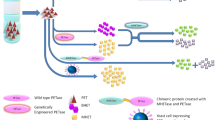
Abstract
Background
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) is one of the most widely used water-soluble polymers with remarkable mechanical properties. However, water-soluble polymers are among the major organic pollutants of streams, river, and marine ecosystems. Once dispersed in aqueous systems, they can directly interfere with the life cycle of aquatic organisms via direct toxic effects. There is thus an urgent need for microorganisms or enzymes that can efficiently degrade them. Oxidized PVA hydrolase plays an important role in the pathway of PVA biodegradation. It is the key enzyme in the second step of the pathway for complete degradation of PVA.
Methods and results
The s-oph gene was cloned from the laboratory-isolated strain Sphingopyxis sp. M19. This gene was expressed in the Escherichia coli system pET32a/s-oph expression vector, with the products forming an inclusion body. By binding with a molecular chaperone, pET32a/s-oph/BL21 (DE3)/pGro7 was successfully constructed, which enabled the s-oph gene to be solubly expressed in E. coli. The protein encoded by the s-oph gene was purified at a yield of 16.8 mg L−1, and its catalytic activity reached 852.71 U mg−1. In the s-oph enzyme reaction system, the efficiency of PVA degradation was increased to 233.5% compared with that of controls.
Conclusions
The s-oph enzyme exhibited the characteristics of being able to degrade PVA with high efficiency, specificity, and stability. This enzyme has good potential for practical application in ameliorating plastic pollution and protecting the environment.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
References
Sapalidis AA (2020) Porous polyvinyl alcohol membranes: preparation methods and applications. Symmetry 12(6):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12060960
Li P, Wang X, Su M, Zou X, Duan L, Zhang H (2021) Characteristics of plastic pollution in the environment: a review. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107(4):577–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02820-1
Geyer R, Jambeck JR, Law KL (2017) Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci Adv 3(7):e1700782. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700782
Ye B, Li Y, Chen Z, Wu QY, Wang WL, Wang T, Hu HY (2017) Degradation of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) by UV/chlorine oxidation: radical roles, influencing factors, and degradation pathway. Water Res 124:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.05.059
Jambeck JR, Geyer R, Wilcox C, Siegler TR, Perryman M, Andrady A, Narayan R, Law KL (2015) Marine pollution. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 347(6223):768–771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260352
Larking DM, Crawford RJ, Christie GB, Lonergan GT (1999) Enhanced degradation of polyvinyl alcohol by Pycnoporus cinnabarinus after pretreatment with Fenton’s reagent. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(4):1798–1800. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.65.4.1798-1800.1999
Mori T, Sakimoto M, Kagi T, Sakai T (1996) Isolation and characterization of a strain of Bacillus megaterium that degrades poly (vinyl alcohol). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60(2):330–332. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.60.330
Kawai F, Hu X (2009) Biochemistry of microbial polyvinyl alcohol degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84(2):227–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2113-6
Yamatsu A, Matsumi R, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2006) Isolation and characterization of a novel poly(vinyl alcohol)-degrading bacterium, Sphingopyxis sp PVA3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72(4):804–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0351-4
Wei Y, Fu J, Wu J, Jia X, Zhou Y, Li C, Dong M, Wang S, Zhang J, Chen F (2017) Bioinformatics analysis and characterization of highly efficient polyvinyl alcohol (pva)-degrading enzymes from the novel PVA degrader Stenotrophomonas rhizophila QL-P4. Appl Environ Microbiol 84(1):e01898–e01817. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01898-17
Bian H, Cao M, Wen H, Tan Z, Jia S, Cui J (2019) Biodegradation of polyvinyl alcohol using cross-linked enzyme aggregates of degrading enzymes from Bacillus niacini. Int J Biol Macromol 124:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.204
Jia D, Yang Y, Peng Z, Zhang D, Li J, Liu L, Du G, Chen J (2014) High efficiency preparation and characterization of intact poly(vinyl alcohol) dehydrogenase from Sphingopyxis sp.113P3 in Escherichia coli by inclusion bodies renaturation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172(5):2540–2551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0703-3
Han T, Ming H, Deng L, Zhu H, Liu Z, Zhang J, Song Y (2017) A novel expression vector for the improved solubility of recombinant scorpion venom in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482(1):120–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.047
Lu Q (2005) Seamless cloning and gene fusion. Trends Biotechnol 23(4):199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2005.02.008
Darabedian N, Thompson JW, Chuh KN, Hsieh-Wilson LC, Pratt MR (2018) Optimization of chemoenzymatic mass tagging by strain-promoted cycloaddition (SPAAC) for the determination of O-GlcNAc stoichiometry by western blotting. Biochemistry 57(40):5769–5774. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00648
Birchfield AS, McIntosh CA (2020) The effect of recombinant tags on citrus paradisi flavonol-specific 3-O glucosyltransferase activity. Plants (Basel) 24(93):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9030402
Klomklang W, Tani A, Kimbara K, Mamoto R, Ueda T, Shimao M, Kawai F (2005) Biochemical and molecular characterization of a periplasmic hydrolase for oxidized polyvinyl alcohol from Sphingomonas sp strain 113P3. Microbiol (Reading) 151(Pt 4):1255–1262. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.27655-0
Hirota-Mamoto R, Nagai R, Tachibana S, Yasuda M, Tani A, Kimbara K, Kawai F (2006) Cloning and expression of the gene for periplasmic poly(vinyl alcohol) dehydrogenase from Sphingomonas sp strain 113P3, a novel-type quinohaemoprotein alcohol dehydrogenase. Microbiol (Reading) 152(Pt 7):1941–1949. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.28848-0
Kaur J, Kumar A, Kaur J (2017) Strategies for optimization of heterologous protein expression in E. coli: Roadblocks and reinforcements. Int J Biol Macromol 106:803–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.080
Carrió MM, Villaverde A (2003) Role of molecular chaperones in inclusion body formation. FEBS Lett 537(1–3):215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00126-1
Malekian R, Sima S, Jahanian-Najafabadi A, Moazen F, Akbari V (2019) Improvement of soluble expression of GM-CSF in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli using chemical and molecular chaperones. Protein Expr Purif 160:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2019.04.002
Farajnia S, Ghorbanzadeh V, Dariushnejad H (2020) Effect of molecular chaperone on the soluble expression of recombinant fab fragment in E. coli. Int J Pept Res Ther 26:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-019-09833-3
Peng S, Chu Z, Lu J, Li D, Wang Y, Yang S, Zhang Y (2016) Co-expression of chaperones from P. furiosus enhanced the soluble expression of the recombinant hyperthermophilic α-amylase in E. coli. Cell Stress Chaperones 21(3):477–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-016-0675-7
Ravitchandirane G, Bandhu S, Chaudhuri TK (2022) Multimodal approaches for the improvement of the cellular folding of a recombinant iron regulatory protein in E. coli. Microb Cell Fact 21(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-022-01749-w
Chant A, Kraemer-Pecore CM, Watkin R, Kneale GG (2005) Attachment of a histidine tag to the minimal zinc finger protein of the aspergillus nidulans gene regulatory protein AreA causes a conformational change at the DNA-binding site. Protein Expr Purif 39(2):152–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2004.10.017
Zhao D, Huang Z (2016) Effect of his-tag on expression, purification, and structure of zinc finger protein, ZNF191(243–368). Bioinorg Chem Appl 2016:8206854. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8206854
Deng A, Boxer SG (2018) Structural insight into the photochemistry of split green fluorescent proteins: a unique role for a his-tag. J Am Chem Soc 140(1):375–381. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b10680
Ahmad F (2022) Protein stability [determination] problems. Front Mol Biosci 9:880358. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.880358
Durban N, Rafrafi Y, Rizoulis A, Albrecht A, Robinet JC, Lloyd JR, Bertron A, Erable B (2018) Nitrate and nitrite reduction at high pH in a cementitious environment by a microbial microcosm. Int Biodeter Biodegr 134:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2018.08.009
Liwarska-Bizukojc E (2021) Effect of (bio)plastics on soil environment: a review. Sci Total Environ 795:148889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148889
De Gisi S, Gadaleta G, Gorrasi G, La Mantia FP, Notarnicola M, Sorrentino A (2022) The role of (bio)degradability on the management of petrochemical and bio-based plastic waste. J Environ Manage 310:114769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114769
Bilal M, Iqbal HMN (2019) Tailoring multipurpose biocatalysts via protein engineering approaches: a review. Catal Lett 149:2204–2217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-02821-8
Abdelmoez W, Dahab I, Ragab EM, Abdelsalam OA, Mustafa A (2021) Bio- and oxo-degradable plastics: insights on facts and challenges. Polym Adv Technol 32:1981–1996. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5253
Emadian SM, Onay TT, Demirel B (2017) Biodegradation of bioplastics in natural environments. Waste Manag 59:526–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.10.006
Singh Jadaun J, Bansal S, Sonthalia A, Rai AK, Singh SP (2022) Biodegradation of plastics for sustainable environment. Bioresour Technol 347:126697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126697
Goswami P, Chinnadayyala SS, Chakraborty M, Kumar AK, Kakoti A (2013) An overview on alcohol oxidases and their potential applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(10):4259–4275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4842-9
Hatanaka T, Hashimoto T, Kawahara T, Takami M, Asahi N, Wada R (1996) Biodegradability of oxidized poly(vinyl alcohol). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60(11):1861–1863. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.60.1861
Pohorille A, Wilson MA, Shannon G (2017) Flexible proteins at the origin of life. Life (Basel) 7(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/life7020023
Paraskevopoulou V, Falcone FH (2018) Polyionic tags as enhancers of protein solubility in recombinant protein expression. Microorganisms 6(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6020047
Ki MR, Pack SP (2020) Fusion tags to enhance heterologous protein expression. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(6):2411–2425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10402-8
Karaiyan P, Chang CCH, Chan ES, Tey BT, Ramanan RN, Ooi CW (2022) In silico screening and heterologous expression of soluble dimethyl sulfide monooxygenases of microbial origin in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106(12):4523–4537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12008-8
Kim DG, Choi Y, Kim HS (2021) Epitopes of protein binders are related to the structural flexibility of a target protein surface. J Chem Inf Model 61(4):2099–2107. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.0c01397
Arcus VL, van der Kamp MW, Pudney CR, Mulholland AJ (2020) Enzyme evolution and the temperature dependence of enzyme catalysis. Curr Opin Struct Biol 65:96–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2020.06.001
Kuo CH, Huang CY, Shieh CJ, Dong CD (2022) Enzymes and biocatalysis. Catalysts 12(9):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090993
Jun LY, Mubarak NM, Yon LS, Bing CH, Khalid M, Jagadish P, Abdullah EC (2019) Immobilization of peroxidase on functionalized MWCNTs-buckypaper/polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite membrane. Sci Rep 9(1):2215. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39621-4
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their deep gratitude to publishers for providing publication support for this work. We also thank NES Institution (http://www.nesediting.com/) for editing the language of a draft of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: U1301231).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Xinyu Wang and Jiaxuan Li. Xiaoshan Lin was responsible for the procurement of laboratory reagents. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Xinyu Wang, Yi Zhang modified the manuscript and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethics declarations
This article does not refer to any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Li, J., Lin, X. et al. The s-oph enzyme for efficient degradation of polyvinyl alcohol: soluble expression and catalytic properties. Mol Biol Rep 50, 8523–8535 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08712-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08712-x