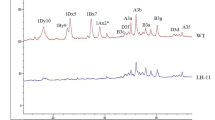
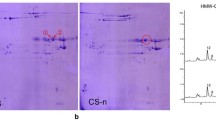
Abstract
Wheat is a major staple food crop worldwide because of the unique properties of wheat flour. High molecular weight glutenin subunits (HMW-GSs), which are among the most critical determinants of wheat flour quality, are responsible for the formation of glutenin polymeric structures via interchain disulfide bonds. We herein describe the identification of a new HMW-GS Dy10 allele (Dy10-m619SN). The amino acid substitution (serine-to-asparagine) encoded in this allele resulted in a partial post-translational cleavage that produced two new peptides. These new peptides disrupted the interactions among gluten proteins because of the associated changes to the number of available cysteine residues for interchain disulfide bonds. Consequently, Dy10-m619SN expression decreased the size of glutenin polymers and weakened glutens, which resulted in wheat dough with improved cookie-making quality, without changes to the glutenin-to-gliadin ratio. In this study, we clarified the post-translational processing of HMW-GSs and revealed a new genetic resource useful for wheat breeding.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC International (2010) Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th ed, St. Paul, MN, 2010. http://methods.aaccnet.org/
Anderson OD, Greene FC (1989) The characterization and comparative analysis of high-molecular-weight glutenin genes from genomes A and B of a hexaploid bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 77:689–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00261246
Barak S, Mudgil D, Khatkar BS (2013) Relationship of gliadin and glutenin proteins with dough rheology, flour pasting and bread making performance of wheat varieties. LWT - Food Sci Technol 51:211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2012.09.011
Barak S, Mudgil D, Khatkar BS (2015) Biochemical and functional properties of wheat gliadins: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 55:357–368. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2012.654863
Barro F, Barceló P, Lazzeri PA et al (2003) Functional properties of flours from field grown transgenic wheat lines expressing the HMW glutenin subunit 1Ax1 and 1Dx5 genes. Mol Breed 12:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026367214120
Blechl A, Lin J, Nguyen S et al (2007) Transgenic wheats with elevated levels of Dx5 and/or Dy10 high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits yield doughs with increased mixing strength and tolerance. J Cereal Sci 45:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2006.07.009
Chen H, Li S, Liu Y et al (2021) Effects of 1Dy12 subunit silencing on seed storage protein accumulation and flour-processing quality in a common wheat somatic variation line. Food Chem 335:127663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127663
Chen Q, Zhang W, Gao Y et al (2019) High molecular weight glutenin subunits 1Bx7 and 1By9 encoded by Glu-B1 locus affect wheat dough properties and sponge cake quality. J Agric Food Chem 67:11796–11804. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05030
Hoseney RC (1986) Principles of cereal science and technology, 2nd ed, St. Paul, MN. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.19870390416
Denery-Papini S, Popineau Y, Quillien L, Van Regenmortel M (1996) Specificity of anti sera raised against synthetic peptide fragments of high Mr glutenin subunits. J Cereal Sci 23:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcrs.1996.0013
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Graveland A, Bosveld P, Lichtendonk WJ et al (1985) A model for the molecular structure of the glutenins from wheat flour. J Cereal Sci 3:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0733-5210(85)80029-1
Gruis D, Schulze J, Jung R (2004) Storage protein accumulation in the absence of the vacuolar processing enzyme family of cysteine proteases. Plant Cell 16:270–290. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.016378
Halford NG, Field JM, Blair H et al (1992) Analysis of HMW glutenin subunits encoded by chromosome 1A of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) indicates quantitative effects on grain quality. Theor Appl Genet 83:373–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224285
Hara-Nishimura I, Inoue K, Nishimura M (1991) A unique vacuolar processing enzyme responsible for conversion of several proprotein precursors into the mature forms. FEBS Lett 294:89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(91)81349-D
Hara-Nishimura I, Shimada T, Hiraiwa N, Nishimura M (1995) Vacuolar processing enzyme responsible for maturation of seed proteins. J Plant Physiol 145:632–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(11)81275-7
Jia F, Wang J, Wang Q et al (2020) Effect of extrusion on the polymerization of wheat glutenin and changes in the gluten network. J Food Sci Technol 57:3814–3822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04413-6
Jiang QT, Wei YM, Wang F et al (2009) Characterization and comparative analysis of HMW glutenin 1Ay alleles with differential expressions. BMC Plant Biol 9:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-9-16
Jie WS, Hui KM, Shan YM et al (2006) Comparison of two sorts of turbidimetry reagents in measurement of wheat glutenin macropolymer content. J Triticeae Crop 20:56–59. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1009-1041.2006.06.013
Kumamaru T, Uemura Y, Inoue Y et al (2010) Vacuolar processing enzyme plays an essential role in the crystalline structure of glutelin in rice seed. Plant Cell Physiol 51:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcp165
Lafiandra D, Turchetta T, D’Ovidio R et al (1999) Conformational polymorphism of high Mr glutenin subunits detected by transverse urea gradient gel electrophoresis. J Cereal Sci 30:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcrs.1999.0260
Laudencia-Chingcuanco D (2012) Isolation and characterization of EMS-induced Dy10 and Ax1 high molecular weight glutenin subunit deficient mutant lines of elite hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cv. Summit. J Cereal Sci 56:296–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2012.06.009
Lawrence GJ, MacRitchie F, Wrigley CW (1988) Dough and baking quality of wheat lines deficient in glutenin subunits controlled by the Glu-A1, Glu-B1 and Glu-D1 loci. J Cereal Sci 7:109–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0733-5210(88)80012-2
León E, Marín S, Giménez MJ et al (2009) Mixing properties and dough functionality of transgenic lines of a commercial wheat cultivar expressing the 1Ax1, 1Dx5 and 1Dy10 HMW glutenin subunit genes. J Cereal Sci 49:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2008.08.002
Li Y, An X, Yang R et al (2014) Dissecting and enhancing the contributions of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits to dough functionality and bread quality. Mol Plant 8:332–334. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssu118
Li Y, Fu J, Shen Q, Yang D (2021) High-molecular-weight glutenin subunits: Genetics, structures, and relation to end use qualities. Int J Mol Sci 22:184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010184
Mudgil D, Barak S, Khatkar BS (2017) Cookie texture, spread ratio and sensory acceptability of cookies as a function of soluble dietary fiber, baking time and different water levels. LWT - Food Sci Technol 80:537–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.03.009
Müntz K (1998) Deposition of storage proteins. Plant Mol Biol 38:77–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5298-3_4
Nunes-Miranda JD, Bancel E, Viala D et al (2017) Wheat glutenin: the “tail” of the 1By protein subunits. J Proteomics 169:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2017.05.019
Payne PI, Holt LM, Law CN (1981) Structural and genetical studies on the high-molecular-weight subunits of wheat glutenin - Part 1: allelic variation in subunits amongst varieties of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Theor Appl Genet 60:229–236.https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02342544
Payne PI, Holt LM, Law CN (1982) Structural and genetical studies on the high-molecular-weight subunits of wheat glutenin - Part 3: telocentric mapping of the subunit genes on the long arms of the homoeologous Group 1 chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 63:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02342544
Payne PI (1987) Genetics of wheat storage proteins and the effect of allelic variation on breadmaking quality. Annu Rev Plant Biol 38:141–153. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.38.060187.001041
Qi PF, Wei YM, Yue YW et al (2006) Biochemical and molecular characterization of gliadins. Mol Biol 40:713–723. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893306050050
Qi PF, Wei YM, Chen Q et al (2011) Identification of novel α-gliadin genes. Genome 54:244–252. https://doi.org/10.1139/G10-114
Roy N, Islam S, Ma J et al (2018) Expressed Ay HMW glutenin subunit in Australian wheat cultivars indicates a positive effect on wheat quality. J Cereal Sci 79:494–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2017.12.009
Samyn B, Sergeant K, Castanheira P et al (2005) A new method for C-terminal sequence analysis in the proteomic era. Nat Methods 2:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth738
Savill GP, Michalski A, Powers SJ et al (2018) Temperature and nitrogen supply interact to determine protein distribution gradients in the wheat grain endosperm. J Exp Bot 69:3117–3126. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery127
Shewry PR, Halford NG, Tatham AS (1992) The high molecular weight subunits of wheat glutenin. J Cereal Sci 15:105–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0733-5210(09)80062-3
Shewry PR, Tatham AS, Halford NG (1999) The prolamins of the Triticeae. In: Seed proteins , Shewry PR, Casey R, Eds, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 35–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-4431-5_3
Shewry PR, Halford NG (2002) Cereal seed storage proteins: Structures, properties and role in grain utilization. J Exp Bot 53:947–958. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.370.947
Shewry PR, Halford NG, Tatham AS et al (2003a) The high molecular weight subunits of wheat glutenin and their role in determining wheat processing properties. Adv Food Nutr Res 45:219–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1043-4526(03)45006-7
Shewry PR, Halford NG, Lafiandra D (2003b) Genetics of wheat gluten proteins. Adv Genet 49:111–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2660(03)01003-4
Shruthi B, Vinodhkumar P, Selvamani M (2016) Proteomics: A new perspective for cancer. Adv Biomed Res 5:67. https://doi.org/10.4103/2277-9175.180636
Tang QY, Zhang CX (2013) Data Processing System (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect Sci 20:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7917.2012.01519.x
Vicente-Carbajosa J, Oñate L, Lara P et al (1998) Barley BLZ: A bZIP transcriptional activator that interacts with endosperm-specific gene promoters. Plant J 13:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.1998.00068.x
Wan Y, Gritsch CS, Hawkesford MJ, Shewry PR (2014) Effects of nitrogen nutrition on the synthesis and deposition of the ω-gliadins of wheat. Ann Bot 113:607–615. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mct291
Wang Y, Zhu S, Liu S et al (2009) The vacuolar processing enzyme OsVPE1 is required for efficient glutelin processing in rice. Plant J 58:606–617. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03801.x
Wang Y, Zheng QY, Guo ZR et al (2016) A missense mutation affects the mobility of high molecular weight glutenin Dy10 subunit in SDS-PAGE. Agri Gene 2:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aggene.2016.09.001
Wang D, Zhang K, Dong L et al (2018a) Molecular genetic and genomic analysis of wheat milling and end-use traits in China: Progress and perspectives. Crop J 6:68–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2017.10.001
Wang Z, Huang L, Wu B et al (2018b) Characterization of an integrated active glu-1ay allele in common wheat from wild emmer and its potential role in flour improvement. Int J Mol Sci 19:923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19040923
Wieser H (2007) Chemistry of gluten proteins. Food Microbiol 24:115–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2006.07.004
Wrigley C, Bekes F, Bushuk W (2006) Gliadin and glutenin. In: The unique balance of wheat quality, 1st ed, AACC International, MN, pp 3–32. https://doi.org/10.1094/9781891127519.002
Xu BJ, Chen Q, Zheng T et al (2018) An overexpressed Q allele leads to increased spike density and improved processing quality in common wheat (Triticum aestivum). G3 Genes, Genomes, Genet 8:771–778. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.117.300562
Yan Y, Hsam SLK, Yu J et al (2003) Allelic variation of the HMW glutenin subunits in Aegilops tauschii accessions detected by sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS-PAGE), acid polyacrylamide gel (A-PAGE) and capillary electrophoresis. Euphytica 130:377–385. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023062316439
Yazar G, Duvarci OC, Tavman S, Kokini JL (2017) LAOS behavior of the two main gluten fractions: gliadin and glutenin. J Cereal Sci 77:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2017.08.014
Yue Y, Liu X, Wang J et al (2019) Change in physicochemical characteristics and molecular weight distribution of glutenin macropolymer induced by postharvest wheat maturation. Qual Assur Saf Crop Foods 11:789–798. https://doi.org/10.3920/QAS2019.1658
Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Zhang Y et al (2007) Effects of solvent retention capacities, pentosan content, and dough rheological properties on sugar snap cookie quality in Chinese soft wheat genotypes. Crop Sci 47:656–664. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2006.05.0357
Zhang YZ, Wei ZZ, Liu CH et al (2017) Linoleic acid isomerase gene FgLAI12 affects sensitivity to salicylic acid, mycelial growth and virulence of Fusarium graminearum. Sci Rep 7:46129. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46129
Zhang P, Ma H, Yao J et al (2016) Effect of HMW-GS deletion on processing quality of soft wheat Ningmai 9. Acta Agron Sin 42:633–640. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1006.2016.00633
Zheng T, Qi PF, Cao YL et al (2018) Mechanisms of wheat (Triticum aestivum) grain storage proteins in response to nitrogen application and its impacts on processing quality. Sci Rep 8:11928. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30451-4
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Peter Shewry at Rothamsted Research and Dr. Yufeng Hu at Sichuan Agricultural University for technical assistance. We acknowledge Liwen Bianji, Edanz Editing China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac) for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 31971939, 31671677, and 32072054), the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (2019YFH0066, 20GJHZ0048, and 2018NZDZX002), and the Designing Future Wheat strategic program (BB/P016855/1) of the UK. Yan Wang acknowledges funding by the China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P. Q and Y. Z designed the experiments. Y. W, Q. C, and P. Q wrote the manuscript. P. Q and Q. C prepared the plant materials. Y. W, Q. C, Y. L, Z. G, C. L, Y. W, M. H, J. Z, W. W, M. W, K. Z, Y. J, Y. Z, Q. X, L. K, Z. P, M. D, Q. J, X. L, J. W, G. C, J. M, Y. Z, Y. W, and P. Q conducted the experiments, analyzed the data, and provided key advice. All authors discussed the results and helped revise the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Plant voucher number and consent for field experiments
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Chen, Q., Li, Y. et al. Post-translational cleavage of HMW-GS Dy10 allele improves the cookie-making quality in common wheat (Triticum aestivum). Mol Breeding 41, 49 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-021-01238-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-021-01238-9