Abstract
Background
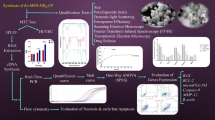
The studies have shown that rutin has great potential as an anticancer and antimicrobial plant base agent; nevertheless, poor bioavailability and low aqueous solubility of rutin limit its application. One of the beneficial routes to increase the solubility and bioavailability of rutin is the development of nanoparticulate material. This study aimed to assess the anticancer and antibacterial effects of rutin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles (RUT-MSNs).
Methods
RUT-MSNs were prepared and physicochemically characterized. The cytotoxicity of RUT-MSNs on the HN5 cells as head and neck cancer cells was evaluated. The expression level of apoptosis-related genes such as Bcl-2 and Bax genes were evaluated. In addition, ROS production of RUT-MSNs treated cells was assessed. In addition, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), biofilm, and attachment inhibitory effects of RUT-MSNs compared with free rutin were assessed against different bacterial strains.
Results
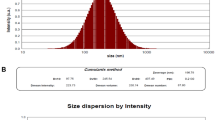
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) showed mesoporous rod-shaped nanoparticles with an average particle size of less than 100 nm. RUT-MSNs displayed the cytotoxic effect with IC50 of 20.23 µM in 48 h of incubation time (p < 0.05). The elevation in the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 was displayed within the IC50 concentration of RUT-MSNs in 48 h (p < 0.05). The antibacterial action of rutin was improved by loading rutin in MSNs to the nano-sized range in the MIC test.
Conclusion
The anticancer and antibacterial effects of RUT-MSNs were considerably more than rutin. RUT-MSNs inhibited the growth of HN5 cells by inducing apoptosis and producing ROS. These results suggest that RUT-MSNs may be useful in the treatment of cancers and infections.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohseni M, Samadi N, Ghanbari P, Yousefi B, Tabasinezhad M, Sharifi S, Nazemiyeh H (2016) Co-treatment by docetaxel and vinblastine breaks down P-glycoprotein mediated chemo-resistance. Iran J basic Med Sci 19:300
Lin S-R, Fu Y-S, Tsai M-J, Cheng H, Weng C-F (2017) Natural compounds from herbs that can potentially execute as autophagy inducers for cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci 18:1412
Sharifi S, Moghaddam FA, Abedi A, Maleki Dizaj S, Ahmadian S, Abdolahinia ED, Khatibi SMH, Samiei M (2020) Phytochemicals impact on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. BioFactors. 46(6):874–893
Samadi N, Ghanbari P, Mohseni M, Tabasinezhad M, Sharifi S, Nazemieh H, Rashidi MR (2014) Combination therapy increases the efficacy of docetaxel, vinblastine and tamoxifen in cancer cells. J Cancer Res Ther 10:715
Armat M, Bakhshaiesh TO, Sabzichi M, Shanehbandi D, Sharifi S, Molavi O, Mohammadian J, Hejazi MS, Samadi N (2016) The role of Six1 signaling in paclitaxel-dependent apoptosis in MCF-7 cell line. Bosnian J basic Med Sci 16:28
Montané X, Kowalczyk O, Reig-Vano B, Bajek A, Roszkowski K, Tomczyk R, Pawliszak W, Giamberini M, Mocek-Płóciniak A (2020) Tylkowski, B. Current perspectives of the applications of polyphenols and flavonoids in cancer therapy. Molecules 25:3342
Sheikh I, Sharma V, Tuli HS, Aggarwal D, Sankhyan A, Vyas P, Sharma AK, Bishayee A (2020) Cancer chemoprevention by flavonoids, dietary polyphenols and terpenoids. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 11:8502–8537
Khezri K, Maleki Dizaj S, Rahbar Saadat Y, Sharifi S, Shahi S, Ahmadian E, Eftekhari A, Dalir Abdolahinia E, Lotfipour F (2021) Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via curcumin-containing nanoscaffolds. Stem Cells Intern. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1520052
Sharifi S, Zununi Vahed S, Ahmadian E, Maleki Dizaj S, Abedi A, Hosseiniyan Khatibi SM, Samiei M (2019) Stem cell therapy: Curcumin does the trick. Phytother Res 33:2927–2937
Samiei M, Abedi A, Sharifi S, Maleki Dizaj S (2021) Early osteogenic differentiation stimulation of dental pulp stem cells by calcitriol and curcumin. Stem Cells Intern. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9980137
Romagnolo DF, Selmin OI (2012) Flavonoids and cancer prevention: a review of the evidence. J Nutr Gerontol Geriatr 31:206–238
Maggioni D, Biffi L, Nicolini G, Garavello W (2015) Flavonoids in oral cancer prevention and therapy. Eur J Cancer Prev 24:517–528
Farha AK, Gan R-Y, Li H-B, Wu D-T, Atanasov AG, Gul K, Zhang J-R, Yang Q-Q, Corke H (2022) The anticancer potential of the dietary polyphenol rutin: Current status, challenges, and perspectives. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 62:832–859
Saha S, Prajapati DG, Ratrey P, Mishra A (2022) Co-delivery nanosystem of Epigallocatechin Gallate and Rutin for anticancer and antibacterial activities. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 70:103191
Ferreira M, Costa D, Sousa  (2022) Flavonoids-Based delivery systems towards cancer therapies. Bioengineering 9:197
Wang M, Zhang Y, Guo P (2017) Effect of florfenicol and thiamphenicol exposure on the photosynthesis and antioxidant system of Microcystis flos-aquae. Aquat Toxicol 186:67–76
Deepika MS, Thangam R, Sakthidhasan P, Arun S, Sivasubramanian S, Thirumurugan R (2018) Combined effect of a natural flavonoid rutin from Citrus sinensis and conventional antibiotic gentamicin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Food Control 90:282–294
Singh A, Gupta R, Pandey R (2016) Rice seed priming with picomolar rutin enhances rhizospheric Bacillus subtilis CIM colonization and plant growth. PLoS ONE 11:e0146013
Al-Shabib NA, Husain FM, Ahmad I, Khan MS, Khan RA, Khan JM (2017) Rutin inhibits mono and multi-species biofilm formation by foodborne drug resistant Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 79:325–332
Deepika MS, Thangam R, Vijayakumar TS, Sasirekha R, Vimala R, Sivasubramanian S, Arun S, Babu MD, Thirumurugan R (2019) Antibacterial synergy between rutin and florfenicol enhances therapeutic spectrum against drug resistant Aeromonas hydrophila. Microb Pathog 135:103612
Cushnie TT, Lamb AJ (2005) Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int J Antimicrob Agents 26:343–356
Orhan DD, Özçelik B, Özgen S, Ergun F (2010) Antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral activities of some flavonoids. Microbiol Res 165:496–504
Gullón B, Lú-Chau TA, Moreira MT, Lema JM, Eibes G, Rutin (2017) A review on extraction, identification and purification methods, biological activities and approaches to enhance its bioavailability. Trends Food Sci Technol 67:220–235
Joye IJ, Davidov-Pardo G, McClements DJ (2014) Nanotechnology for increased micronutrient bioavailability. Trends Food Sci Technol 40:168–182
Manocha S, Dhiman S, Grewal AS, Guarve K, Nanotechnology, (2022) An approach to overcome bioavailability challenges of nutraceuticals. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103418
Amna T, Hassan MS, Gharsan FN, Rehman S, Sheikh FA (2022) Nanotechnology in drug delivery systems: Ways to boost bioavailability of drugs. Berlin, pp 223–236
Li J, Ding Z, Li Y, Miao J, Wang W, Nundlall K, Chen S (2020) Reactive oxygen species-sensitive thioketal-linked mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug carrier for effective antibacterial activity. Mater Design 195:109021
Park SS, Jung MH, Lee Y-S, Bae J-H, Kim S-H, Ha C-S (2019) Functionalised mesoporous silica nanoparticles with excellent cytotoxicity against various cancer cells for pH-responsive and controlled drug delivery. Mater Design 184:108187
Raza A, Sime FB, Cabot PJ, Maqbool F, Roberts JA, Falconer, (2019) J.R. Solid nanoparticles for oral antimicrobial drug delivery: a review. Drug Discov Today. 24:858–866
Argyo C, Weiss V, Bräuchle C, Bein T (2014) Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a universal platform for drug delivery. Chem Mater 26:435–451
Liu J, Luo Z, Zhang J, Luo T, Zhou J, Zhao X, Cai K (2016) Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles facilitated drug delivery via cascade pH stimuli in tumor microenvironment for tumor therapy. Biomaterials 83:51–65. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.01.008
Alyassin Y, Sayed EG, Mehta P, Ruparelia K, Arshad MS, Rasekh M, Shepherd J, Kucuk I, Wilson PB, Singh N et al (2020) Application of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for chemotherapeutic agents. Drug Discovery Today 25:1513–1520. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2020.06.006
Mai WX, Meng H (2013) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A multifunctional nano therapeutic system. Integr biology: Quant Biosci nano macro 5:19–28. doi:https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ib20137b
Freidus LG, Kumar P, Marimuthu T, Pradeep P, Choonara YE (2021) Theranostic Mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with a curcumin-naphthoquinone conjugate for potential cancer intervention. Front Mol Biosci 8:670792
Ruggiero I, Terracciano M, Martucci NM, De Stefano L, Migliaccio N, Tatè R, Rendina I, Arcari P, Lamberti A, Rea, (2014) Diatomite silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:1–7
Bohlouli S, Jafarmadar Gharehbagh F, Dalir Abdolahinia E, Kouhsoltani M, Ebrahimi G, Roshangar L, Imani A, Sharifi S, Maleki Dizaj S (2021) Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of rutin nanocrystals as an anticancer agent against head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9980451
Weinstein MP, Lewis JS (2020) The clinical and laboratory standards institute subcommittee on antimicrobial susceptibility testing: background, organization, functions, and processes. J Clin Microbiol 58: e01864–19
Ghorbani H, Memar MY, Sefidan FY, Yekani M, Ghotaslou R (2017) In vitro synergy of antibiotic combinations against planktonic and biofilm Pseudomonas aeruginosa. GMS hygiene and infection control. https://doi.org/10.3205/dgkh000302
Eruslanov E, Kusmartsev S (2010) Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry. Berlin, pp 57–72
Boy HIA, Rutilla AJH, Santos KA, Ty AMT, Alicia IY, Mahboob T, Tangpoong J, Nissapatorn V (2018) Recommended medicinal plants as source of natural products: a review. Digit Chin Med 1:131–142
Shakya AK (2016) Medicinal plants: Future source of new drugs. Int J Herb Med 4:59–64
Gacche RN, Shaikh RU, Pund MM (2011) In vitro evaluation of anticancer and antimicrobial activity of selected medicinal plants from Ayurveda. Asian J Trad Med 6:1–7
Siddiqui AJ, Jahan S, Singh R, Saxena J, Ashraf SA, Khan A, Choudhary RK, Balakrishnan S, Badraoui R, Bardakci F (2022) Plants in anticancer drug discovery: from molecular mechanism to chemoprevention. BioMed Res Intern. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5425485
Ng PQ, Ling LS, Chellian J, Madheswaran T, Panneerselvam J, Kunnath AP, Gupta G, Satija S, Mehta M, Hansbro PM (2020) Applications of nanocarriers as drug delivery vehicles for active phytoconstituents. Curr Pharm Design 26:4580–4590
Khan T, Gurav P, PhytoNanotechnology (2018) Enhancing delivery of plant based anti-cancer drugs. Front Pharmacol 8:1002
Zhang Z, Li X, Sang S, McClements DJ, Chen L, Long J, Jiao A, Jin Z, Qiu C (2022) Polyphenols as plant-based nutraceuticals: health effects, encapsulation, nano-delivery, and application. Foods 11:2189
AbouAitah K, Lojkowski W (2021) Delivery of natural agents by means of mesoporous silica nanospheres as a promising anticancer strategy. Pharmaceutics 13:143
Mourdikoudis S, Pallares RM, Thanh NT (2018) Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 10:12871–12934
Dowding JM, Das S, Kumar A, Dosani T, McCormack R, Gupta A, Sayle TX, Sayle DC, von Kalm L, Seal SJ (2013) Cellular interaction and toxicity depend on physicochemical properties and surface modification of redox-active nanomaterials. ACS Nano 7:4855–4868
Bakand S, Hayes A (2016) Toxicological considerations, toxicity assessment, and risk management of inhaled nanoparticles. Intern J Mol Sci. 17:929
Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM, Wechsler ME, Peppas NA, Langer RJ (2021) Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:101–124
Lowry GV, Hill RJ, Harper S, Rawle AF, Hendren CO, Klaessig F, Nobbmann U, Sayre P, Rumble JJ (2016) Guidance to improve the scientific value of zeta-potential measurements in nanoEHS. Environ Sci. 3:953–965
Naushad M, Alqadami AA, AlOthman ZA, Alsohaimi IH, Algamdi MS, Aldawsari AMJ (2019) Adsorption kinetics, isotherm and reusability studies for the removal of cationic dye from aqueous medium using arginine modified activated carbon. J Mol Liq. 293:111442
Geng Y, Dalhaimer P, Cai S, Tsai R, Tewari M, Minko T, Discher DE (2007) Shape effects of filaments versus spherical particles in flow and drug delivery. Nat Nanotechnol. 2:249–255
Li D, Tang Z, Gao Y, Sun H, Zhou SJ (2016) A bio-inspired rod-shaped nanoplatform for strongly infecting tumor cells and enhancing the delivery efficiency of anticancer drugs. Adv Funct Mater 26:66–79
Zhao Y, Wang Y, Ran F, Cui Y, Liu C, Zhao Q, Gao Y, Wang D, Wang SJS (2017) Comparison between sphere and rod nanoparticles regarding their in vivo biological behavior and pharmacokinetics. Sci Rep 7:1–11
Purnawira B, Purwaningsih H, Ervianto Y, Pratiwi V, Susanti D, Rochiem R, Purniawan A (2019) Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNp) MCM 41 from natural waste rice husk. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, p 012018
Cai Q, Lin W-Y, Xiao F-S, Pang W-Q, Chen X-H, Zou B-SJM, Materials M (1999) The preparation of highly ordered MCM-41 with extremely low surfactant concentration. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 32:1–15
Karimzadeh M, Rashidi L, Ganji FJD (2017) Pharmacy, i. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient rivastigmine hydrogen tartrate delivery into SY5Y cells. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 43:628–636
Costa JA, de Jesus RA, Santos DO, Mano JF, Romao LP, Paranhos CM (2020) Recent progresses in the adsorption of organic, inorganic, and gas compounds by MCM-41-based mesoporous materials. Micropor and Mesopor Mat 291:109698
Paudel KR, Wadhwa R, Tew XN, Lau NJX, Madheswaran T, Panneerselvam J, Zeeshan F, Kumar P, Gupta G, Anand K (2021) Rutin loaded liquid crystalline nanoparticles inhibit non-small cell lung cancer proliferation and migration in vitro. Life Sci 276:119436
Hoai TT, Yen PT, Dao TTB, Long LH, Anh DX, Minh LH, Anh BQ, Thuong NT (2020) Evaluation of the cytotoxic effect of rutin prenanoemulsion in lung and colon cancer cell lines. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8867669
Blanco E, Shen H, Ferrari M (2015) Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol 33:941–951
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science. 281(5381):1309–1312
Rao L, White E (1997) Bcl-2 and the ICE family of apoptotic regulators: making a connection. Curr Opin Genet Dev 7:52–58
Huynh H (2002) Induction of apoptosis in rat ventral prostate by finasteride is associated with alteration in MAP kinase pathways and Bcl-2 related family of proteins. Int J Oncol 20:1297–1303
Firouzai-Amandi A, Tarahomi M, Rahmani Youshanlouie H, Mosaddeghi Heris R, Jafari-Gharabaghlou D, Zarghami N, Dadashpour M (2022) Development, Characterization, and In Vitro Evaluation of Cytotoxic Activity of Rutin Loaded PCL-PEG Nanoparticles Against Skov3 Ovarian Cancer Cell. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 23:1951–1957
Manoto SL, Sekhejane PR, Houreld NN, Abrahamse H (2012) Localization and phototoxic effect of zinc sulfophthalocyanine photosensitizer in human colon (DLD-1) and lung (A549) carcinoma cells (in vitro). Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 9:52–59
Sekhejane PR, Houreld NN, Abrahamse H (2014) Multiorganelle localization of metallated phthalocyanine photosensitizer in colorectal cancer cells (DLD-1 and CaCo-2) enhances efficacy of photodynamic therapy. Intern J Photoenergy. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/383027
Wiseman H, Halliwell B (1996) Damage to DNA by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: role in inflammatory disease and progression to cancer. Biochem J 313:17
Saraste A, Pulkki K (2000) Morphologic and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Cardiovascular Res 45:528–537
Raj L, Ide T, Gurkar AU, Foley M, Schenone M, Li X, Tolliday NJ, Golub TR, Carr SA, Shamji AF (2011) Selective killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targeting the stress response to ROS. Nature 475:231–234
Wang T, Wu X, Song Y, Cheng H (2020) Curcumin induces G2/M arrest and triggers autophagy, ROS generation and cell senescence in cervical cancer cells. J Cancer 11:6704
Gilardini Montani MS, Santarelli R, Granato M, Gonnella R, Torrisi M, Faggioni A, Cirone M (2019) EBV reduces autophagy, intracellular ROS and mitochondria to impair monocyte survival and differentiation. Autophagy 15:652–667
Samiei M, Farjami A, Dizaj SM, Lotfipour F (2016) Nanoparticles for antimicrobial purposes in Endodontics: A systematic review of in vitro studies. Mater Sci Engineering: C 58:1269–1278
Memar MY, Yekani M, Sharifi S, Dizaj SM (2023) Antibacterial and biofilm inhibitory effects of rutin nanocrystals 13:132
Bharathi D, Ranjithkumar R, Chandarshekar B, Bhuvaneshwari V (2019) Preparation of chitosan coated zinc oxide nanocomposite for enhanced antibacterial and photocatalytic activity: As a bionanocomposite. Int J Biol Macromol 129:989–996
Bharathi D, Ranjithkumar R, Vasantharaj S, Chandarshekar B, Bhuvaneshwari V (2019) Synthesis and characterization of chitosan/iron oxide nanocomposite for biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol 132:880–887
Singh TA, Kundu M, Chatterjee S, Pandey SK, Thakur N, Tejwan N, Sharma A, Das J, Sil PC (2022) Synthesis of Rutin loaded nanomagnesia as a smart nanoformulation with significant antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Inorg Chem Commun 140:109492
Sun F, Qu F, Ling Y, Mao P, Xia P, Chen H, Zhou D (2013) Biofilm-associated infections: antibiotic resistance and novel therapeutic strategies. Future Microbiol 8:877–886
Wu H, Moser C, Wang H-Z, Høiby N (2015) Song, Z.-J. Strategies for combating bacterial biofilm infections. Int J Oral Sci 7:1
Hwang I-s, Hwang JH, Choi H, Kim K-J, Lee DG (2012) Synergistic effects between silver nanoparticles and antibiotics and the mechanisms involved. J Med Microbiol 61:1719–1726
Acknowledgements
The financial support of the Vice-Chancellor for Research (under grant number 69579) at Tabriz University of Medical Sciences is appreciated.
Funding
Funding was provided by Tabriz University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 69579).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest has been expressed by the authors.
Ethical approval
The Ethics Committee Team of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences with the code of IR.TBZMED.VCR.REC.1401.004 approved this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Memar, M.Y., Dalir Abdolahinia, E., Yekani, M. et al. Preparation of rutin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles and evaluation of its physicochemical, anticancer, and antibacterial properties. Mol Biol Rep 50, 203–213 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07953-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07953-6