Abstract
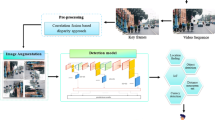
Background subtraction is a key prerequisite for intelligent video surveillance, but most of the methods employed are still affected by dynamic changes in the illumination conditions, e.g., shadows cast by passing clouds occur frequently in outdoor scenes. To resolve this problem, a novel approach based on the underlying structure of the difference image is introduced in this study. In particular, local binary patterns (LBPs) are computed based on the frame differencing result, i.e., moving LBP, and then compared with the background model, which is updated according to an online interpolation scheme, in order to determine whether the current pixel belongs to the background. An important advantage of the proposed method is that it efficiently smoothes unexpected noise between frames while also preserving the boundaries of the moving objects by using an edge-aware filtering technique. Experimental results obtained using two benchmark data sets demonstrated that the proposed method is more robust to variable illumination in outdoor scenes compared with previously proposed approaches.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Candes EJ, Li X, Ma Y, Wright J (2011) Robust principal component analysis? J ACM 58(3):11–37
Cheng L, Gong M, Schuurmans D, Caelli T (2011) Real-time discriminative background subtraction. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(5):1401–1414
Chua TW, Wang Y, Leman K (2012) Adaptive texture-color based background subtraction for video surveillance. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp 49– 52
Cui J, Liu Y, Xu Y, Zhao H, Zha H (2013) Tracking generic human motion via fusion of low- and high-dimensional approaches. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 43(4):996–1002
Davis J, Sharma V (2007) Background-subtraction using contour-based fusion of thermal and visible imagery. Comput Vis Image Underst 106(2):162–182
Fisher Box J (1987) Guinness, gosset, fisher, and small samples. Stat Sci 2 (1):45–52
Guo L, Xu D, Qiang Z (2016) Background subtraction using local SVD binary pattern. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp 1159–1167
He K, Sun J, Tang X (2013) Guided image filtering. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(6):1397–1409
IEEE International Workshop on Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance [Online]. Available: ftp://ftp.pets.rdg.ac.uk/pub/pets2001
Kim W, Han J-J (2017) Directional coherence-based spatiotemporal descriptor for object detection in static and dynamic scenes. Mach Vis Appl 28(1):49–59
Kim C, Hwang J-N (2002) Fast and automatic object segmentation and tracking for content-based applications. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 12(2):122–129
Kim W, Kim Y (2016) Background subtraction using illumination-invariant structural complexity. IEEE Signal Process Lett 23(5):634–638
Kim W, Suh S, Hwang W, Han J-J (2014) SVD face: illumination-invariant face representation. IEEE Signal Process Lett 21(11):1336–1340
Klare B, Sarkar S (2009) Background subtraction in varying illuminations using an ensemble based on an enlarged feature set. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp 66–73
Li Y, Yan J, Zhou Y, Yang J (2010) Optimum subspace learning and error correction for tensors. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp 790–803
Liu Y, Zhang X, Cui J, Wu C, Aghajan H, Zha H (2010) Visual analysis of child-adult interactive behaviors in video sequences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Virtual Systems and Multimedia, pp 26–33
Liu Y, Cui J, Zhao H, Zha H (2012) Fusion of low-and high-dimensional approaches by tracker sampling for generic human motion tracking. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp 898–901
Liu X, Zhao G, Yao J, Qi C (2015) Background subtraction based on low-rank and structured sparse decomposition. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(8):2502–2514
Liu L, Cheng L, Liu Y, Jia Y, Rosenblum DS (2016) Recognizing complex activities by a probabilistic interval-based model. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 1266– 1272
Liu Y, Liang Y, Liu S, Rosenblum DS, Zheng Y (2016) Predicting urban water quality with ubiquitous data. arXiv:1610.09462, pp 1-14
Liu Y, Nie L, Han L, Zhang L, Rosenblum DS (2016) Action2Activity: recognizing complex activities from sensor data. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 1617–1623
Liu Y, Nie L, Liu L, Rosenblum DS (2016) From action to activity: sensor-based activity recognition. Neurocomputing 181(3):108–115
Liu Y, Zhang L, Nie L, Yan Y, Rosenblum DS (2016) Fortune teller: predicting your career path. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 201–207
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Liang Y, Liu S, Rosenblum DS (2016) Urban water quality prediction based on multi-task multi-view learning. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 2576–2582
Lu Y, Wei Y, Liu L, Zhong J, Sun L, Liu Y (2017) Towards unsupervised physical activity recognition using smartphone accelerometers. Multimed Tools Appl 76(8):10701–10719
Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Maenpaa T (2002) Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(7):971–987
Pilet J, Strecha C, Fua P (2008) Making background subtraction robust to sudden illumination changes. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp 567–580
Preotiuc-Pietro D, Liu Y, Hopkins DJ, Ungar L (2017) Beyond binary labels: political ideology prediction of twitter users. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 729–740
Sajid H, Cheung S-CS (2017) Universal multimode background subtraction. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(7):3249–3260
Shen Y, Hu W, Yang M, Liu J, Wei B, Lucey S, Chou CT (2016) Real-time and robust compressive background subtraction for embedded camera networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 15(2):406–418
Sobral A, Javed S, Jung SK, Bouwmans T, Zahzah E -H (2015) Online stochastic tensor decomposition for background subtraction in multispectral video sequences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp 946–953
St-Charles P-L, Bilodeau G-A, Bergevin R (2016) Universal background subtraction using word consensus models. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(10):4768–4781
Stauffer C, Grimson WEL (1999) Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 246–252
Them K, Kaul MG, Jung C, Hofmann M, Mummert T, Werner F, Knopp T (2016) Sensitivity enhancement in magnetic particle imaging by background subtraction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(3):893–900
Xue G, Sun J, Song L (2010) Background subtraction based on phase and distance transform under sudden illumination change. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp 3465–3468
Yin H, Yang H, Su H, Zhang C (2013) Dynamic background subtraction based on appearance and motion pattern. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops, pp 1–6
Zeng Z, Jia J, Yu D, Chen Y, Zhu Z (2016) Pixel modeling using histograms based on fuzzy partitions for dynamic background subtraction. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 25(3):584–593
Zhang W, Fang X, Yang XK, Wu QMJ (2007) Moving cast shadows detection using ratio edge. IEEE Trans Multimed 9(6):1202–1214
Zhang S, Yao H, Liu S (2008) Dynamic background modeling and subtraction using spatio-temporal local binary patterns. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp 1556–1559
Zhang X, Zhu C, Wu H, Liu Z, Xu Y (2017) An imbalance compensation framework for background subtraction. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2017.2701645
Zhao S, Chen L, Yao H, Zhang Y, Sun X (2015) Strategy of dynamic 3D depth data matching towards robust action retrieval. Neurocomputing 151(2):533–543
Zhou X, Yang C, Yu W (2013) Moving object detection by detecting contiguous outliers in the low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(3):597–610
Zivkovic Z (2004) Improved adaptive Gaussian mixture model for background subtraction. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp 28–31
Zivkovic Z, Heijden FVD (2006) Efficient adaptive density estimation per image pixel for the task of background subtraction. Pattern Recogn Lett 27(7):773–780
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, W. Background subtraction with variable illumination in outdoor scenes. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 19439–19454 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5410-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5410-6