Abstract
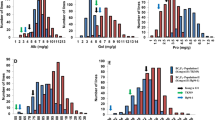
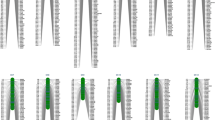
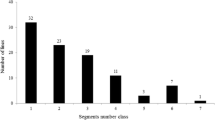
Wx is considered to be the most important gene controlling eating and cooking qualities and pasting properties in rice (Oryza sativa L.). In this study, a recombinant inbred line population derived from indica rice parents differing in apparent amylose content (AAC) was used to detect quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for ten grain quality parameters for rice quality improvement. QTL mapping was performed on the whole population and on two sub-populations based on Wx genotypes. A total of 29 QTLs were found in the whole population. Ten QTLs for 7 traits were detected in the two sub-populations, four of which (qPRO3.1, qPV9, qHPV9, and qCS7) were also detected in the whole population, whereas the other six were QTLs with minor effects that might be covered by the Wx locus. Besides the Wx locus with the largest effect on AAC and most pasting properties, there were another six QTL clusters contributing to grain quality located on chromosomes 2, 3, 5, 6 and 9. It was also found that some QTLs for peak viscosity, breakdown and consistency were closely linked to rice grain shape related QTLs on chromosome 3. A QTL cluster on chromosome 9 for peak viscosity, hot paste viscosity and cold paste viscosity was detectable in the whole population, which was close to the isoamylase 3 (ISA3) locus. A QTL cluster for both peak time and pasting temperature on chromosome 6 was near to the starch synthase I locus, and was potentially a new QTL with minor effect for peak time and pasting temperature. These findings will promote better understanding of the genetic regulation of rice eating and cooking qualities.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao JS (2008) Accurate measurement of pasting temperature by the rapid visco-analyser: a case study using rice flour. Rice Sci 15:69–72
Bao JS (2012) Toward understanding the genetic and molecular bases of the eating and cooking qualities of rice. Cereal Foods World 57:148–156
Bao JS, Zheng XW, Xia YW, He P, Shu QY, Lu X, Chen Y, Zhu LH (2000) QTL mapping for the paste viscosity characteristics in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:280–284
Bao JS, Wu YR, Hu B, Wu P, Cui HR, Shu QY (2002) QTL for rice grain quality based on a DH population derived from parents with similar apparent amylose content. Euphytica 128:317–324
Bao JS, Corke H, Sun M (2006a) Nucleotide diversity in starch synthase IIa and validation of single nucleotide polymorphisms in relation to starch gelatinization temperature and other physicochemical properties in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:1171–1180
Bao JS, Shen SQ, Sun M, Corke H (2006b) Analysis of genotypic diversity in the starch physicochemical properties of nonwaxy rice: apparent amylose content, pasting viscosity and gel texture. Starch-Starke 58:259–267
Bligh HF, Larkin P, Roach P, Jones C, Fu H, Park W (1998) Use of alternate splice sites in granule-bound starch synthase mRNA from low-amylose rice varieties. Plant Mol Biol 38:407–415
Chrastil J (1994) Stickiness of oryzenin and starch mixtures from preharvest and postharvest rice grains. J Agric Food Chem 42:2147–2151
Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112(6):1164–1171
Gao ZY, Zeng DL, Cui X, Zhou YH, Yan M, Huang D, Li JY, Qian Q (2003) Map-based cloning of the ALK gene, which controls the gelatinization temperature of rice. Sci China Ser C 46:661–668
Gravois KA, Webb BD (1997) Inheritance of long grain rice amylograph viscosity characteristics. Euphytica 97:25–29
Han YP, Xu ML, Liu XY, Yan CJ, Korban SS, Chen XL, Gu MH (2004) Genes coding for starch branching enzymes are major contributors to starch viscosity characteristics in waxy rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci 166:357–364
Hirano HY, Eiguchi M, Sano Y (1998) A single base change altered the regulation of the Waxy gene at the posttranscriptional level during the domestication of rice. Mol Biol Evol 15:978–987
Hsu YC, Tseng MC, Wu YP, Lin MY, Wei FJ, Hwu KK, Hsing YI, Lin YR (2014) Genetic factors responsible for eating and cooking qualities of rice grains in a recombinant inbred population of an inter-subspecific cross. Mol Breed 34:655–673
Larkin PD, Park WD (2003) Association of waxy gene single nucleotide polymorphisms with starch characteristics in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 12:335–339
Larkin PD, McClung AM, Ayres NM, Park WD (2003) The effect of the Waxy locus (Granule Bound Starch Synthase) on pasting curve characteristics in specialty rices (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 131:243–253
Li X, Ma W, Wang Z, Guo Y, Liu F, Wu H (2014) Study on integration of QTLs related to amylose content of rice. J Northeast Agric Univ 45:8–14
Likitwattanasade T, Hongsprabhas P (2010) Effect of storage proteins on pasting properties and microstructure of Thai rice. Food Res Int 43:1402–1409
Lyon BG, Champagne ET, Vinyard BT, Windham WR, Barton FE, Webb BD, McClung AM, Moldenhauer KA, Linscombe S, McKenzie KS, Kohlwey DE (1999) Effects of degree of milling, drying condition, and final moisture content on sensory texture of cooked rice. Cereal Chem 76:56–62
Martin M, Fitzgerald M (2002) Proteins in rice grains influence cooking properties. J Cereal Sci 36:285–294
McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:11–14
Nakamura Y, Francisco PB, Hosaka Y, Sato A, Sawada T, Kubo A, Fujita N (2005) Essential amino acids of starch synthase IIa differentiate amylopectin structure and starch quality between japonica and indica rice varieties. Plant Mol Biol 58:213–227
Peng C, Wang YH, Liu F, Ren YL, Zhou KN, Lv J, Zheng M, Zhao SL, Zhang L, Wang CM, Jiang L, Zhang X, Guo XP, Bao YQ, Wan JM (2014) FLOURY ENDOSPERM6 encodes a CBM48 domain-containing protein involved in compound granule formation and starch synthesis in rice endosperm. Plant J 77:917–930
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39:623–630
Traore K, McClung AM, Chen MH, Fjellstrom R (2011) Inheritance of flour paste viscosity is associated with a rice Waxy gene exon 10 SNP marker. J Cereal Sci 53:37–44
Wanchana S, Toojinda T, Tragoonrung S, Vanavichit A (2003) Duplicated coding sequence in the waxy allele of tropical glutinous rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci 165:1193–1199
Wang LQ, Liu WJ, Xu Y, He YQ, Luo LJ, Xing YZ, Xu CG, Zhang QF (2007) Genetic basis of 17 traits and viscosity parameters characterizing the eating and cooking quality of rice grain. Theor Appl Genet 115:463–476
Xie LH, Chen N, Duan BW, Zhu ZW, Liao XY (2008) Impact of proteins on pasting and cooking properties of waxy and non-waxy rice. J Cereal Sci 47:372–379
Xu FF, Zhang G, Tong C, Sun X, Corke H, Sun M, Bao JS (2013) Association mapping of starch physicochemical properties with starch biosynthesizing genes in waxy rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agric Food Chem 61:10110–10117
Xu FF, Sun X, Chen YL, Huang Y, Tong C, Bao JS (2015) Rapid identification of major QTLs associated with rice grain weight and their utilization. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122206
Yan CJ, Tian ZX, Fang YW, Yang YC, Li JA, Zeng SY, Gu SL, Xu CW, Tang SZ, Gu MH (2011) Genetic analysis of starch paste viscosity parameters in glutinous rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 122:63–76
Yan B, Tondi Yacouba N, Chen J, Wang Y, Gao G, Zhang Q, Liu X, He Y (2014) Analysis of minor quantitative trait loci for eating and cooking quality traits in rice using a recombinant inbred line population derived from two indica cultivars with similar amylose content. Mol Breed 34:2151–2163
Zhang WW, Bi JC, Chen LM, Zheng LN, Ji SL, Xia YM, Xie K, Zhao ZG, Wang YH, Liu LL, Jiang L, Wan JM (2008) QTL mapping for crude protein and protein fraction contents in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Cereal Sci 48:539–547
Zhang XJ, Wang JF, Huang J, Lan HX, Wang CL, Yin CF, Wu YY, Tang HJ, Qian Q, Li JY, Zhang HS (2012) Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:21534–21539
Zheng L, Zhang W, Chen X, Ma J, Chen W, Zhao Z, Zhai H, Wan J (2011) Dynamic QTL analysis of rice protein content and protein index using recombinant inbred lines. J Plant Bio 54:321–328
Acknowledgments
We thank Yafang Shao, Gan Zhang and Fufu Tang for their technical assistance. This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2011FZA6011), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LZ13C130001), and the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201103007) from the Ministry of Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Feifei Xu and Chengxiao Sun have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Sun, C., Huang, Y. et al. QTL mapping for rice grain quality: a strategy to detect more QTLs within sub-populations. Mol Breeding 35, 105 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0296-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0296-3