Abstract
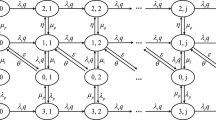
As an enabling technology for dynamic spectrum access (DSA), cognitive radio (CR) is widely regarded as one of the most promising technologies for future the fifth generation (5G) wireless communications. Although there have been significant prior researches to combat interference on primary users (PUs), the problem of mitigating mutual interference between secondary users (SUs), -which is tightly coupled with SU’s spectrum leasing- is still not understood well. This paper proposes a DSA algorithm based on game theory, which jointly performs spectrum leasing and interference mitigation among SUs. The problem is modeled as an oligopolistic competition using Stackelberg model. We have carefully studied the SU’s spectrum utilization behavior with respect to various criteria of the proposed game theoretic model. Simulation results shows that, Compared with Cournot game model, the proposed scheme enables SUs to efficiently utilize the licensed spectrum shared with PUs in a dynamic environment while maximizing the spectrum utilization.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badoi C-I, Prasad N, Croitoru V, Prasad R (2011) 5G based on cognitive radio. Wirel Pers Commun 57(3):441–464
Wang X, Vasilakos AV, Chen M, Liu Y (2012) Ted Taekyoung Kwon, A survey of green mobile networks: opportunities and challenges. Mob Netw Appl 17(1):4–20
Ying-Chang L, Kwang-Cheng C, Geoffrey Ye L, Petri M (2011) Cognitive radio networking and communications: an overview. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 60(7):3386–3407
Zhao Y, Mao S, Neel JO, Reed JH (2009) Performance evaluation of cognitive radios: metrics, utility functions, and methodology. Proc IEEE 97(4):642–658
Borhan J, Rongbo Z, Hooman S, Mehul M (2014) An optimal cross-layer framework for cognitive radio network under interference temperature model. IEEE Syst J, pp. 1–9
Jin L, Eryk D, Ren Ping L, Rein V (2015) Opportunistic spectrum access with two channel sensing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 14(1):126–138
Demestichas PP, Stavroulaki V-AG, Papadopoulou L-MI, Vasilakos AV, Theologou ME (2004) Service configuration and traffic distribution in composite radio environments. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C Appl Rev 34(1):69–81
Zheng M, Zheng QZ, Zhi GD, Ping ZF, Heng CL (2015) Key techniques for 5G wireless communications: network architecture, physical layer, and MAC layer perspectives, Science China Information Sciences, vol. 58, no. 4
Hong X, Wang J, Wang C-X, Shi J (2014) Cognitive radio in 5G: a perspective on energy-spectral efficiency trade-off. IEEE Commun Mag 52(7):46–53
Mitola J, Gerald Q, Maguire JR (1999) Cognitive radios: making software radios more personal. IEEE Pers Commun 6(4):13–18
Yang M, Li Y, Jin D, Zeng L, Xin W, Vasilakos AV (2015) Software-defined and virtualized future mobile and wireless networks: a survey. Mob Netw Appl 20(1):4–18
Yong N, Yong L, Depeng J, Li S, Athanasios VV (2015) A survey of millimeter wave communications (mmWave) for 5G: opportunities and challenges, Wireless Networks, pp. 1–20
Alireza A, Helen T, Vasilakos AV, Richard Yu F, Leung VCM (2012) A survey of security challenges in cognitive radio networks: solutions and future research directions. Proc IEEE 100(12):3172–3186
Sheng Z, Yang S, Yifan Y, Vasilakos A, McCann J, Leung K (2013) A survey on the ietf protocol suite for the internet of things: standards, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Wirel Commun 20(6):91–98
Shankhanaad M, Rajiv D, Roya Arab L, Bhargava VK (2015) Robust resource optimization for cooperative cognitive radio networks with imperfect CSI. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 14(2):907–920
Zhenguo W, Xiaozhu L, Yan Z, Hooman S, Rongbo Z (2015) Backup Routing Algorithm Based on Delay Constraint in Cognitive Radio Sensor Networks. Int J Distributed Sens Netw vol. 2015, Article ID 937104, pp. 1–11
Zhu R, Wang J (2012) Power-efficient spatial reusable channel assignment scheme in WLAN mesh networks. ACM Mob Netw Appl 17(1):53–63
Boyd SW, Michael Frye J, Pursley MB, Royster IV TC (2012) Spectrum monitoring during reception in dynamic spectrum access cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Commun 60(2):547–558
Vahid A, Sonia A (2012) Spectrum sharing in cognitive radio systems: ergodic and outage capacities. IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference 2012, VTC Fall 2012
Cui S, Cai J (2012) Demand-matching spectrum sharing in cognitive radio networks: a classified game, Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences. Social-Inf Telecommun Eng 98:534–546
Youssef M, Ibrahim M, Abdelatif M, Chen L, Vasilakos AV (2014) Routing metrics of cognitive radio networks: a survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 16(1):92–109
Beibei W, Yongle W, Ray Liu KJ (2010) Game theory for cognitive radio networks: an overview. Comput Netw 54(14):2537–2561
Hu-sheng L (2010) Socially optimal queuing control in cognitive radio systems: pricing and learning, IEEE WCNC
Jiang T, Wang H, Vasilakos AV (2012) QoE-driven channel allocation schemes for multimedia transmission of priority-based secondary users over cognitive radio networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 30(7):1215–1224
Manzoor Ahmed K, Hamidou T, Vasilakos AV (2012) Game dynamics and cost of learning in heterogeneous 4G networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 30(1):198–213
Ligia CC, Dumitrescu D, Réka N, Noemi G (2012) Cognitive radio simultaneous spectrum access/one-shot game modeling, 8th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP 2012), pp. 1–6
Chonggang W, Kazem S, Rittwik J, Lusheng J, Mahmoud D (2011) Network selection for secondary users in cognitive radio system, IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 2741–2749
Tie L, Motani M, Srinivasan V (2009) Cooperative asynchronous multi-channel MAC: design, analysis, and implementation. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 8(3):338–352
Alcaraz JJ, Van Der Mihaela S (2014) Coalitional games with intervention: application to spectrum leasing in cognitive radio. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 13(11):6166–6179
Nguyen Duy D, Madhukumar AS (2014) Non-cooperative power control and spectrum allocation in cognitive radio networks: a game theoretic perspective. Wirel Commun Mob Comput 14(5):516–525
Niyato D, Hossain E (2008) Competitive pricing for spectrum sharing in cognitive networks: dynamic game, inefficiency of nash equilibrium and collision. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 26(1):192–202
Byun S-S, Balashingham I, Vasilakos AV, Lee H-N (2014) Computation of an equilibrium in spectrum markets for cognitive radio networks. Source: IEEE Trans Comput 63(2):304–316
Lopez-Perez D, Chu X, Vasilakos AV, Claussen H (2013) On distributed and coordinated resource allocation for interference mitigation in self-organizing lte networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Networking 21(4):1145–1158
Lopez-Perez D, Chu X, Vasilakos AV, Claussen H (2014) Power minimization based resource allocation for interference mitigation in OFDMA femtocell networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 32(2):333–344
Sang-Seon B, Ilangko B, Athanasios VV (2011) A market-clearing model for spectrum trade in cognitive radio networks, International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing (MobiHoc), 2011
Chakravarthy V, Li X, Zhiqiang W, Temple MA, Garber F, Kannan R, Vasilakos A (2009) Novel overlay/underlay cognitive radio waveforms using SD-SMSE framework to enhance spectrum efficiency-part I: theoretical framework and analysis in AWGN channel. IEEE Trans Commun 57(12):3794–3804
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61272497, No. 61103019, No. 60902053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhu, R., Jalaian, B. et al. Dynamic Spectrum Access Algorithm Based on Game Theory in Cognitive Radio Networks. Mobile Netw Appl 20, 817–827 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-015-0623-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-015-0623-2