Abstract
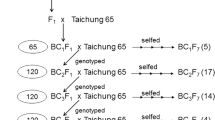
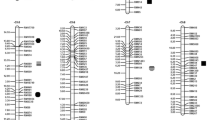
Asian cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) has two subspecies, indica and japonica, which display clear differences in yield-related traits and environmental adaptation. Here, we developed a set of chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) from an advanced backcross between japonica variety C418, as the recipient, and indica variety IR24, as the donor. Through evaluating the genotypes and phenotypes of 181 CSSLs, a total of 85 quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for 14 yield-related traits were detected, with individual QTLs explaining from 6.2 to 42.9% of the phenotypic variation. Moreover, twenty-six of these QTLs could be detected in the two trial sites (Beijing and Hainan). Among these loci, the QTLs for flag leaf width and effective tiller number, qFLW4.2 and qETN4.2, were delimited to an approximately 256-kb interval on chromosome 4. Through a comparison of nucleotide sequences and expression levels in “C418” and the CSSL CR31 containing qFLW4.2 and qETN4.2, we found that the NAL1 (LOC_Os04g52479) gene was the candidate gene for qFLW4.2 and qETN4.2. Our results show that CSSLs are powerful tools for identifying and fine-mapping QTLs, while the novel QTLs identified in this study will also provide new genetic resources for rice improvement.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets supporting the results of this article are included within the article and its supplementary information files.
References
Ali ML, Sanchez PL, Yu SB, Lorieux M, Eizenga GC (2010) Chromosome segment substitution lines: a powerful tool for the introgression of valuable genes from Oryza wild species into cultivated rice (O. sativa). Rice 3:218–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12284-010-9058-3
Ashikari M, Sakakibara H, Lin S, Yamamoto T, Takashi T, Nishimura A, Angeles ER, Qian Q, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2005) Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production. Science 309:741–745. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1113373
Balakrishnan D, Surapaneni M, Mesapogu S, Neelamraju S (2019) Development and use of chromosome segment substitution lines as a genetic resource for crop improvement. Theor Appl Genet 132:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3219-y
Chen M, Luo J, Shao G, Wei X, Tang S, Sheng Z, Song J, Hu P (2012) Fine mapping of a major QTL for flag leaf width in rice, qFLW4, which might be caused by alternative splicing of NAL1. Plant Cell Rep 31:863–872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1207-7
Cheng C, Motohashi R, Tsuchimoto S, Fukuta Y, Ohtsubo H, Ohtsubo R (2003) Polyphyletic origin of cultivated rice: based on the interspersion pattern of SINEs. Mol Biol Evol 20:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msg004
Cho SH, Yoo SC, Zhang H, Pandeya D, Koh HJ, Hwang JY, Kim GT, Paek NC (2013) The rice narrow leaf 2 and narrow leaf 3 loci encode WUSCHEL-related homeobox 3A (OsWOX3A) and function in leaf, spikelet, tiller and lateral root development. New Phytol 198:1071–1084. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12231
Dong H, Fei GL, Wu CY, Wu FQ, Sun Y, Chen MJ, Ren YL, Zhou KN, Cheng ZJ, Wang JL, Jiang L, Zhang X, Guo XP, Lei CL, Su N, Wang H, Wan JM (2013) A rice virescent-yellow leaf mutant reveals new insights into the role and assembly of plastid caseinolytic protease in higher plants. Plant Physiol 162:1867–1880. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.217604
Fujita D, Trijatmiko KR, Tagle AG, Sapasap MV, Koide Y, Sasaki K, Tsakirpaloglou N, Gannaban RB, Nishimura T, Yanagihara S, Fukuta Y, Koshiba T, Slamet-Loedin IH, Ishimaru T, Kobayashi N (2013) NAL1 allele from a rice landrace greatly increases yield in modern indica cultivars. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:20431–20436. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1310790110
Gathala MK, Ladha JK, Kumar V, Saharawat YS, Kumar V, Sharma PK, Sharma S, Pathak H (2011) Tillage and crop establishment affects sustainability of South Asian rice-wheat system. Agron J 103:961–971. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2010.0394
Guo T, Yu H, Qiu J, Li JY, Han B, Lin HX (2019) Advances in rice genetics and breeding by molecular design in China. Scientia Sinica Vitae 49:1185–1212. https://doi.org/10.1360/SSV-2019-0209
Hu J, Zhu L, Zeng D, Gao Z, Guo L, Fang Y, Zhang G, Dong G, Yan M, Liu J, Qian Q (2010) Identification and characterization of NARROW AND ROLLED LEAF 1, a novel gene regulating leaf morphology and plant architecture in rice. Plant Mol Biol 73:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-010-9614-7
Huang X, Qian Q, Liu Z, Sun H, He S, Luo D, Xia G, Chu C, Li J, Fu X (2009) Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice. Nat Genet 41:494–497. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.352
Huang Y, Zhao S, Fu Y, Sun H, Ma X, Tan L, Liu F, Sun X, Sun H, Gu P, Xie D, Sun C, Zhu Z (2018) Variation in the regulatory region of FZP causes increases in secondary inflorescence branching and grain yield in rice domestication. Plant J 96:716–733. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14062
Huo X, Wu S, Zhu Z, Liu F, Fu Y, Cai H, Sun X, Gu P, Xie D, Sun C (2017) NOG1 increases grain production in rice. Nat Commun 8:1497. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01501-8
Kubo T, Aida Y, Nakamura K, Tsunematsu H, Doi K, Yoshimura A (2002) Reciprocal chromosome segment substitution series derived from japonica and indica cross of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci 52:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.52.319
Li R, Guo M, Lu Y, Yang Y, Liu M, Zhu Q, Wei C, Gu M, Yan C (2015) Genetic dissection of hybrid breakdown in an indica/japonica cross and fine mapping of a quantitative trait locus qSF-12 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breeding 35:144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0331-4
Li X, Chen Z, Zhang G, Lu H, Qin P, Qi M, Yu Y, Jiao B, Zhao X, Gao Q, Wang H, Wu Y, Ma J, Zhang L, Wang Y, Deng L, Yao S, Cheng Z, Yu D, Zhu L, Xue Y, Chu C, Li A, Li S, Liang C (2020) Analysis of genetic architecture and favorable allele usage of agronomic traits in a large collection of Chinese rice accessions. Sci China Life Sci 63:1688–1702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-1682-6
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lu G, Coneva V, Casaretto JA, Ying S, Mahmood K, Liu F, Nambara E, Bi YM, Rothstein SJ (2015) OsPIN5b modulates rice (Oryza sativa) plant architecture and yield by changing auxin homeostasis, transport and distribution. Plant J 83:913–925. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12939
Ma X, Fu Y, Zhao X, Jiang L, Zhu Z, Gu P, Xu W, Su Z, Sun C, Tan L (2016) Genomic structure analysis of a set of Oryza nivara introgression lines and identification of yield-associated QTLs using whole-genome resequencing. Sci Rep 6:27425. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27425
Meng L, Li H, Zhang L, Wang J (2015) QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J 3:269–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2015.01.001
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Ouyang X, Zhong X, Chang S, Qian Q, Zhang Y, Zhu X (2022) Partially functional NARROW LEAF 1 balances leaf photosynthesis and plant architecture for greater rice yield. Plant Physiol 189:772–789. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiac135
Qi J, Qian Q, Bu Q, Li S, Chen Q, Sun J, Liang W, Zhou Y, Chu C, Li X, Ren F, Palme K, Zhao B, Chen J, Chen M, Li C (2008) Mutation of the rice Narrow leaf 1 gene, which encodes a novel protein, affects vein patterning and polar auxin transport. Plant Physiol 147:1947–1959. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.118778
Shim RA, Angeles ER, Ashikari M, Takashi T (2010) Development and evaluation of Oryza glaberrima Steud. chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) in the background of O. sativa L. cv. Koshihikari. Breed Sci 60:613–619. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.60.613
Takai T, Nonoue Y, Yamamoto SI, Yamanouchi U, Matsubara K, Liang ZW, Lin HX, Ono N, Uga Y, Yano M (2007) Development of chromosome segment substitution lines derived from backcross between indica donor rice cultivar ‘Nona Bokra’ and japonica recipient cultivar ‘Koshihikari.’ Breed Sci 57:257–261. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.57.257
Takai T, Adachi S, Taguchi-Shiobara F, Sanoh-Arai Y, Iwasawa N, Yoshinaga S, Hirose S, Taniguchi Y, Yamanouchi U, Wu J, Matsumoto T, Sugimoto K, Kondo K, Ikka Y, Ando T, Kono I, Ito S, Shomura A, Ookawa T, Hirasawa T, Yano M, Kondo M, Yamamoto T (2013) A natural variant of NAL1, selected in high-yield rice breeding programs, pleiotropically increases photosynthesis rate. Sci Rep 3:2149. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02149
Tan L, Liu F, Xue W, Wang G, Ye S, Zhu Z, Fu Y, Wang X, Sun C (2007) Development of Oryza rufipogon and O. sativa introgression lines and assessment for yield-related quantitative trait loci. J Integr Plant Biol 49:871–884. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00497.x
Tester M, Langridge P (2010) Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 327:818–822. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183700
Tian F, Li DJ, Fu Q, Zhu ZF, Fu YC, Wang XK, Sun CQ (2006) Construction of introgression lines carrying wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) segments in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) background and characterization of introgressed segments associated with yield-related traits. Theor Appl Genet 112:570–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0165-2
Tsukaya H (2005) Leaf shape: genetic controls and environmental factors. Int J Dev Biol 49:547–555. https://doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.041921ht
Wang X, Jin L, Zhu H, Wang S, Zhang G, Liu G (2017) QTL epistatic analysis for yield components with single-segment substitution lines in rice. Plant Breeding 137:346–354. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12578
Wei X, Xu J, Guo H, Jiang L, Chen S, Yu C, Zhou Z, Hu P, Zhai H, Wan J (2010) DTH8 suppresses flowering in rice, influencing plant height and yield potential simultaneously. Plant Physiol 153:1747–1758. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.156943
Weng J, Gu S, Wan X, Gao H, Guo T, Su N, Lei C, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Guo X, Wang J, Jiang L, Zhai H, Wan J (2008) Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res 18:1199–1209. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.307
Wu W, Zheng X, Lu G, Zhong Z, Gao H, Chen L, Wu C, Wang H, Wang Q, Zhou K, Wang JL, Wu F, Zhang X, Guo X, Cheng Z, Lei C, Lin Q, Jiang L, Wang H, Ge S, Wang J (2013) Association of functional nucleotide polymorphisms at DTH2 with the northward expansion of rice cultivation in Asia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:2775–2780. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1213962110
Yan WH, Wang P, Chen HX, Zhou HJ, Li QP, Wang CR, Ding ZH, Zhang YS, Yu SB, Xing YZ, Zhang QF (2011) A major QTL, Ghd8, plays pleiotropic roles in regulating grain productivity, plant height, and heading date in rice. Mol Plant 4:319–330. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssq070
Yang Y, Guo M, Li R, Shen L, Wang W, Liu M, Zhu Q, Hu Z, He Q, Xue Y, Tang S, Gu M, Yan C (2015) Identification of quantitative trait loci responsible for rice grain protein content using chromosome segment substitution lines and fine mapping of qPC-1 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breeding 35:130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0328-z
Yin C, Li H, Li S, Xu L, Zhao Z, Wang J (2015) Genetic dissection on rice grain shape by the two-dimensional image analysis in one japonica × indica population consisting of recombinant inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 128:1969–1986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2560-7
Yin C, Li H, Zhao Z, Wang Z, Liu S, Chen L, Liu X, Tian Y, Ma J, Xu L, Zhang D, Zhu S, Li D, Wan J, Wang J (2017) Genetic dissection of top three leaf traits in rice using progenies from a japonica × indica cross. J Integr Plant Biol 59:866–880. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12597
Zhang ZY, Li JJ, Yao GX, Zhang HL, Dou HJ, Shi HL, Sun XM, Li ZC (2011) Fine mapping and cloning of the grain number per-panicle gene (Gnp4) on chromosome 4 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agr Sci China 10:1825–1833. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1671-2927(11)60182-X
Zhang GH, Li SY, Wang L, Ye WJ, Zeng DL, Rao YC, Peng YL, Hua J, Yang YL, Xu J, Ren DY, Gao ZY, Zhu L, Dong GJ, Hua XM, Yan MX, Guo LB, Li CY, Qian Q (2014) LSCHL4 from japonica cultivar, which is allelic to NAL1, increases yield of indica super rice 93–11. Mol Plant 7:1350–1364. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssu055
Zhang B, Shang L, Ruan B, Zhang A, Yang S, Jiang H, Liu C, Hong K, Lin H, Gao Z, Hu J, Zeng D, Guo L, Qian Q (2019) Development of three sets of high-throughput genotyped rice chromosome segment substitution lines and QTL mapping for eleven traits. Rice 12:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-019-0293-y
Zhang T, Wang S, Sun S, Zhang Y, Li J, You J, Su T, Chen W, Ling Y, He G, Zhao F (2020) Analysis of QTL for grain size in a rice chromosome segment substitution line Z1392 with long grains and fine mapping of qGL-6. Rice 13:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-020-00399-z
Zhang C, Sun Y, Wang D, Sun W, Yu Y, Hu Z, Yu S (2021) Dissection of heterotic loci for grain yield using interconnected chromosome segment substitution lines in rice. Crop J 10:323–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2021.07.002
Zhou Y, Xie Y, Cai J, Liu C, Zhu H, Jiang R, Zhong Y, Zhang G, Tan B, Liu G, Fu X, Liu Z, Wang S, Zhang G, Zeng R (2017) Substitution mapping of QTLs controlling seed dormancy using single segment substitution lines derived from multiple cultivated rice donors in seven cropping seasons. Theor Appl Genet 130:1191–1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2881-9
Zhu H, Liu Z, Fu X, Dai Z, Wang S, Zhang G, Zeng R, Liu G (2015) Detection and characterization of epistasis between QTLs on plant height in rice using single segment substitution lines. Breed Sci 65:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.65.192
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (32125029) and the self-regulated project of the State Key Laboratory of Agrobiotechnology (2022SKLAB1-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LT conceived and designed the experiments; SL performed most of the experiments; JZ, JF, and DG provided technical assistance and developed the CSSL population; LT and SL performed data analysis and wrote the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Zou, J., Fan, J. et al. Identification of quantitative trait loci for important agronomic traits using chromosome segment substitution lines from a japonica × indica cross in rice. Mol Breeding 42, 73 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01343-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01343-3