Abstract
Background
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the types of bacteria that arises resistance toward fluoroquinolos antibiotics remarkably in recent years.
Methods
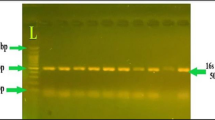
Fifty P. aeruginosa isolates were isolated from one hundred clinical samples, investigated the antibiogram activity toward eight different groups of antibiotics. Screening about gyrA gene was done by conventional PCR further more qualitative gene expression of mexA gene was done by using Real-time PCR in 22 MDR isolates, furthermore Relative gene expression analysis of gyrA and mexA was done.
Results
The rate of P. aeruginosa isolates was (41.6%) from total clinical samples, the antibiogram test showed high resistance toward Ceftazidime, Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin and Gentamicin (100%), while the sensitivity was observed towards colistin (100%). Screening of gyrA that was achieved by PCR technique showed 22 positive isolates. Furthermore, the 22 isolates appeared high expression level of the efflux pump resistance gene mexA and gyrA gene compared with housekeeping gene rspL gene within fold change ranging (0.18–36 and 1–28.84 respectively) with a mean of 18.46 ct and 18.59 (respectively).
Conclusions
All P. aeruginosa isolates were MDR with high level of efflux pump expression of mexA gene as well as gyrA gene.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awad BA, Turkey AM (2016) Study gene expression for phzA gene for PHzA gene responsible of pyocyanin production of P. aeruginosa by qPCR. Anbar Univ J Pure Sci 10(3):62–67
Al-Azzawi SNA (2018) Molecular study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance that isolated from wounds and burns treated with antiseptics. A Thesis Master of Science in Biology/Microbiology. College of Education For Pure Sciences/Ibn Al-Haitham/University of Baghdad
Auda IG, Al-Kadmy IMS, Kareem SM, Lafta AK, A’Affus MHO, Khit IAA, Al Kheraif AA, Divakar DD, Ravikumar Ramakrishnaiah R (2017) RAPD- and ERIC-based typing of clinical and environmental Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. J AOAC Int 100(2):532–536. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.16-0267
Bassetti M, Vena A, Croxatto A, Righi E, Guery B (2018) How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Drugs Context 7:212527. https://doi.org/10.7573/dic.212527
Horna G, Lopez M, Guerra H, Saenz Y, Ruiz J (2018) Interplay between MexABOprM and MexEF-OprN in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Rep 8:16463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2018.02.005
Naser HH, Aubaid AH (2020) Molecular detection and quantification gene expression of efflux pump antibiotic resistance genes in extensive drug resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from clinical infection patients in Al Diwaniyah City of Iraq. Medico-Legal Update 20(4):1–7
Kareem SM, Al-Kadmy IMS, Kazaal SS, Mohammed Ali AN, Aziz SN, Makharita RR, Algammal AM, Salim Al-Rejaie S, Behl T, Batiha GE, El-Mokhtar MA, Hetta HF (2021) Detection of gyra and parc mutations and prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Drug Resist 14:555–563. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S275852
Ugwuanyi FC, Ajayi A, Ojo DA, Adeleye AI, Smith SI (2021) Evaluation of efflux pump activity and biofilm formation in multidrug resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from a Federal Medical Center in Nigeria. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12941-021-00417-y
Lin D, Foley SL, Qi Y, Han J, Ji C, Li R, Wu C, Shen J, Wang Y (2012) Characterization of antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from canine infections. J Appl Microbiol 113(1):16–23
Amsalu A, Sapula SA, De Barros Lopes M, Hart BJ, Nguyen AH, Drigo B, Turnidge J, Leong LE, Venter H (2020) Efflux pump-driven antibiotic and biocide cross-resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from different ecological niches: a case study in the development of multidrug resistance in environmental hotspots. Microorganisms 8(11):1647
Espy MJ, Uhl JR, Sloan LM, Buckwalter SP, Jones MF, Vetter EA, Yao JDC, Wengenack NL, Rosenblatt JE, Cockerill III FR, Smith T (2006) Real-time PCR in clinical microbiology: applications for routine laboratory testing. Clin Microbiol Rev 19(1):165–256
Merchant S, Proudfoot EM, Quadri HN, McElroy HJ, Wright WR, Gupta A, Sarpong EM (2010) Risk factors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections consequences of inappropriate initial antimicrobial therapy: a systematic literature review meta-analysis. J Glob Antibiot Resist 14:33–44
Abbas HA, El-Ganiny A, Kamel HA (2018) Phenotype and genotypic detection of antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from urinary tract infections. Afri Health Sci 18(1):11–21
Odumosu BT, Adeniyi BA, Chandra R (2013) Analysis of integrons and associated gene cassettes in clinical isolates of multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa from southwest Nigeria. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 12:29
Pan Y, Xu Y, Wang Z, Fang Y, Shen J (2016) Overexpression of MexAB-OprM efflux pump in carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1215-7
Adabi M, Talebi-Taher M, Arbabi L (2015) Spread of efflux pump overexpressing-mediated fluoroquinolone resistance and multidrug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by using an efflux pump inhibitor. Infect Chemother 47(2):98–104
Helmy OM, Kashef MT (2017) Different phenotypic and molecular mechanisms associated with multidrug resistance in Gram-negative clinical isolates from Egypt. Infect Drug Resist 10:479–498
Gorgani N, Ahlbrand S, Patterson A, Pourmand N (2009) Detectionof point mutations associated with antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Antimicrob Agents 34:414–418
Lee JK, Lee YS, Park YK, Kim BS (2005) Alterations in the GyrA and GyrB subunits of topoisomerase II and the ParC and ParEsubunits of topoisomerase IV in ciprofloxacin-resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Antimicrob Agents 25:290–295
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mustansiriyah University (https://uomustansiriyah.edu.iq/)/Baghdad, Iraq for its support to complete this work.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally in writing—original draft preparation, All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The Ethics Committee of the Mustansiriyah University approved and oversaw this study.
Informed consent
All patients gave their written informed consents before inclusion.
Consent to publish
All authors agree to publish this work.
Research involving human and animals participants
This study involved the 120 from patients who are suffering from infections of burns and wounds in Baghdad hospitals, Baghdad, Iraq.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abed, W.H., Kareem, S.M. Molecular detection of gyrA and mexA genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Biol Rep 48, 7907–7912 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06820-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06820-0