Abstract
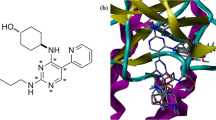
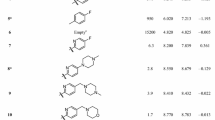
In the present work, a molecular modeling study was carried out using 2D and 3D quantitative structure-activity relationships for the various series of compounds known as B-Raf\(^{\mathrm{V600E}}\) inhibitors. For 2D-QSAR analysis, a linear model was developed by MLR based on GA-OLS with appropriate results \((Q^{2}_{\mathrm{LOO}}= 0.796, R^{2}_{\mathrm{train}}= 0.827)\), which was validated by several external validation techniques. To perform a 3D-QSAR analysis, CoMFA and CoMSIA methods were used. The selected CoMFA model could provide reliable statistical values \((Q^{2}_{\mathrm{LOO}} = 0.683, r^{2} = 0.947)\) based on the training set in the biases of the selected alignment. Using the same selected alignment, a statistically reliable CoMSIA model, out of thirty-one different combinations, was also obtained \((Q^{2}_{\mathrm{LOO}}= 0.645, r^{2} = 0.897)\). The predictive accuracy of the derived models was rigorously evaluated with the external test set of nineteen compounds based on several validation techniques. Molecular docking simulations and pharmacophore analyses were also performed to derive the true conformations of the most potent inhibitors with B-Raf\(^{\mathrm{V600E}}\) kinase.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gray-Schopfer V, Dias S, Marais R (2005) The role of B-RAF in melanoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24:165–183. doi:10.1007/s10555-005-5865-1
Morrison D, Daar I (2006) RAS and the RAF/MEK/ERK Cascade. In: Der C (ed) RAS Family GTPases. Proteins and cell regulation, vol 4. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 67–93. doi:10.1007/1-4020-4708-8_4
Zebisch A, Troppmair J (2006) Back to the roots: the remarkable RAF oncogene story. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1314–1330. doi:10.1007/s00018-006-6005-y
Basto D, Trovisco V, Lopes J, Martins A, Pardal F, Soares P, Reis R (2005) Mutation analysis of B-RAF gene in human gliomas. Acta Neuropathol 109:207–210. doi:10.1007/s00401-004-0936-x
McCubrey J, Bertrand F, Steelman L, Chang F, Terrian D, Franklin R (2007) Critical roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in apoptosis and drug resistance. In: Srivastava R (ed) Apoptosis, cell signaling, and human diseases. Humana Press, New York, pp 101–134. doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-199-4_5
Brown MD, Sacks DB (2008) Compartmentalised MAPK pathways. In: Klussmann E, Scott J (eds) Protein-protein interactions as new drug targets, vol 186 of handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer, Berlin, pp 205–235. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-72843-6_9
Nucera C, Goldfarb M, Hodin R, Parangi S (2009) Role of B-Raf\(^{{\rm V600E}}\) in differentiated thyroid cancer and preclinical validation of compounds against B-Raf\(^{{\rm V600E}}\). BBA-Rev Cancer 1795:152–161. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2009.01.003
Hooijkaas AI, Gadiot J, van der Valk M, Mooi WJ, Blank CU (2012) Targeting BRAFV600E in an inducible murine model of melanoma. Am J Pathol 181:785–794. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.06.002
Shepherd C, Puzanov I, Sosman J (2010) B-RAF inhibitors: an evolving role in the therapy of malignant melanoma. Curr Oncol Rep 12:146–152. doi:10.1007/s11912-010-0095-2
Gray-Schopfer V, Dias S, Marais R (2005) Erratum, the role of B-RAF in melanoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24:367–367. doi:10.1007/s10555-005-1585-9
Stellwagen JC, Adjabeng GM, Arnone MR, Dickerson SH, Han C, Hornberger KR, King AJ, Mook RA Jr, Petrov KG, Rheault TR, Rominger CM, Rossanese OW, Smitheman KN, Waterson AG, Uehling DE (2011) Development of potent B-RafV600E inhibitors containing an arylsulfonamide headgroup. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:4436–4440. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.06.021
Wang X, Berger DM, Salaski EJ, Torres N, Hu Y, Levin JI, Powell D, Wojciechowicz D, Collins K, Frommer E (2009) Discovery of highly potent and selective type I B-Raf kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:6571–6574. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.10.030
Ren L, Ahrendt KA, Grina J, Laird ER, Buckmelter AJ, Hansen JD, Newhouse B, Moreno D, Wenglowsky S, Dinkel V, Gloor SL, Hastings G, Rana S, Rasor K, Risom T, Sturgis HL, Voegtli WC, Mathieu S (2012) The discovery of potent and selective pyridopyrimidin-7-one based inhibitors of B-Raf\(^{{\rm V600E}}\) kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:3387–3391. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.04.015
Chapman P, Flaherty K (2012) Targeted Inhibition of B-Raf. In: Gajewski TF, Hodi FS (eds) Targeted therapeutics in melanoma. Current clinical oncology. Springer, New York, pp 63–76. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-407-0_5
Fedorenko IV, Paraiso KHT, Smalley KSM (2011) Acquired and intrinsic BRAF inhibitor resistance in BRAF V600E mutant melanoma. Biochem Pharmacol 82:201–209. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2011.05.015
Ramurthy S, Costales A, Jansen JM, Levine B, Renhowe PA, Shafer CM, Subramanian S (2012) Design and synthesis of 6,6-fused heterocyclic amides as raf kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:1678–1681. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.12.112
Wenglowsky S, Moreno D, Laird ER, Gloor SL, Ren L, Risom T, Rudolph J, Sturgis HL, Voegtli WC (2012) Pyrazolopyridine inhibitors of B-Raf\(^{{\rm V600E}}\). Part 4: rational design and kinase selectivity profile of cell potent type II inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:6237–6241. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.08.007
Ren L, Wenglowsky S, Miknis G, Rast B, Buckmelter AJ, Ely RJ, Schlachter S, Laird ER, Randolph N, Callejo M, Martinson M, Galbraith S, Brandhuber BJ, Vigers G, Morales T, Voegtli WC, Lyssikatos J (2011) Non-oxime inhibitors of B-Raf\(^{{\rm V600E}}\) kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:1243–1247. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.12.061
Wenglowsky S, Ahrendt KA, Buckmelter AJ, Feng B, Gloor SL, Gradl S, Grina J, Hansen JD, Laird ER, Lunghofer P, Mathieu S, Moreno D, Newhouse B, Ren L, Risom T, Rudolph J, Seo J, Sturgis HL, Voegtli WC, Wen Z (2011) Pyrazolopyridine inhibitors of B-Raf\(^{{\rm V600E}}\). Part 2: structure-activity relationships. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:5533–5537. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.06.097
Wenglowsky S, Moreno D, Rudolph J, Ran Y, Ahrendt KA, Arrigo A, Colson B, Gloor SL, Hastings G (2012) Pyrazolopyridine inhibitors of B-Raf\(^{{\rm V600E}}\). Part 3: an increase in aqueous solubility via the disruption of crystal packing. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:912–915. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.12.030
Wenglowsky S, Ren L, Ahrendt KA, Laird ER, Aliagas I, Alicke B, Buckmelter AJ, Choo EF, Dinkel V, Feng B, Gloor SL, Gould SE, Gross S, Gunzner-Toste J, Hansen Joshua D, Hatzivassiliou G, Liu Bonnie, Malesky K, Mathieu S, Newhouse B, Raddatz NJ, Ran Y, Rana S, Randolph N, Risom T, Rudolph J, Savage S, Selby LT, Shrag M, Song K, Sturgis HL, Voegtli WC, Wen Z, Willis BS, Woessner RD, Wu W-I, Young WB, Grina J (2011) Pyrazolopyridin e Inhibitors of B-Raf\(^{{\rm V600E}}\). Part 1: the development of selective, orally bioavailable, and efficacious inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett 2:342–347. doi:10.1021/ml200025q
Habibi-Yangjeh A, Pourbasheer E, Danandeh-Jenagharad M (2008) Prediction of basicity constants of various pyridines in aqueous solution using a principal component-genetic algorithm-artificial neural network. Monatsh Chem 139:1423–1431. doi:10.1007/s00706-008-0951-z
Pourbasheer E, Riahi S, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P (2010) QSAR study on melanocortin-4 receptors by support vector machine. Eur J Med Chem 45:1087–1093. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2009.12.003
Riahi S, Ganjali M, Pourbasheer E, Norouzi P (2008) QSRR study of GC retention indices of essential-oil compounds by multiple linear regression with a genetic algorithm. Chroma 67:917–922. doi:10.1365/s10337-008-0608-4
Riahi S, Pourbasheer E, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P (2009) Investigation of different linear and nonlinear chemometric methods for modeling of retention index of essential oil components: concerns to support vector machine. J Hazard Mater 166:853–859. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.097
Pourbasheer E, Aalizadeh R, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P (2013) QSAR study of \(\alpha \)1\(\beta \)4 integrin inhibitors by GA-MLR and GA-SVM methods. Struct Chem 25:355–370. doi:10.1007/s11224-013-0300-7
Cherkasov A, Muratov EN, Fourches D, Varnek A, Baskin II, Cronin M, Dearden J, Gramatica P, Martin YC, Todeschini R, Consonni V, Kuz’min VE, Cramer R, Benigni R, Yang C, Rathman J, Terfloth L, Gasteiger J, Richard A, Tropsha A (2013) QSAR modeling: Where have you been? Where are you going to? J Med Chem 57:4977–5010. doi:10.1021/jm4004285
Li J, Gramatica P (2010) The importance of molecular structures, endpoints’ values, and predictivity parameters in QSAR research: QSAR analysis of a series of estrogen receptor binders. Mol Divers 14:687–696. doi:10.1007/s11030-009-9212-2
Pourbasheer E, Riahi S, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P (2010) Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) study of interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 4 (IRAK-4) inhibitor activity by the genetic algorithm and multiple linear regression (GA-MLR) method. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 25:844–853. doi:10.3109/14756361003757893
Pourbasheer E, Riahi S, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P (2011) Prediction of solubility of fullerene C60 in various organic solvents by genetic algorithm-multiple linear regression. Fuller Nanotub Car N 19:585–598. doi:10.1080/1536383x.2010.504952
Habibi-Yangjeh A, Pourbasheer E, Danandeh-Jenagharad M (2009) Application of principal component-genetic algorithm-artificial neural network for prediction acidity constant of various nitrogen-containing compounds in water. Monatsh Chem 140:15–27. doi:10.1007/s00706-008-0049-7
Khajehsharifi H, Sadeghi M, Pourbasheer E (2009) Spectrophotometric simultaneous determination of ceratine, creatinine, and uric acid in real samples by orthogonal signal correction-partial least squares regression. Monatsh Chem 140:685–691. doi:10.1007/s00706-009-0155-1
Pourbasheer E, Aalizadeh R, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P (2013) QSAR study of IKK\(\beta \) inhibitors by the genetic algorithm: multiple linear regressions. Med Chem Res 23:57–66. doi:10.1007/s00044-013-0611-7
Garcia-Domenech R, Zanni R, Galvez-Llompart M, Galvez J (2015) Predicting antiprotozoal activity of benzyl phenyl ether diamine derivatives through QSAR multi-target and molecular topology. Mol Divers 19:357–366. doi:10.1007/s11030-015-9575-5
Fratev F, Benfenati E (2005) 3D-QSAR and molecular mechanics study for the differences in the azole activity against yeastlike and filamentous fungi and their relation to P450DM inhibition, part 1. 3-Substituted-4(3H)-quinazolinones. J Chem Inf Model 45:634–644. doi:10.1021/ci0496494
Hopfinger AJ, Wang S, Tokarski JS, Jin B, Albuquerque M, Madhav PJ, Duraiswami C (1997) Construction of 3D-QSAR models using the 4D-QSAR analysis formalism. J Am Chem Soc 119:10509–10524. doi:10.1021/ja9718937
Bhonsle JB, Venugopal D, Huddler DP, Magill AJ, Hicks RP (2007) Application of 3D-QSAR for identification of descriptors defining bioactivity of antimicrobial peptides. J Med Chem 50:6545–6553. doi:10.1021/jm070884y
Scott JS, Goldberg FW, Turnbull AV (2013) Medicinal chemistry of inhibitors of \(11\beta \)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (\(11\beta \)-HSD1). J Med Chem 57:4466–4486. doi:10.1021/jm4014746
Nandi S, Bagchi M (2010) 3D-QSAR and molecular docking studies of 4-anilinoquinazoline derivatives: a rational approach to anticancer drug design. Mol Divers 14:27–38. doi:10.1007/s11030-009-9137-9
Du Q-S, Gao J, Wei Y-T, Du L-Q, Wang S-Q, Huang R-B (2012) Structure-based and multiple potential three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (SB-MP-3D-QSAR) for inhibitor design. J Chem Inf Model 52:996–1004. doi:10.1021/ci300066y
Tosco P, Balle T (2011) A 3D-QSAR-driven approach to binding mode and affinity prediction. J Chem Inf Model 52:302–307. doi:10.1021/ci200411s
Tuccinardi T, Ortore G, Santos MAl, Marques SrM, Nuti E, Rossello A, Martinelli A (2009) Multitemplate alignment method for the development of a reliable 3D-QSAR model for the analysis of MMP3 inhibitors. J Chem Inf Model 49:1715–1724. doi:10.1021/ci900118v
Cramer RD, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA), part 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967. doi:10.1021/ja00226a005
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) Molecular similarity indices in a comparative analysis (CoMSIA) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological activity. J Med Chem 37:4130–4146. doi:10.1021/jm00050a010
HyperChem (2002) Molecular modeling system. 7.03 edn. Hypercube, Inc., Gainesville
Todeschini R, Consonni V, Mauri A, Pavan M (2005) DRAGON. Software for the calculation of molecular descriptors, 5.3 edn., Talete Srl, Milan
Waller CL, Bradley MP (1999) Development and validation of a novel variable selection technique with application to multidimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship studies. J Chem Inf Comp Sci 39:345–355. doi:10.1021/ci980405r
Leardi R, Boggia R, Terrile M (1992) Genetic algorithms as a strategy for feature selection. J Chemom 6:267–281. doi:10.1002/cem.1180060506
Hunger J, Huttner G (1999) Optimization and analysis of force field parameters by combination of genetic algorithms and neural networks. J Comput Chem 20:455–471. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(199903)20:4<455::AID-JCC6>3.0.CO;2-1
Gramatica P, Chirico N, Papa E, Cassani S, Kovarich S (2013) QSARINS: a new software for the development, analysis, and validation of QSAR MLR models. J Comput Chem 34:2121–2132. doi:10.1002/jcc.23361
Manual HT (2006) SYBYL 7.3. Tripos International, St. Louis, Missouri
Clark M, Cramer RD, Van Opdenbosch N (1989) Validation of the general purpose tripos 5.2 force field. J Comput Chem 10:982–1012. doi:10.1002/jcc.540100804
Gasteiger J, Marsili M (1980) Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 36:3219–3228. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(80)80168-2
Folkers G, Merz A, Rognan D (1993) 3D-QSAR in drug design, theory, methods and applications. In: Kubinyi H (ed) ESCOM, Leiden, pp 583–618
Viswanadhan VN, Ghose AK, Revankar GR, Robins RK (1989) Atomic physicochemical parameters for three dimensional structure directed quantitative structure-activity relationships. 4. Additional parameters for hydrophobic and dispersive interactions and their application for an automated superposition of certain naturally occurring nucleoside antibiotics. J Chem Inf Comp Sci 29:163–172. doi:10.1021/ci00063a006
Wold S, Ruhe A, Wold H, Dunn IW (1984) The collinearity problem in linear regression. The partial least squares (PLS) approach to generalized inverses. SIAM J Sci Stat Comp 5:735–743. doi:10.1137/0905052
Bush B, Nachbar R Jr (1993) Sample-distance partial least squares: PLS optimized for many variables, with application to CoMFA. J Comput Aid Mol Des 7:587–619. doi:10.1007/bf00124364
Martin YC, Willett P (1998) Designing bioactive molecules: three-dimensional techniques and applications. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC
Wehrens R, Putter H, Buydens LMC (2000) The bootstrap: a tutorial. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 54:35–52. doi:10.1016/S0169-7439(00)00102-7
Pourbasheer E, Aalizadeh R, Ardabili JS, Ganjali MR (2015) QSPR study on solubility of some fullerenes derivatives using the genetic algorithms—multiple linear regression. J Mol Liquids 204:162–169. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2015.01.028
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30:2785–2791. doi:10.1002/jcc.21256
Singh UC, Kollman PA (1984) An approach to computing electrostatic charges for molecules. J Comput Chem 5:129–145. doi:10.1002/jcc.540050204
Wolber G, Langer T (2004) LigandScout: 3-D pharmacophores derived from protein-bound ligands and their use as virtual screening filters. J Chem Inf Model 45:160–169. doi:10.1021/ci049885e
Roy K, Chakraborty P, Mitra I, Ojha PK, Kar S, Das RN (2013) Some case studies on application of “rm2” metrics for judging quality of quantitative structure-activity relationship predictions: emphasis on scaling of response data. J Comput Chem 34:1071–1082. doi:10.1002/jcc.23231
Golbraikh A, Tropsha A (2002) Beware of q2!. J Mol Graph Model 20(4):269–276. doi:10.1016/S1093-3263(01)00123-1
Eriksson L, Johansson E, Müller M, Wold S (2000) On the selection of the training set in environmental QSAR analysis when compounds are clustered. J Chemometr 14:599–616. doi:10.1002/1099-128x(200009/12)14:5/6<599::aid-cem619>3.0.co;2-8
Pourbasheer E, Aalizadeh R, Shokouhi Tabar S, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P, Shadmanesh J (2014) 2D and 3D-QSAR study of hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitors by CoMFA and CoMSIA methods. J Chem Inf Model 54:2902–2914. doi:10.1021/ci500216c
He S, Shao Y, Fan L, Che Z, Xu H, Zhi X, Wang J, Yao X, Qu H (2013) Synthesis and quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) study of novel 4-acyloxypodophyllotoxin derivatives modified in the a and c rings as insecticidal agents. J Agric Food Chem 61:618–625. doi:10.1021/jf305011n
Pourbasheer E, Bazl R, Amanlou M (2014) Molecular docking and 3D-QSAR studies on the MAPKAP-K2 inhibitors. Med Chem Res 23:2252–2263. doi:10.1007/s00044-013-0820-0
Hall LH, Kier LB (1995) Electrotopological state indices for atom types: a novel combination of electronic, topological, and valence state information. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 35:1039–1045. doi:10.1021/ci00028a014
Todeschini R, Consonni V (2000) Handbook of molecular descriptors. Wiley, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/9783527613106
Acknowledgments
Reza Aalizadeh would like to thank the State Scholarships’ Foundation of Greece (I.K.Y.) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aalizadeh, R., Pourbasheer, E. & Ganjali, M.R. Analysis of B-Raf\(^{\mathrm{V600E}}\) inhibitors using 2D and 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and pharmacophore studies. Mol Divers 19, 915–930 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-015-9626-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-015-9626-y