Abstract
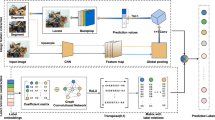
Multi-label image classification is a fundamental and vital task in computer vision. The latest methods are mostly based on deep learning and exhibit excellent performance in understanding images. However, in previous studies, only capture the image content information has been captured using convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and the semantic structure information and implicit dependencies between labels and image regions have been ignored. Therefore, it is necessary to develop more effective methods for integrating semantic information and visual features in multi-label image classification. In this study, we propose a novel framework for multi-label image classification, named FLNet, which simultaneously takes advantage of the visual features and semantic structure. Specifically, to enhance the association between semantic annotations and image regions, we first integrate the attention mechanism with a CNN to focus on the target regions while ignoring other useless surrounding information and then employ graph convolutional network (GCN) to capture the structure information between multiple labels. Based on our architecture, we also introduce the lateral connections to repeatedly inject the label system into the CNN backbone during the GCN learning process to improve performance and, consequently, learn interdependent classifiers for each image label. We apply our method to multi-label image classification. The experiments on two public multi-label benchmark datasets, namely, MS-COCO and PASCAL visual object classes challenge (VOC 2007), demonstrate that our approach outperforms other existing state-of-the-art methods. Our method learns specific target regions and enhances the association between labels and image regions by using semantic information and attention mechanism. Thus, we combine the advantages of both visual and semantic information to further improve the image classification performance. Finally, the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed method are proven by visualizing the classifier results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016. p. 770–778.
Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:14091556. 2014.
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016. p. 2818–2826.
Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2017. p. 4700–4708.
Alkhateeb A, Zhou L, Tabl AA, Rueda L. Deep Learning Approach for Breast Cancer InClust 5 Prediction based on Multiomics Data Integration. In: Proceedings of the 11th ACM International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Health Informatics. 2020. p. 1–6.
Wang J, Yang Y, Mao J, Huang Z, Huang C, Xu W. CNN-RNN: A unified framework for multi-label image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016. p. 2285–2294.
Li Q, Qiao M, Bian W, Tao D. Conditional graphical lasso for multi-label image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016. p. 2977–2986.
Yazici VO, Gonzalez-Garcia A, Ramisa A, Twardowski B, Weijer JVD. Orderless Recurrent Models for Multi-label Classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020. p. 13440–13449.
Chen ZM, Wei XS, Wang P, Guo Y. Multi-label image recognition with graph convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019. p. 5177–5186.
Wei Y, Xia W, Lin M, Huang J, Ni B, Dong J, et al. HCP: A flexible CNN framework for multi-label image classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2015;38(9):1901–7.
Wang Z, Chen T, Li G, Xu R, Lin L. Multi-label image recognition by recurrently discovering attentional regions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2017. p. 464–472.
Zhu F, Li H, Ouyang W, Yu N, Wang X. Learning spatial regularization with image-level supervisions for multi-label image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2017. p. 5513–5522.
Ge W, Yang S, Yu Y. Multi-evidence filtering and fusion for multi-label classification, object detection and semantic segmentation based on weakly supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018. p. 1277–1286.
Lee CW, Fang W, Yeh CK, Frank Wang YC. Multi-label zero-shot learning with structured knowledge graphs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018. p. 1576–1585.
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE; 2009. p. 248–255.
Lin TY, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, et al. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer; 2014. p. 740–755.
Chen Q, Song Z, Hua Y, Huang Z, Yan S. Hierarchical matching with side information for image classification. In: 2012 IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE; 2012. p. 3426–3433.
Tsoumakas G, Katakis I. Multi-label classification: an overview. International Journal of Data Warehousing and Mining (IJDWM). 2007;3(3):1–13.
Gong Y, Jia Y, Leung T, Toshev A, Ioffe S. Deep convolutional ranking for multi-label image annotation. arXiv preprint arXiv:13124894. 2013.
Chatfield K, Simonyan K, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A. Return of the devil in the details: Delving deep into convolutional nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:14053531. 2014.
Wu F, Wang Z, Zhang Z, Yang Y, Luo J, Zhu W, et al. Weakly semi-supervised deep learning for multi-label image annotation. IEEE Transactions on Big Data. 2015;1(3):109–22.
Ghamrawi N, McCallum A. Collective multi-label classification. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. 2005. p. 195–200.
Guo Y, Gu S. Multi-label classification using conditional dependency networks. In: IJCAI Proceedings-International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 22. Citeseer; 2011. p. 1300.
Xue X, Zhang W, Zhang J, Wu B, Fan J, Lu Y. Correlative multi-label multi-instance image annotation. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE; 2011. p. 651–658.
Tehrani AF, Ahrens D. Modeling label dependence for multi-label classification using the Choquistic regression. Pattern Recogn Lett. 2017;92:75–80.
Marino K, Salakhutdinov R, Gupta A. The more you know: Using knowledge graphs for image classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:161204844. 2016.
Wang X, Gupta A. Videos as space-time region graphs. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV); 2018. p. 399–417.
Kipf TN, Welling M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:160902907. 2016.
Hamilton W, Ying Z, Leskovec J. Inductive representation learning on large graphs. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2017. p. 1024–1034.
Xu J, Tian H, Wang Z, Wang Y, Chen F, Kang W. Joint Input and Output Space Learning for Multi-Label Image Classification. IEEE Trans Multimedia. 2020.
Wang Y, Zhang T, Cui Z, Xu C, Yang J. Instance-Aware Graph Convolutional Network for Multi-Label Classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:200808407. 2020.
Wang Y, He D, Li F, Long X, Zhou Z, Ma J, et al. Multi-label classification with label graph superimposing. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34; 2020. p. 12265–12272.
Li Q, Peng X, Qiao Y, Peng Q. Learning label correlations for multi-label image recognition with graph networks. Pattern Recogn Lett. 2020;138:378–84.
Wang F, Jiang M, Qian C, Yang S, Li C, Zhang H, et al. Residual attention network for image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2017. p. 3156–3164.
Li X, Zhong Z, Wu J, Yang Y, Lin Z, Liu H. Expectation-maximization attention networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019. p. 9167–9176.
Chu Q, Ouyang W, Li H, Wang X, Liu B, Yu N. Online multi-object tracking using CNN-based single object tracker with spatial-temporal attention mechanism. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2017. p. 4836–4845.
Ba J, Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K. Multiple object recognition with visual attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:14127755. 2014.
Mnih V, Heess N, Graves A, et al. Recurrent models of visual attention. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2014. p. 2204–2212.
Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R, Cho K, Courville A, Salakhudinov R, et al. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. 2015. p. 2048–2057.
Chen SF, Chen YC, Yeh CK, Wang YCF. Order-free rnn with visual attention for multi-label classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:170705495. 2017.
Uijlings JR, Van De Sande KE, Gevers T, Smeulders AW. Selective search for object recognition. Int J Comput Vis. 2013;104(2):154–71.
Zhang Z, Liu Y, Chen X, Zhu Y, Cheng MM, Saligrama V, et al. Sequential optimization for efficient high-quality object proposal generation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2017;40(5):1209–23.
Chen T, Xu M, Hui X, Wu H, Lin L. Learning semantic-specific graph representation for multi-label image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019. p. 522–531.
Everingham M, Van Gool L, Williams CK, Winn J, Zisserman A. The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge. Int J Comput Vis. 2010;88(2):303–38.
Pennington J, Socher R, Manning CD. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP). 2014. p. 1532–1543.
Zhang J, Wu Q, Shen C, Zhang J, Lu J. Multilabel image classification with regional latent semantic dependencies. IEEE Trans Multimedia. 2018;20(10):2801–13.
Yang H, Tianyi Zhou J, Zhang Y, Gao BB, Wu J, Cai J. Exploit bounding box annotations for multi-label object recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016. p. 280–288.
Chen T, Wang Z, Li G, Lin L. Recurrent attentional reinforcement learning for multi-label image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:171207465. 2017.
Maaten Lvd, Hinton G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J Mach Learn Res. 2008;9(Nov):2579–2605.
Funding
This study is funded in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.U20A20398, 62076005, 61906002), the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2008085MF191, 2008085QF306), and the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province, China (GXXT-2021-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Informed consent was not required as no human or animals were involved.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, D., Ma, L., Ding, Z. et al. An Attention-Driven Multi-label Image Classification with Semantic Embedding and Graph Convolutional Networks. Cogn Comput 15, 1308–1319 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-021-09977-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-021-09977-9