.pdf.
Chatterjee P, Yalchin A, Shelton J, Roy K, Yuan X, Edoh KD (2019) Presentation attack detection using wavelet transform and deep residual neural net, vol 11637. Springer International Publishing, LNCS
Chen C, Ross A (2018) “A Multi-Task Convolutional Neural Network for Joint Iris Detection and Presentation Attack Detection,” no. March
Choudhary M, Tiwari V, Venkanna U (2019) An approach for iris contact lens detection and classification using ensemble of customized DenseNet and SVM. Futur Gener Comput Syst 101:1259–1270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.07.003
Czajka A (2015) Pupil dynamics for iris liveness detection. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(4):726–735. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2015.2398815
Czajka A, Bowyer KW (2018) Presentation attack detection for iris recognition: An assessment of the state-of-the-art. ACM Comput Surv 51(4). https://doi.org/10.1145/3232849
Czajka A, Bowyer KW, Krumdick M, Vidalmata RG (2017) Recognition of image-orientation-based Iris spoofing. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 12(9):2184–2196. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2017.2701332
Das P et al. (2020) “Iris Liveness Detection Competition (LivDet-Iris) - The 2020 Edition,” IJCB 2020 - IEEE/IAPR Int. Jt. Conf. Biometrics, https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCB48548.2020.9304941.
Daugman J (1994) “Biometric Personal Identification System Based on Iris Analysis,” no. 19
Dronky MR, Khalifa W, Roushdy M (2021) Using residual images with BSIF for iris liveness detection. Expert Syst Appl 182(March 2020):115266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115266
“FAKE IRIS DETECTION USING STRUCTURED LIGHT Connell J, N Ratha, James Gentile, Ruud Bolle (2013) Yorktown Heights , NY 10598 { jconnell , ratha } @ us . ibm . com,” pp. 8692–8696
Fang M, Damer N, Boutros F, Kirchbuchner F, Kuijper A (2020) “Deep learning multi-layer fusion for an accurate iris presentation attack detection,” Proc. 2020 23rd Int. Conf. Inf. Fusion, FUSION 2020, https://doi.org/10.23919/FUSION45008.2020.9190424.
Fang Z, Czajka A, Bowyer KW (2021) Robust iris presentation attack detection fusing 2D and 3D information. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 16:510–520. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2020.3015547
Fang M, Damer N, Boutros F, Kirchbuchner F, Kuijper A (2021) Cross-database and cross-attack Iris presentation attack detection using micro stripes analyses. Image Vis Comput 105:104057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2020.104057
Farmanbar M, Toygar Ö (2017) Spoof detection on face and palmprint biometrics. Signal, Image Video Process 11(7):1253–1260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1082-y
Galbally J, Marcel S, Fierrez J (2014) Image quality assessment for fake biometric detection: application to Iris, fingerprint, and face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(2):710–724. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2013.2292332
Gautam G, Mukhopadhyay S (2018) “Contact Lens Detection using Transfer Learning with Deep Representations,” Proc. Int. Jt. Conf. Neural Networks, vol. 2018-July, pp. 1–8, https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2018.8489590.
Gomez-Barrero M, Rathgeb C, Li G, Ramachandra R, Galbally J, Busch C (2018) Multi-biometric template protection based on bloom filters. Inf Fusion 42:37–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2017.10.003
Goshtasby AAA (2012) Advances in computer vision and pattern recognition
Gragnaniello D, Sansone C, Verdoliva L (2015) Iris liveness detection for mobile devices based on local descriptors. Pattern Recogn Lett 57:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2014.10.018
Gragnaniello D, Poggi G, Sansone C, Verdoliva L (2015) An investigation of local descriptors for biometric spoofing detection. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(4):849–863. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2015.2404294
Gupta R, Sehgal P (2016) A survey of attacks on iris biometric systems. Int J Biometeorol 8(2):145–178. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBM.2016.077833
Gupta P, Behera S, Vatsa M, Singh R (2014) On iris spoofing using print attack. Proc - Int Conf Pattern Recognit:1681–1686. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2014.296
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) “Deep residual learning for image recognition,” Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., vol. 2016-Decem, pp. 770–778, https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Hu Y, Sirlantzis K, Howells G (2016) Iris liveness detection using regional features. Pattern Recogn Lett 82:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2015.10.010
Hu Q, Yin S, Ni H, Huang Y (2020) An end to end deep neural network for Iris recognition. Procedia Comput Sci 174(2019):505–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.06.118
Huang X, Ti C, Hou QZ, Tokuta A, Yang R (2013) An experimental study of pupil constriction for liveness detection. Proc IEEE Work Appl Comput Vis:252–258. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2013.6475026
Hughes K, Bowyer KW (2013) Detection of contact-lens-based iris biometric spoofs using stereo imaging. Proc Annu Hawaii Int Conf Syst Sci:1763–1772. https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2013.172
Ishfaq DSR, Selwal A (2021) “Fingerprint Spoofing Attacks and their Deep Learning-enabled Remediation: State-of-the-art, Taxonomy, and Future Directions,” pp. 22–28
Jain AK, Ross A, Prabhakar S (2004) An introduction to biometric recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 14(1):4–20. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2003.818349
Jain AK, Flynn P, Ross AA (2007) Handbook of biometrics
Jamdar SD et al (2017) Biometrics: A Tool for Information Security Anil. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 1(Iccmc):125–143
Kapur PK, Singh G, Klochkov YS, Kumar U (2020) Decision analytics applications in industry.
Kaur B (2020) Iris spoofing detection using discrete orthogonal moments. Multimed Tools Appl 79(9–10):6623–6647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08281-x
Kaur B, Singh S, Kumar J (2019) Cross-sensor iris spoofing detection using orthogonal features. Comput Electr Eng 73:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2018.12.002
Kohli N, Yadav D, Vatsa M, Singh R (2013) Revisiting iris recognition with color cosmetic contact lenses. Proc - 2013 Int Conf Biometrics, ICB 2013 1. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICB.2013.6613021
Kohli N, Yadav D, Vatsa M, Singh R, Noore A (2018) “Synthetic iris presentation attack using iDCGAN,” IEEE Int. Jt. Conf. Biometrics, IJCB 2017, vol. 2018-Janua, pp. 674–680 https://doi.org/10.1109/BTAS.2017.8272756.
O. V Komogortsev, S. Marcos, A. Karpov, and S. Marcos (2013) “Liveness Detection via Oculomotor Plant Characteristics : Attack of Mechanical Replicas”
Kuehlkamp A, Pinto A, Rocha A, Bowyer KW, Czajka A (2019) Ensemble of Multi-View Learning Classifiers for cross-domain Iris presentation attack detection. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 14(6):1419–1431. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2018.2878542
Liu N, Li H, Zhang M, Liu J, Sun Z, Tan T (2016) Accurate iris segmentation in non-cooperative environments using fully convolutional networks. 2016 Int Conf Biometrics, ICB:2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICB.2016.7550055
Liu M, Zhou Z, Shang P, Xu D (2020) Fuzzified image enhancement for deep learning in Iris recognition. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(1):92–99. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2912576
Long M, Zeng Y (2019) “Detecting Iris Liveness with Batch Normalized Convolutional Neural Network,” vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 493–504, https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2019.04378.
Mehmood R, Selwal A (2020) Polynomial based fuzzy vault technique for template security in fingerprint biometrics. Int Arab J Inf Technol 17(6):926–934. https://doi.org/10.34028/iajit/17/6/11
Menotti D, Chiachia G, Pinto A, Robson Schwartz W, Pedrini H, Xavier Falcao A, Rocha A (2015) Deep representations for Iris, face, and fingerprint spoofing detection. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(4):864–879. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2015.2398817
Minaee S, Abdolrashidi A (2019) “DeepIris: Iris Recognition Using A Deep Learning Approach,” [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1907.09380.
Pala F Bhanu B (2017) “Iris Liveness Detection by Relative Distance Comparisons,” IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. Work., vol. 2017-July, pp. 664–671 https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.95.
“Presentation attack detection algorithm for face and iris biometrics” (2014) pp. 1387–1391
Puhan NB, Sudha N, Hegde S (2011) A new iris liveness detection method against contact lens spoofing. Proc Int Symp Consum Electron ISCE:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCE.2011.5973786
Raghavendra R, Busch C (2014) Presentation attack detection on visible spectrum iris recognition by exploring inherent characteristics of Light Field Camera. IJCB 2014–2014 IEEE/IAPR Int Jt Conf Biometrics. https://doi.org/10.1109/BTAS.2014.6996226
Raghavendra R, Busch C (2015) Robust scheme for iris presentation attack detection using multiscale binarized statistical image features. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(4):703–715. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2015.2400393
Raja KB, Raghavendra R, Busch C (2015) “Presentation attack detection using Laplacian decomposed frequency response for visible spectrum and Near-Infra-Red iris systems,” 2015 IEEE 7th Int. Conf. Biometrics Theory, Appl. Syst. BTAS 2015, https://doi.org/10.1109/BTAS.2015.7358790.
Ratha NK, Connell JH, Bolle RM (2001) An analysis of minutiae matching strength. Lect Notes Comput Sci (including Subser Lect Notes Artif Intell Lect Notes Bioinformatics) 2091 LNCS(2015):223–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45344-x_32
Ribeiro E, Uhl A (2017) Exploring Texture Transfer Learning via Convolutional Neural Networks for Iris Super Resolution. Lect Notes Informatics (LNI), Proc - Ser Gesellschaft fur Inform (00736):0–4. https://doi.org/10.23919/BIOSIG.2017.8053505
Rigas I, Komogortsev OV (2015) Eye movement-driven defense against iris print-attacks. Pattern Recogn Lett 68:316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2015.06.011
Rui Z, Yan Z (2019) A survey on biometric authentication: toward secure and privacy-preserving identification. IEEE Access 7(c):5994–6009. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2889996
Sardar M, Banerjee S, Mitra S (2020) Iris segmentation using interactive deep learning. IEEE Access 8:219322–219330. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3041519
Selwal A, Gupta S, Kumar S (2016) A Scheme for Template Security At Feature Fusion Level in Multimodal Biometric System. Adv Sci Technol Res J 10(31):23–30. https://doi.org/10.12913/22998624/64062
Selwal A, Gupta SK, Surender (2017) Low overhead octet indexed template security scheme for multi-modal biometric system. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 32(5):3325–3337. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-169274
Sequeira AF, Oliveira HP, Monteiro JC, Monteiro JP, Cardoso JS (2014) “MobILive 2014 - Mobile Iris Liveness Detection Competition,” IJCB 2014–2014 IEEE/IAPR Int. Jt. Conf. Biometrics, https://doi.org/10.1109/BTAS.2014.6996290.
Sharma D, Selwal A (2021) An intelligent approach for fingerprint presentation attack detection using ensemble learning with improved local image features, no. 0123456789. Springer US.
Sharma D, Selwal A (2021) FinPAD: State-of-the-art of fingerprint presentation attack detection mechanisms, taxonomy and future perspectives. Pattern Recogn Lett 152(March 2005):225–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2021.10.013
Sharma D, Selwal A (2021) HyFiPAD : a hybrid approach for fingerprint presentation attack detection using local and adaptive image features. Vis Comput 38(0123456789):2999–3025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02173-8
Silva P, Luz E, Baeta R, Pedrini H, Falcao AX, Menotti D (2015) “An Approach to Iris Contact Lens Detection Based on Deep Image Representations,” Brazilian Symp. Comput. Graph. Image Process., vol. 2015-Octob, pp. 157–164https://doi.org/10.1109/SIBGRAPI.2015.16.
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) “Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition,” 3rd Int. Conf. Learn. Represent. ICLR 2015 - Conf. Track Proc., pp. 1–14
Singh M, Singh R, Ross A (2019) A comprehensive overview of biometric fusion. Inf Fusion 52:187–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2018.12.003
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z (2016) Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. Proc IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2016:2818–2826. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.308
Tan M, Le QV (2019) “EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks,” 36th Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. ICML 2019, vol. 2019-June, pp. 10691–10700
Tann H, Zhao H, Reda S (2019) A resource-efficient embedded iris recognition system using fully convolutional networks. ACM J Emerg Technol Comput Syst 16(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1145/3357796
Tapia JE, Gonzalez S, Busch C (2022) Iris liveness detection using a Cascade of dedicated deep learning networks. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 17:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2021.3132582
Therar HM, Mohammed LDEA, Ali APDAJ (2021) “Multibiometric System for Iris Recognition Based Convolutional Neural Network and Transfer Learning,” IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., vol. 1105, no. 1, p. 012032, https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/1105/1/012032.
Tirunagari S, Poh N, Windridge D, Iorliam A, Suki N, Ho ATS (2015) Detection of face spoofing using visual dynamics. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(4):762–777. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2015.2406533
Tobji R, Di W, Ayoub N (2019) FMnet: Iris segmentation and recognition by using fully and multi-scale CNN for biometric security. Appl Sci 9(10):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102042
Varkarakis V, Bazrafkan S, Corcoran P (2018) “A deep learning approach to segmentation of distorted iris regions in head-mounted displays,” 2018 IEEE Games, Entertain. Media Conf. GEM 2018, pp. 402–406 https://doi.org/10.1109/GEM.2018.8516446
Yadav D, Kohli N, Doyle JS, Singh R, Vatsa M, Bowyer KW (2014) Unraveling the effect of textured contact lenses on iris recognition. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 9(5):851–862. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2014.2313025
Yambay D, Doyle JS, Bowyer KW, Czajka A, Schuckers S (2014) “LivDet-iris 2013 - Iris Liveness Detection Competition 2013,” IJCB 2014–2014 IEEE/IAPR Int. Jt. Conf. Biometrics, https://doi.org/10.1109/BTAS.2014.6996283.
Yambay D, Czajka A, Ii F (2015) “LivDet-Iris 2015 – Iris liveness detection competition 2015 University of Naples”
Yambay D et al. (2018) “LivDet iris 2017 - Iris liveness detection competition 2017,” IEEE Int. Jt. Conf. Biometrics, IJCB 2017, vol. 2018-Janua, pp. 733–741, https://doi.org/10.1109/BTAS.2017.8272763.
Yang Y, Shen P, Chen C (2019) A robust iris segmentation using fully convolutional network with dilated convolutions. Proc - 2018 IEEE Int Symp Multimedia, ISM 2018:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISM.2018.00010
Zhang H, Sun Z, Tan T (2010) Contact lens detection based on weighted LBP. Proc - Int Conf Pattern Recognit:4279–4282. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2010.1040
Zhang H, Sun Z, Tan T, Wang J (2011) “Learning hierarchical visual codebook for Iris liveness detection”
Zhao Z, Kumar A (2017) “Towards More Accurate Iris Recognition Using Deeply Learned Spatially Corresponding Features,” Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., vol. 2017-Octob, pp. 3829–3838, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.411.
Zhao Z, Kumar A (2019) A deep learning based unified framework to detect, segment and recognize irises using spatially corresponding features. Pattern Recogn 93:546–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.04.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All the authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, P., Selwal, A. & Sharma, D. A survey on data-driven iris spoof detectors: state-of-the-art, open issues and future perspectives. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 19745–19792 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14014-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14014-4