Abstract
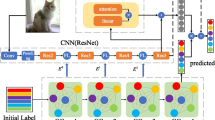
Recently, remarkable progress on multi-label image classification has been achieved by locating semantic-agnostic image regions and extracting their features with deep convolutional neural networks. However, existing pipelines depend on the hypothesis region generation step, which typically brings about extra computational costs, e.g., generating hundreds of meaningless proposals and extracting their features. Moreover, the contextual dependencies among these localized regions are usually ignored or oversimplified during the learning and inference stages. To resolve these issues, we develop a novel attentive transformer-localizer (ATL) module that contains differential transformations (e.g., translation, scale), which can automatically discover the discriminative semantic-aware regions from input images in terms of multi-label recognition. This module can be flexibly incorporated with recurrent neural networks such as the long short-term memory (LSTM) network for memorizing and updating the contextual dependencies of the localized regions. We thus build a unified multi-label image recognition framework. Specifically, the ATL module is applied to progressively localize the attentive regions from the convolutional feature maps in a proposal-free manner, and the LSTM network sequentially predicts label scores for the localized regions and updates the parameters of the ATL module while capturing the global dependencies among these regions. To associate the localized regions with semantic labels over diverse locations and scales, we further design three constraints together with the ATL module. Extensive experiments and evaluations on two large-scale benchmarks (i.e., PASCAL VOC and Microsoft COCO) show that the proposed approach achieves superior performance over existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of both performance and efficiency.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The range of coordinates is rescaled to [-1, 1]
References
Chatfield K, Simonyan K, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A (2014) Return of the devil in the details: Delving deep into convolutional nets. In: Proceedings of the british machine vision conference
Chen L, Wang R, Yang J, Xue L, Hu M (2019) Multi-label image classification with recurrently learning semantic dependencies. Vis Comput 35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-01615-0
Chen Q, Song Z, Hua Y, Huang Z, Yan S (2012) Hierarchical matching with side information for image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3426–3433
Chen T, Lin L, Hui X, Chen R, Wu H (2020) Knowledge-guided multi-label few-shot learning for general image recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Chen T, Pu T, Wu H, Xie Y, Lin L (2021) Structured semantic transfer for multi-label recognition with partial labels. arXiv:2112.10941
Chen T, Pu T, Wu H, Xie Y, Liu L, Lin L (2021) Cross-domain facial expression recognition: a unified evaluation benchmark and adversarial graph learning. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence
Chen T, Xu M, Hui X, Wu H, Lin L (2019) Learning semantic-specific graph representation for multi-label image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 522–531
Cho K, Courville A, Bengio Y (2015) Describing multimedia content using attention-based encoder-decoder networks. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 17(11):1875–1886
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2005. CVPR 2005. vol 1, IEEE, pp 886–893
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2009. CVPR 2009. IEEE, pp 248–255
Dong J, Xia W, Chen Q, Feng J, Huang Z, Yan S (2013) Subcategory-aware object classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 827–834
Everingham M, Van Gool L, Williams CK, Winn J, Zisserman A (2010) The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int J Comput Vis 88 (2):303–338
Ghamrawi N, McCallum A (2005) Collective multi-label classification. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM international conference on Information and knowledge management, ACM, pp 195–200
Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J (2014) Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 580–587
Glorot X, Bengio Y (2010) Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In: Aistats, vol 9, pp 249–256
Gong Y, Jia Y, Leung T, Toshev A, Ioffe S (2013) Deep convolutional ranking for multilabel image annotation. arXiv:1312.4894
Guo Y, Gu S (2011) Multi-label classification using conditional dependency networks. In: IJCAI Proceedings-international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1300
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1026–1034
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9(8):1735–1780
Jaderberg M, Simonyan K, Zisserman A et al (2015) Spatial transformer networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 2017–2025
Jia Y, Shelhamer E, Donahue J, Karayev S, Long J, Girshick R, Guadarrama S, Darrell T (2014) Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In: Proceedings of ACM international conference on Multimedia, pp 675–678
Kingma D, Ba J (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980
Krizhevsky A (2009) Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Computer Science Department University of Toronto
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1097–1105
Kuen J, Wang Z, Wang G (2016) Recurrent attentional networks for saliency detection. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp 3668–3677
LeCun Y, Boser BE, Denker JS, Henderson D, Howard RE, Hubbard WE, Jackel LD (1990) Handwritten digit recognition with a back-propagation network. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 396–404
Li L, Tang S, Zhang Y, Deng L, Tian Q (2017) Gla: Global–local attention for image description. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 20(3):726–737
Li Z, Lu W, Sun Z, Xing W (2018) Improving multi-label classification using scene cues. Multimedia Tools and Applications, pp 77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4517-0
Lin TY, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollar P (2017) Focal loss for dense object detection. In: 2017 IEEE International conference on computer vision (ICCV), IEEE, pp 2999–3007
Lin TY, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollár P., Zitnick CL (2014) Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: European conference on computer vision, Springer, pp 740–755
Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu CY, Berg AC (2016) Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In: European conference on computer vision, Springer, pp 21–37
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Lyu F, Hu F, Sheng V, Wu Z, Fu Q, Fu B (2018) Coarse to fine: Multi-label image classification with global/local attention. pp 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISC2.2018.8656664
Mnih V, Heess N, Graves A et al (2014) Recurrent models of visual attention. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 2204–2212
Nair V, Hinton GE (2010) Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 27th international conference on machine learning (ICML-10), pp 807–814
Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A (2016) You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 779–788
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 91–99
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M et al (2015) Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Sharif Razavian A, Azizpour H, Sullivan J, Carlsson S (2014) Cnn features off-the-shelf: an astounding baseline for recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 806–813
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: Proceedings of international conference on learning representations
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A, Rick Chang JH et al (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Tang S, Li Y, Deng L, Zhang Y (2017) Object localization based on proposal fusion. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 19(9):2105–2116
Uijlings JR, Van De Sande KE, Gevers T, Smeulders AW (2013) Selective search for object recognition. Int J Comput Vis 104(2):154–171
Wang J, Yang Y, Mao J, Huang Z, Huang C, Xu W (2016) Cnn-rnn: a unified framework for multi-label image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2285–2294
Wang M, Luo C, Hong R, Tang J, Feng J (2016) Beyond object proposals: random crop pooling for multi-label image recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(12):5678–5688
Wang Z, Chen T, Li G, Xu R, Lin L (2017) Multi-label image recognition by recurrently discovering attentional regions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 464–472
Wang Z, Fang Z, Li D, Yang H, Du W (2021) Semantic supplementary network with prior information for multi-label image classification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Vid Technol, pp 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3083978
Wei Y, Xia W, Lin M, Huang J, Ni B, Dong J, Zhao Y, Yan S (2016) Hcp: a flexible cnn framework for multi-label image classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(9):1901–1907
Williams RJ (1992) Simple statistical gradient-following algorithms for connectionist reinforcement learning. Mach Learn 8(3-4):229–256
Xiao T, Xu Y, Yang K, Zhang J, Peng Y, Zhang Z (2015) The application of two-level attention models in deep convolutional neural network for fine-grained image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 842–850
Xiong C, Merity S, Socher R (2016) Dynamic memory networks for visual and textual question answering. In: Proceedings of The 33rd international conference on machine learning, pp 2397–2406
Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R, Cho K, Courville A, Salakhudinov R, Zemel R, Bengio Y (2015) Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: International conference on machine learning, pp 2048–2057
Xue X, Zhang W, Zhang J, Wu B, Fan J, Lu Y (2011) Correlative multi-label multi-instance image annotation. In: 2011 International conference on computer vision, IEEE, pp 651–658
Yang H, Tianyi Zhou J, Zhang Y, Gao BB, Wu J, Cai J (2016) Exploit bounding box annotations for multi-label object recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 280–288
Zhang J, Wu Q, Shen C, Zhang J, Lu J (2018) Multi-label image classification with regional latent semantic dependencies. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
Zhang K, Sun M, Han TX, Yuan X, Guo L, Liu T (2018) Residual networks of residual networks: multilevel residual networks. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Techn 28(6):1303–1314
Zhang Y, Jin R, Zhou ZH (2010) Understanding bag-of-words model: a statistical framework. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 1(1-4):43–52
Zhao B, Wu X, Feng J, Peng Q, Yan S (2017) Diversified visual attention networks for fine-grained object classification. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 19(6):1245–1256
Zhu F, Li H, Ouyang W, Yu N, Wang X (2017) Learning spatial regularization with image-level supervisions for multi-label image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Zitnick CL, Dollár P (2014) Edge boxes: Locating object proposals from edges. In: European conference on computer vision, Springer, pp 391–405
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work is supported by Deeply promote the innovation-driven booster project of Foshan City (NO.2021020) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61976095).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, L., Chen, T., Wang, Z. et al. Multi-label image recognition with attentive transformer-localizer module. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 7917–7940 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11818-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11818-8