Abstract
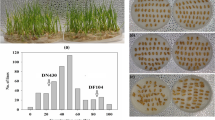
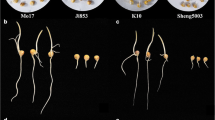
Maize (Zea mays L.) is the most important food crop in the world, with significant acreage and production across the globe. However, it is affected by low temperatures throughout its growth process, especially during germination. Therefore, it is important to identify more QTLs or genes associated with germination under low-temperature conditions. For the QTL analysis of traits related to low-temperature germination, we used a high-res genetic map of 213 lines of the intermated B73 × Mo17 (IBM) Syn10 doubled haploid (DH) population, which had 6618 bin markers. We detected 28 QTLs of eight phenotypic characteristics associated with low-temperature germination, while they explained the phenotypic contribution rate of 5.4 ~ 13.34%. Additionally, 14 overlapping QTLs produced six QTL clusters on every chromosome, except for 8 and 10. RNA-Seq found six genes related to low-temperature tolerance in these QTLs, while qRT-PCR analysis demonstrated that the expression trends of the Zm00001d045568 gene in the LT_BvsLT_M group and the CK_BvsCK_M group were highly significantly different at all four-time points (P < 0.01), and encoded the RING zinc finger protein. It was located on qRTL9-2 and qRSVI9-1 and is related to the total length and simple vitality index. These results provided potential candidate genes for further gene cloning and improving the low-temperature tolerance of maize.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Relevant raw data will be freely available to any researcher wishing to use them for non-commercial purposes, without breaching participant confidentiality (Table S7).
Abbreviations
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- RNA-seq:
-
RNA sequencing
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative RT PCR
- qRTL :
-
QTL of relative total length
- qRSVI :
-
QTL of relative simple vitality index
References
Allam M, Revilla P, Djemel A, Tracy WF, Ordás B (2016) Identification of QTLs involved in cold tolerance in sweet × field corn. Euphytica 208(2):353–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1609-7
Båga M, Chodaparambil SV, Limin AE, Pecar M, Fowler DB, Chibbar RN (2007) Identification of quantitative trait loci and associated candidate genes for low-temperature tolerance in cold-hardy winter wheat. Funct Integr Genomics 7(1):53–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-006-0030-7
Bao Y, Aggarwal P, Robbins NE, Sturrock CJ, Thompson MC, Tan HQ, Tham C, Duan L, Rodriguez PL, Vernoux T, Mooney SJ, Bennett MJ, Dinneny JR (2014) Plant roots use a patterning mechanism to position lateral root branches toward available water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(25):9319–9324. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1710709115
Bhosale SU, Rymen B, Beemster GTS, Melchinger AE, Reif JC (2007) Chilling tolerance of central European maize lines and their factorial crosses. Ann Bot 100(6):1315–1321. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcm215
Bouis HE, Welch RM (2010) Biofortification—a sustainable agricultural strategy for reducing micronutrient malnutrition in the global south. Crop Sci 50:S20–S32. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2009.09.0531
Broman KW, Wu H, Sacute S, a, Churchill GA, (2003) Rqtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19(7):889–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg112
Bucherl CA, Jarsch IK, Schudoma C, Segonzac C, Mbengue M, Robatzek S, MacLean D, Ott T, Zipfel C (2017) Plant immune and growth receptors share common signalling components but localise to distinct plasma membrane nanodomains. eLife 6:1–28
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138(3):963–971. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/138.3.963
Crosbie TM, Mock JJ, Smith OS (1980) Comparison of gains predicted by several selection methods for cold tolerance traits of two maize populations. Crop Sci 20(5):649–655. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1980.0011183X002000050027x
Dai YS, Dong Z, Wei LI, Dai LY (2013) Research advance on ubiquitin ligase E3 in rice. Crop Research:23–35. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-5280.2013.03.19
Doerge RW, Churchill GA (1996) Permutation tests for multiple loci affecting a quantitative character. Genetics 142(1):285–294. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/142.1.285
Don LS, Jin-Gyu H, Gyo JC, Sun-Goo H, Jun-Cheol M, Seong JC (2013) Comprehensive analysis of the rice RING E3 ligase family reveals their functional diversity in response to abiotic stress. DNA Res 20(3):299–314. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dst011
Du QL, Cui WZ, Zhang CH, Yu DY (2010) GmRFP1 encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase in Soybean (Glycine max). Mol Biol Rep 37(2):685–693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9535-1
Fang HM, Meng QL, Zhang HS, Huang J (2016) Knock-down of a RING finger gene confers cold tolerance. Bioengineered 7(1):39–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2015.1131368
Feiler HS, Desprez T, Santoni V, Kronenberger J, Caboche M, Traas J (1995) The higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a functional CDC48 homologue which is highly expressed in dividing and expanding cells. Embo J 14(22):5626–5637. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00250.x
Fracheboud Y, Jompuk C, Ribaut JM, Stamp P, Leipner J (2004) Genetic analysis of cold-tolerance of photosynthesis in maize. Plant MolBiol 56(2):241–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-004-3353-6
Frascaroli E, Landi P (2013) Divergent selection in a maize population for germination at low temperature in controlled environment: study of the direct response, of the trait inheritance and of correlated responses in the field. Theor Appl Genet 126(3):733–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-2014-4
Frascaroli E, Landi P (2016) Cold tolerance in field conditions, its inheritance, agronomic performance and genetic structure of maize lines divergently selected for germination at low temperature. Euphytica 209(3):771–788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1680-8
Fujino K, Sekiguchi H, Matsuda Y, Sugimoto K, Ono K, Yano M (2008) Molecular identification of a major quantitative trait locus, qLTG3-1, controlling low-temperature germinability in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(34):12623–12628. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805303105
Gelli M, Konda AR, Liu K, Zhang C, Clemente TE, Holding DR, Dweikat IM (2017) Validation of QTL mapping and transcriptome profiling for identification of candidate genes associated with nitrogen stress tolerance in sorghum. BMC Plant Biol 17 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1064-9
Greaves JA (1996) Improving suboptimal temperature tolerance in maize- the search for variation. J Exp Bot 47(3):307–323. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/47.3.307
Guerra-Peraza O, Leipner J, Reimer R, Nguyen HT, Stamp P, Fracheboud Y (2011) Temperature at night affects the genetic control of acclimation to cold in maize seedlings. Maydica 56(4):367–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-010-0235-5
H L, L X, Z G, M I, B S, K ZJ (2001) The Arabidopsis HOS1 gene negatively regulates cold signal transduction and encodes a RING finger protein that displays cold-regulated nucleo--cytoplasmic partitioning. Genes Dev 15 (7):912-924. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.866801
Hai DC, Manu A, Yiyue Z, Qi X, Kang ZJ (2006) The negative regulator of plant cold responses, HOS1, is a RING E3 ligase that mediates the ubiquitination and degradation of ICE1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(21):8281–8286. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0602874103
Han QH, Shen Y, Lv L, Lee M, Lubberstedt T, Zhao GW (2020) QTL analysis of deep-sowing tolerance during seed germination in the maize IBM Syn4 RIL population. Plant Breed 139(6):1125–1134. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12864
He F, Shen H, Lin C, Fu H, Sheteiwy MS, Guan Y, Huang Y, Hu J (2017) Transcriptome analysis of chilling-imbibed embryo revealed membrane recovery related genes in maize. Front Plant Sci 7:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01978
Hodges DM, Charest C, Hamilton RI (1994) A chilling resistance test for inbred maize lines. Can J Plant Sci 74(4):687–691
Hou FX, Zhou X, Liu P, Yuan GS, Zou CY, Lubberstedt T, Pan GT, Ma LL, Shen Y (2021) Genetic dissection of maize seedling traits in an IBM Syn10 DH population under the combined stress of lead and cadmium. Mol Genet Genomics 296(5):1057–1070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-021-01800-2
Hu S, Lübberstedt T, Zhao G, Lee M (2016) QTL Mapping of low-temperature germination ability in the maize IBM Syn4 RIL population. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0152795. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0152795
Hu G, Li Z, Lu Y, Li C, Gong S, Yan S, Li G, Wang M, Ren H, Guan H, Zhang Z, Qin D, Chai M, Yu J, Li Y, Yang D, Wang T, Zhang Z (2017) Genome-wide association study identified multiple genetic loci on chilling resistance during germination in maize. Sci Rep 7(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11318-6
Hund A, Fracheboud Y, Soldati A, Frascaroli E, Salvi S, Stamp P (2004) QTL controlling root and shoot traits of maize seedlings under cold stress. Theor Appl Genet 109(3):618–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1665-1
Hussain T, Tausend P, Graham G, Ho J (2007) Registration of IBM2 SYN10 doubled haploid mapping population of maize. J Plant Regist 1(1):81–81. https://doi.org/10.3198/jpr2005.11.0414crs
Jin Y, Zhang Z, Xi Y, Yang Z, Xiao Z, Guan S, Qu J, Wang P, Zhao R (2021) Identification and functional verification of cold tolerance genes in spring maize seedlings based on a genome-wide association study and quantitative trait locus mapping. Front Plant Sci 12(2939):1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.776972
Jompuk C, Fracheboud Y, Stamp P, Leipner J (2005) Mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with chilling tolerance in maize ( Zea mays L.) seedlings grown under field conditions. J Exp Bot 56(414):1153–1163. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri108
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M, Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, Okuda S, Tokimatsu T, Yamanishi Y (2008) KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res 36(suppl1):D480-484. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm882
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM (1985) Exact confidence intervals for heritability on a progeny mean basis. Crop Sci 25(1):192–194. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1985.0011183X002500010046x
Ko JH, Yang SH, Han KH (2006) Upregulation of an arabidopsis RING-H2 gene, XERICO, confers drought tolerance through increased abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant J 47(3):343–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02782.x
Lee M, Sharopova N, Beavis WD, Grant D, Katt M, Blair D, Hallauer A (2002) Expanding the genetic map of maize with the intermated B73 × Mo17 (IBM) population. Plant MolBiol 48(5–6):453–461. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014893521186
Lei L, Zheng HL, Bi YL, Yang LM, Liu HL, Wang JG, Sun J, Zhao HW, Li XW, Li JM, Lai YC, Zou DT (2020) Identification of a major QTL and candidate gene analysis of salt tolerance at the bud burst stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using QTL-Seq and RNA-Seq. Rice 13 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-020-00416-1
Li HM, Chiu CC (2010) Protein transport into chloroplasts. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61(1):157–180. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112222
Li XJ, Luu DT, Maurel C, Lin JX (2013) Probing plasma membrane dynamics at the single-molecule level. Trends Plant Sci 18(11):617–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2013.07.004
Li X, Wang G, Fu J, Li L, Jia G, Ren L, Lubberstedt T, Wang G, Wang J, Gu R (2018) QTL mapping in three connected populations reveals a set of consensus genomic regions for low temperature germination ability in Zea mays L. Front Plant Sci 9:65–75. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00065
Li Q, Zhou SZ, Liu WY, Zhai ZS, Pan YT, Liu CC, Chern MS, Wang HW, Huang M, Zhang ZX, Tang JH, Du HW (2021) A chlorophyll a oxygenase 1 gene ZmCAO1 contributes to grain yield and waterlogging tolerance in maize. J Exp Bot 72(8):3155–3167. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erab059
Liu H, Niu Y, Gonzalez-Portilla PJ, Zhou H, Wang L, Zuo T, Qin C, Tai S, Jansen C, Shen Y, Lin H, Lee M, Ware D, Zhang Z, Lübberstedt T, Pan G (2015) An ultra-high-density map as a community resource for discerning the genetic basis of quantitative traits in maize. BMC Genomics 16:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2242-5
Liu HJ, Zhang L, Wang JC, Li CS, Zeng X, Xie SP, Zhang YZ, Liu SS, Hu SL, Wang JH, Lee M, Lubberstedt T, Zhao GW (2017) Quantitative trait locus analysis for deep-sowing germination ability in the maize IBM Syn10 DH population. Front Plant Sci 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00813
Livak JKD, Schmittgen T (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lu G, Wu FQ, Wu W, Wang HJ, Zheng XM, Zhang Y, Chen X, Zhou K, Jin M, Cheng Z, Li X, Jiang L, Wang H, Wan J (2014) Rice LTG 1 is involved in adaptive growth and fitness under low ambient temperature. Plant J 78(3):468–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12487
Marchler-Bauer A, Bo Y, Han LY, He JE, Lanczycki CJ, Lu SN, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Lu F, Marchler GH, Song JS, Thanki N, Wang ZX, Yamashita RA, Zhang DC, Zheng CJ, Geer LY, Bryant SH (2017) CDD/SPARCLE: functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acids Res 45(D1):D200-203. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1129
Martins SM, Brito GGd, Gonalves WdC, Tripode BMD, Giband M (2020) PhenoRoots: an inexpensive non-invasive phenotyping system to assess the variability of the root system architecture. Sci Agric 77(5):e20180420. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-992X-2018-0420
Mock JJ, Mcneill MJ (1979) Cold tolerance of maize inbred lines adapted to various latitudes in North America1. Crop Sci 19(2):239–242. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1979.0011183X001900020017x
Paila YD, Richardson LGL, Schnell DJ (2015) New insights into the mechanism of chloroplast protein import and its integration with protein quality control, organelle biogenesis and development. J Mol Biol 427(5):1038–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2014.08.016
Pandit E, Tasleem S, Barik SR, Mohanty DP, Nayak DK, Mohanty SP, Das S, Pradhan SK (2017) Genome-wide association mapping reveals multiple QTLs governing tolerance response for seedling stage chilling stress in Indica rice. Front Plant Sci 8:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00552
Parsa AT, Waldron JS, Panner A, Crane CA, Parney IF, Barry JJ, Cachola KE, Murray JC, Tihan T, Jensen MC, Mischel PS, Stokoe D, Pieper RO (2007) Loss of tumor suppressor PTEN function increases B7–H1 expression and immunoresistance in glioma. Nat Med 13(1):84–88. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1517
Peters JM, Walsh MJ, Franke WW (1990) An abundant and ubiquitous homo-oligomeric ring-shaped ATPase particle related to the putative vesicle fusion proteins Sec18p and NSF. Embo J 9(6):1757–1767. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08300.x
Presterl T, Ouzunova M, Schmidt W, Möller EM, Röber FK, Knaak C, Ernst K, Westhoff P, Geiger HH (2007) Quantitative trait loci for early plant vigour of maize grown in chilly environments. Theor Appl Genet 114(6):1059–1070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0499-4
Rácz F, Hadi G, Szőke C, Záborszky S, Marton C (2007) Cold tolerance of seed from inbred maize lines sown at various sowing dates in different years. Cereal Res Commun 35(2):697–700. https://doi.org/10.1556/CRC.35.2007.2.133
Rancour DM, Dickey CE, Park S, Bednarek SY (2002) Characterization of AtCDC48 Evidence for multiple membrane fusion mechanisms at the plane of cell division in plants. Plant Physiol 130(3):1241–1253. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.011742
Revilla P, Rodriguez VM, Ordas A, Rincent R, Charcosset A, Giauffret C, Melchinger AE, Schon CC, Bauer E, Altmann T, Brunel D, Moreno-Gonzalez J, Campo L, Ouzunova M, Alvarez A, de Galarreta JIR, Laborde J, Malvar RA (2016) Association mapping for cold tolerance in two large maize inbred panels. BMC Plant Biol 16:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0816-2
Robbins NE, Dinneny JR (2015) The divining root: moisture-driven responses of roots at the micro- and macro-scale. J Exp Bot 66(8):2145–2154. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru496
Rodríguez VM, Butrón A, Malvar RA, Ordás A, Revilla P (2008) Quantitative trait loci for cold tolerance in the maize IBM population. Int J Plant Sci 169(4):551–556. https://doi.org/10.1086/528755
Rodríguez VM, Butrón A, Rady MOA, Soengas P, Revilla P (2014) Identification of quantitative trait loci involved in the response to cold stress in maize ( Zea mays L). Mol Breed 33(2):363–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9955-4
Rosnoblet C, Begue H, Blanchard C, Pichereaux C, Besson-Bard A, Aime S, Wendehenne D (2017) Functional characterization of the chaperon-like protein Cdc48 in cryptogein-induced immune response in tobacco. Plant Cell Environ 40(4):491–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12686
Ryu MY, Cho SK, Kim WT (2010) The arabidopsis C3H2C3-type RING E3 ubiquitin ligase AtAIRP1 is a positive regulator of an abscisic acid-dependent response to drought stress. Plant Physiol 154(4):1983–1997. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.164749
Sallam A, Arbaoui M, El-Esawi M, Abshire N, Martsch R (2016) Identification and verification of QTL associated with frost tolerance using linkage mapping and GWAS in winter faba bean. Front Plant Sci 7:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01098
Serrano M, Guzman P (2004) Isolation and gene expression analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana mutants with constitutive expression of ATL2, an early elicitor-response RING-H2 zinc-finger gene. Genetics 167(2):919–929. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.104.028043
Ss L, Herborg H, Andrew T, Jill H, Edward K, Judy C (2005) Functional analysis of the RING-type ubiquitin ligase family of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 137(1):13–30. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.052423
Verheul MJ, Picatto C, Stamp P (1996) Growth and development of maize ( Zea mays L.) seedlings under chilling conditions in the field. Eur J Agron 5(1):31–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1161-0301(96)02007-2
Vogel C, Marcotte EM (2012) Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nat Rev Genet 13(4):227–232. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3185
Wang G, Sun X, Wang G, Wang F, Gao Q, Sun X, Tang Y, Chang C, Lai J, Zhu L, Xu Z, Song R (2011) Opaque7 encodes an acyl-activating enzyme-like protein that affects storage protein synthesis in maize endosperm. Genetics 189(4):1281–1295. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.111.133967
Wu XM, Wang B, Xie FG, Zhang LP, Gong J, Zhu W, Li XQ, Feng FQ, Huang J (2020) QTL mapping and transcriptome analysis identify candidate genes regulating pericarp thickness in sweet corn. BMC Plant Biol 20 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-2295-8
Xu RQ, Li QSQ (2003) A RING-H2 zinc-finger protein gene RIE1 is essential for seed development in Arabidopsis. Plant MolBiol 53(1):37–50. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLAN.0000009256.01620.a6
Yang YL, Xu J, Huang LC, Leng YJ, Dai LP, Rao YC, Chen L, Wang YQ, Tu ZJ, Hu J, Ren DY, Zhang GH, Zhu L, Guo LB, Qian Q, Zeng DL (2016) PGL, encoding chlorophyllide a oxygenase 1, impacts leaf senescence and indirectly affects grain yield and quality in rice. J Exp Bot 67(5):1297–1310. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv529
Yue J, Li C, Liu YW, Yu JJ (2014) A remorin gene SiREM6, the target gene of SiARDP, from Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) promotes high salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 9(6):e100772. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100772
Zeng DE, Hou P, Xiao FM, Liu YS (2014) Overexpressing a novel RING-H2 finger protein gene, OsRHP1, enhances drought and salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L). J Plant Biol 57(6):357–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-013-0481-z
Zhang WB, Hw J, Qiu PC, Liu CY, Chen FL, Xin DW, Li CD, Hu GH, Chen QS (2012) Genetic overlap of QTL associated with low-temperature tolerance at germination and seedling stage using BILs in soybean. Can J Plant Sci 92(7):1381–1388. https://doi.org/10.4141/CJPS2011-098
Zhang Z, Li J, Pan Y, Li J, Zhou L, Shi H, Zeng Y, Guo H, Yang S, Zheng W, Yu J, Sun X, Li G, Ding Y, Ma L, Shen S, Dai L, Zhang H, Yang S, Guo Y, Li Z (2017) Natural variation in CTB4a enhances rice adaptation to cold habitats. Nat Commun 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14788
Zhang XX, Guan ZR, Li ZL, Liu P, Ma LL, Zhang YC, Pan L, He SJ, Zhang YL, Li P, Ge F, Zou CY, He YC, Gao SB, Pan GT, Shen YO (2020) A combination of linkage mapping and GWAS brings new elements on the genetic basis of yield-related traits in maize across multiple environments. Theor Appl Genet 133(10):2881–2895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03639-4
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Prof. Hongjun Liu of Shandong Agricultural University for providing the plant material.
Funding
This work was supported by “Countless Project” engineering and technology major project of Heilongjiang province (2019ZX16B03-3) and Backbone of Young Talent Scholar Project (to Yu Zhou, 20XG23).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ and ZHW conceived and designed the experiment. HD, LZ, LD, XZ, and XJL prepared materials. HZ and QYX conducted the experiments. QYX, HZ, and HZZ analyzed the data. QYX, XRW, and YHW wrote the manuscript. ML provided experimental materials. YZ and ZHW revised the final version of the paper. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No animal or human research subjects were used in this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Wang, X., Wang, Y. et al. Combined QTL mapping and RNA-Seq pro-filing reveal candidate genes related to low-temperature tolerance in maize. Mol Breeding 42, 33 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01297-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01297-6