Abstract
Background:
Many genotoxicity tests allow us to understand the mechanism of damages on genetic material occurring in living organisms against various physical and chemical agents. One of them is the Comet test. The current study aimed to evaluate genotoxic caused by picloram and dicamba to root meristems of Allium cepa utilizing comet assay.
Methods:
Two different protocols were used for rooting and auxin/pesticide application. (i) A. cepa bulbs were rooted in MS medium and then treated with Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium (control) and 0.67, 1.34, 2.01, 2.68, 3.35, 4.02, and 8.04 mg/L of picloram and dicamba using aseptic tissue culture techniques. (ii) A. cepa bulbs were then rooted in bidistilled water and treated with 0 (control), 0.67, 1.34, 2.01, 2.68, 3.35, 4.02, and 8.04 mg/L of picloram and dicamba in distilled water. The A. cepa root tip cells in both treatment groups were examined using comet test to find the possible DNA damaging effects of picloram and dicamba.
Results
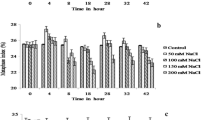
The results obtained at all the concentrations were statistically compared with their control groups. Almost at all the concentrations of Picloram and dicamba increased comet tail intensity (%) and tail moment in roots treated in MS medium. Two highest concentrations revealed toxic effect. On the other hand, DNA damaging effect of both auxins was only noted on the highest (> 4.02 mg/L) in roots treated in distilled water.
Conclusions
This study approve and confirm genotoxic effects of how growth regulators on plants. These findings give an evidence of DNA damage in A. cepa. Therefore, both picloram and dicamba should only be used in appropriate and recommended concentrations in agriculture to conserve ecosystem and to pose minimum threat to life.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study is included in this article.
References
Phillips GC, Garda M (2019) Plant tissue culture media and practices: an overview. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 55(3):242–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-019-09983-5
Oerke EC (2006) Crop losses to pests. J Agricultural Sci 144(1):31–43. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859605005708
Herman EB (2015) Recent advances in plant tissue culture XXI. Media and techniques for growth, regeneration, and storage: 2011–2015. Agritech Consultants Inc., Shrub Oak, NY
Bombardi LM (2017) Geografia do Uso de Agrotóxicos no Brasil e Conexões com a União Europeia [Geography of the use of agrochemicals in Brazil and connections with the European Union]. https://ecotoxbrasil.org.br/upload/587ed92192e9dbe77bddfd31cbe25a7-e-book_atlas_agrot_ axico_2017_larissa_bombardi.pdf. (2017)Accessed 10 January 2021
Fairchild JF, Feltz KPC, Allert AL, Nelson KJ, Valle J (2009) An ecological risk assessment of the acute, Sappington, L. and chronic toxicity of the herbicide picloram to the threatened bull trout (Salvelinus confluentus) and the rainbow trout (Onchorhyncus mykiss). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56:761–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9227-1
EPA (1995) United States Environmental Protection Agency Report. Reregistration Eligibility Decision–Picloram. Office of Pesticide Programs. Washington, DC. Accessed 26 January 2022
Harp PR Dicamba. In Hayes’ Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology (pp. 1849–1852). Academic Press
Montgomery GB, McClure AT, Hayes RM, Walker FR, Senseman SA, Steckel LE(2010) (2018) Dicamba-tolerant soybean combined cover crop to control palmer amaranth. Weed Technol 32:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1017/wet.2017.96
Miller JG, Jamwal A, Ilnytskyy Y, Hontela A, Wiseman SB (2020) Dicamba elevates concentrations of S-adenosyl methionine but does not induce oxidative stress or alter DNA methylation in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics 36:100744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbd.2020.100744
Ismail AA, Wang K, Olson JR, Bonner MR, Hendy O, Abdel Rasoul G, Rohlman DS (2017) The impact of repeated organophosphorus pesticide exposure on biomarkers and neurobehavioral outcomes among adolescent pesticide applicators. J Toxicol Environ Health A 80:542–555. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2017.1362612
Nicolopoulou-Stamati P, Maipas S, Kotampasi C, Stamatis P, Hens L (2016) Chemical pesticides and human health: The urgent need for a new concept in agriculture. Front Public Health 4:148. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2016.00148
Weichenthal S, Moase C, Chan P (2010) A review of pesticide exposure and cancer incidence in the agricultural health study cohort. Environ Health Perspect 118:1117–1125. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901731
Paszko T, Muszynski P, Materska M, Bojanowska M, Kostecka M, Jackowska I (2016) Adsorption and degradation of phenoxy alkanoic acid herbicides in soils: a review. Environ Toxicol Chem 35:271–286. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3212
Samanic C, Rusiecki J, Dosemeci M, Hou L, Hoppin JA, Sandler DP, Lubin J, Blair A, Alavanja MCR (2006) Cancer incidence among pesticide applicators exposed to dicamba in the agricultural health study. Environ Health Perspect 114:1521–1526. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9204
Lerro CC, Hofmann JN, Andreotti G, Koutros S, Parks CG, Blair A, Albert PS, Lubin JH, Sandler DP (2020) Dicamba use and cancer incidence in the agricultural health study: an updated analysis. Int J Epidemiol 49(4):1326–1337. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyaa066
Glei M, Schneider T, Schlörmann W (2016) Comet assay: an essential tool in toxicological research. Arch Toxicol 90(10):2315–2336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1767-y
Gichner T, Znidar I, Wagner E, Plewa M (2016) In: Toxicology, Dhawan A, Anderson D (eds) The use of higher plants in the Comet Assay, in: The Comet Assay. Royal Society of Chemistry, London, pp 112–133. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781782622895-00112
Ventura L, Giovannini A, Savio M, Donà M, Macovei A, Buttafava A (2013) Single Cell Gel Electrophoresis (Comet) assay with plants: research on DNA repair and ecogenotoxicity testing. Chemosphere 92:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.03.006
Liman R, Ciğerci IH, Öztürk NS (2015) Determination of genotoxic effects of Imazethapyr herbicide in Allium cepa root cells by mitotic activity, chromosome aberration, and comet assay. Pestic BiochEM Phys 118:38–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.11.007
Santos CL, Pourrut B, Oliveira JMP (2015) The use of comet assay in plant toxicology: recent advances. Front Genet 6:216. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2015.00216
Özkul M, Özel ÇA, Yüzbaşıoğlu D, Ünal F(2016) Does 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) induce enotoxic effects in tissue-culturedAllium roots? Cytotechnology68(6):2395–2405. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-9956-3
Erikel E, Yuzbasioglu D, Unal F (2020) Genotoxic and antigenotoxic potential of amygdalin on isolated human lymphocytes by the comet assay. J Food Biochem 44(10):e13436. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13436
Çakmak E, Uncuoğlu AA, Aydın Y (2019) Evaluation of in vitro genotoxic effects induced by in vitro anther culture conditions in sunflower. Plant Signal Behav 14(9):1633885. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2019.1633885
Özel CA, Ozkul M, Unal F, Yuzbasioglu D (2018) Evalutaion of genotoxicity of picloram by Allium test in plant tissue culture. Fresenius Environ Bull 27(12):8133–8138
Bellani L, Muccifora S, Barbieri F, Tassi E, Castiglione MR, Giorgetti L (2020) Genotoxicity of the food additive E171, titanium dioxide, in the plants Lens culinaris L. and Allium cepa L. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 849:503142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2020.503142
Taspinar MS, Aydin M, Sigmaz B, Yildirim N, Agar G (2017) Protective role of humic acids against picloram-induced genomic instability and DNA methylation in Phaseolus vulgaris. Environ Sci Pollut Environmental 24(29):22948–22953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9936-y
Mohammed KB, Ma TH (1999) Tradescantia-micronucleus and-stamen hair mutation assays on the genotoxicity of the gaseous and liquid forms of pesticides. Mutat Res-Fund Mol M 426(2):193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0027-5107(99)00067-6
Aydin M, Taspinar MS, Arslan E, Sigmaz B, Agar G (2015) Auxin effects on somaclonal variation and plant regeneration from the mature embryo of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Pak J Bot 47(5):1749–1757
Abass MH, Al-Utbi SD, Al-Samir EA (2017) Genotoxicity assessment of high concentrations of 2, 4-D, NAA, and Dicamba on date palm callus (Phoenix dactylifera L.) using protein profile and RAPD markers. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 15(1):87–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2016.12.003
Arslan E (2020) Putrescine in Herbicide Stress Protection: Modulate the Genomic Instability and DNA Methylation Changes in Wheat European. J Sci Technol (EJOSAT) 19:442–448. https://doi.org/10.31590/ejosat.720065
Reynoso MS, Alvarez CM, De la Cruz L, Escoto MD, Sánchez JJG (2015) Evaluation of the genotoxic activity of dicamba and atrazine herbicides in several Mexican and South American varieties of sweetcorn (Zea mays L.). Genet Mol 14(4):16585–16593
Cenkci S, Yıldız M, Ciğerci İH, Bozdağ A, Terzi H, Terzi ESA (2010) Evaluation of 2, 4-D, and Dicamba genotoxicity in bean seedlings using comet and RAPD assays. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73(7):1558–1564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.07.033
Sigmaaldrich (2018) https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/technical-documents/protocols/biology/growth-regulators.html#Auxins Accessed 20January 2022
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Juchimiuk J, Gnys A, Maluszynska J (2006) DNA damage induced by mutagens in plant and human cell nuclei in the acellular comet assay. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 44:127–131
Pazmino DM, Rodriguez-Serrano M, Romero-Puertas MC, Archilla-Ruiz A, Del Rio LD, Sandalio L (2011) Differential response of young and adult leaves to herbicide 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in pea plants: role of reactive oxygen species. Plant Cell Environ 34:1874–1889
Bhaskaran J, Panneerselvam R (2013) Accelerated reactive oxygen scavenging system and membrane integrity of two Panicum species varying in salt tolerance. Cell Biochem Biophys 67:1–8
Semane BA, Cuypers Smeets K, Van Belleghem F, Horemans N, Schat H, Vangronsveld J (2007) Cadmium responses in Arabidopsis thaliana: glutathione metabolism and antioxidative defence system. Physiol Plant 129:519–528
Sterling TM, Hall JC (1997) Mechanism of action of natural auxins and the auxinic herbicides. In: Michael R, Roe JD, Burton RJ, Kuhr (eds) Herbicide activity toxicology. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. IOS Press,US, pp 111–141
Filkowski J, Besplug J, Burke P, Kovalchuk I, Kovalchuk O (2003) Genotoxicity of 2,4-D and dicamba revealed by transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants harboring recombination and point mutation markers. Mutat Res 542:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2003.07.008
Fan C, Yang J, Liang Y, Dong H, Zhang W, Tang G, Cao Y (2019) Effective tuning guanidinium ionic liquid as a greener solvent for fast and sensitive determination of auxin herbicides. Microchem J 144:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.08.054
EPA (2001) United States Environmental Protection Agency Report. Environmental hazard assessment and ecological risk assessment methodology. Appendix H Washington. Accessed 05 February 2022
EPA (2002) United States Environmental Protection Agency Report. Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. Fifth edition. USEPA 821-R-02-012 Washington, DC. Accessed 05 February 2022
Leão MB, Gonçalves DF, Miranda GM, da Paixão GM, Dalla Corte CL (2019) Toxicological evaluation of the herbicide Palace® in Drosophila melanogaster. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A 82(22):1172–1185. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2019.1709109
Balderrama-Carmona AP, Valenzuela-Rincón M, Zamora-Álvarez LA, Adan-Bante NP, Leyva-Soto LA, Silva-Beltrán NP, Morán-Palacio EF (2020) Herbicide biomonitoring in agricultural workers in Valle del Mayo, Sonora Mexico. Environ Sci Pollut 27(23):28480–28489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07087-6
Usmani Z, Rani R, Gupta P, Prasad MNV (2020) Vermiremediation of agrochemicals. Agrochemicals Detection, Treatment and Remediation. Butterworth-Heinemann, pp 329–367
Pakdaman Sardrood B, Mohammadi Goltapeh E (2018) Weeds, Herbicides and Plant Disease Management. Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 31. Springer, Cham, pp 41–178
Baweja P, Kumar S, Kumar G (2020) Fertilizers and pesticides: their impact on soil health and environment. Soil Health. Springer, Cham, pp 265–285
Beebee TJ (2005) Conservation genetics of amphibians. Heredity 95:423–427
Jones DK, Hammond JI, Relyea RA (2009) Very highly toxic effects of endosulfan across nine species of tadpoles: lag effects and familylevel sensitivity. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1939–1945
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Gazi University Research Fund under the project number 04/2016-03.
Funding
This study was supported by Gazi University Research Fund under the project number 04/2016-03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.A. Ozel and D. Yuzbasioglu designed the research and carried out the experimental stages, collected the experimental data and wrote the article. F. Unal contributed the comet assay and the statistical analyses and write up of the article. E. Avuloglu-Yilmaz and E. Erikel contributed to all the experimental stages including writing of the article. S. Mirici contributed to tissue culture stages. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests:
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozel, C.A., Unal, F., Avuloglu-Yilmaz, E. et al. Determination of genotoxic damages of picloram and dicamba with comet assay in Allium cepa rooted in tissue culture and distilled water. Mol Biol Rep 49, 11273–11280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07712-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07712-7