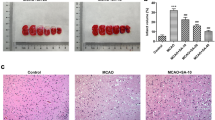
Abstract
The protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase/eukaryotic initiation factor 2ɑ (PERK/eIF2α), the branch of unfolded protein response (UPR), is responsible for transient arrest in translation to counter the enhanced levels of misfolded or unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) following any acute condition. In neurological disorders, overactivation of PERK-P/eIF2-P signaling, leads to a prolonged decline in global protein synthesis resulting in synaptic failure and neuronal death. Our study has shown, PERK/ATF4/CHOP pathway gets activated following cerebral ischemia in rats. We have further demonstrated, PERK inhibitor, GSK2606414 ameliorates ischemia induced neuronal damage by preventing additional neuronal loss, minimizing brain infarct, reducing brain edema, and preventing neurological symptoms from appearing. GSK2606414 was found to improve the neurobehavioral deficits and reduce the pyknotic neurons in ischemic rats. Also, it decreased glial activation and apoptotic protein mRNA expression while enhanced the synaptic protein mRNA expression in rat brain following cerebral ischemia. In conclusion, our findings suggest that PERK/ATF4/CHOP activation play a vital role in cerebral ischemia. Thus, PERK inhibitor, GSK2606414 might be a potential neuroprotective agent in cerebral ischemia.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ATF4:
-
Activating transcription factor 4
- ATF6:
-
Activating transcription factor 6
- CHOP:
-
C/EBP homologous protein
- EIF2AK3:
-
Eukaryotic translational initiation factor 2α kinase-3
- IRE1:
-
Inositol requiring enzyme 1
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- PERK:
-
Protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- NOR:
-
Novel object recognition
- P-eIF2ɑ:
-
Phosphorylated eukaryotic initiation factor 2ɑ
- SAH:
-
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
- TTC:
-
2,3,5-triphenyl-tetrazolium chloride
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- RT-PCR:
-
Real time polymerase chain reaction
References
Axten JM, Medina JR, Feng Y, Shu A, Romeril SP, Grant SW, Li WHH, Heerding DA, Minthorn E, Mencken T, Atkins C, Liu Q, Rabindran S, Kumar R, Hong X, Goetz A, Stanley T, Taylor JD, Sigethy SD et al (2012) Discovery of 7-methyl-5-(1-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetyl}-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-5-yl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (GSK2606414), a potent and selective first-in-class inhibitor of protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK). J Med Chem 55:7193–7207. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm300713s
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H (1986) Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17:472–476. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.17.3.472
Bingham D, Martin SJ, Macrae IM, Carswell HVO (2012) Watermaze performance after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat: the role of sensorimotor versus memory impairments. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:989–999. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2012.16
Broughton BRS, Reutens DC, Sobey CG (2009) Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 40:e331–e339. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.531632
Caldeira MV, Salazar IL, Curcio M, Canzoniero LMT, Duarte CB (2014) Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in brain ischemia: friend or foe? Prog Neurobiol 112:50–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.003
Campbell BCV, De Silva DA, Macleod MR, Coutts SB, Schwamm LH, Davis SM, Donnan GA (2019) Ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5:70. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0118-8
Cheng YD, Al-Khoury L, Zivin JA (2004) Neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: two decades of success and failure. NeuroRx 1:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1602/neurorx.1.1.36
da Silva H, Nucci MP, Mamani JB, Mendez-Otero R, Nucci LP, Tannus A, Gamarra LF (2018) Evaluation of temperature induction in focal ischemic thermocoagulation model. PLoS One 13:e0200135. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0200135
Dhir N, Medhi B, Prakash A, Goyal MK, Modi M, Mohindra S (2020) Pre-clinical to clinical translational failures and current status of clinical trials in stroke therapy: a brief review. Curr Neuropharmacol 18:596–612. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X18666200114160844
Dong R, Huang R, Wang J, Liu H, Xu Z (2021) Effects of microglial activation and polarization on brain injury after stroke. Front Neurol 12:620948. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.620948
Ennaceur A, Delacour J (1988) A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 31:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(88)90157-x
Fei H, Xiang P, Luo W, Tan X, Gu C, Liu M, Chen M, Wang Q, Yang J (2021) CTRP1 attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via the PERK signaling pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:700854. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.700854
Feng L, Han C-X, Cao S-Y, Zhang H-M, Wu G-Y (2020) Deficits in motor and cognitive functions in an adult mouse model of hypoxia-ischemia induced stroke. Sci Rep 10:20646. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77678-8
Gerriets T, Stolz E, Walberer M, Müller C, Kluge A, Bachmann A, Fisher M, Kaps M, Bachmann G (2004) Noninvasive quantification of brain edema and the space-occupying effect in rat stroke models using magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 35:566–571. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000113692.38574.57
Han J, Back SH, Hur J, Lin Y-H, Gildersleeve R, Shan J, Yuan CL, Krokowski D, Wang S, Hatzoglou M, Kilberg MS, Sartor MA, Kaufman RJ (2013) ER-stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nat Cell Biol 15:481–490. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2738
Han Y, Yuan M, Guo Y-S, Shen X-Y, Gao Z-K, Bi X (2021) Mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress in cerebral ischemia. Front Cell Neurosci 15:704334. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.704334
Harding HP, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Wek R, Schapira M, Ron D (2000) Regulated translation initiation controls stress-induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell 6:1099–1108. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00108-8
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Novoa I, Lu PD, Calfon M, Sadri N, Yun C, Popko B, Paules R, Stojdl DF, Bell JC, Hettmann T, Leiden JM, Ron D (2003) An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol Cell 11:619–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00105-9
Herbert TP, Laybutt DR (2016) A reevaluation of the role of the unfolded protein response in islet dysfunction: maladaptation or a failure to adapt? Diabetes 65:1472–1480. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-1633
Hughes D, Mallucci GR (2019) The unfolded protein response in neurodegenerative disorders - therapeutic modulation of the PERK pathway. FEBS J 286:342–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14422
Isayama K, Pitts LH, Nishimura MC (1991) Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining to delineate rat brain infarcts. Stroke 22:1394–1398. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.22.11.1394
Jansone B, Dzirkale Z, Jekabsons K, Pilipenko V, Beitnere U, Māgure I, Skumbiņš R, Klētnieks U, Vanaga I, Muceniece R, Kluša V (2016) Spruce needle Polyprenols protect against atorvastatin-induced muscle weakness and do not influence central nervous system functions in rats. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci Sect B Nat Exact Appl Sci 70:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1515/prolas-2016-0003
Jiang X, Wei Y, Zhang T, Zhang Z, Qiu S, Zhou X, Zhang S (2017) Effects of GSK2606414 on cell proliferation and endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated gene expression in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep 15:3105–3110. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6418
Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR, Zampaglione N, Gillette JR (1974) Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 11:151–169. https://doi.org/10.1159/000136485
Kaufman RJ (2002) Orchestrating the unfolded protein response in health and disease. J Clin Invest 110:1389–1398. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI16886
Lin C-L (2015) Attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress as a treatment strategy against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regeneration Res 10:1930–1931. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.169615
Liu G, Wang T, Wang T, Song J, Zhou Z (2013) Effects of apoptosis-related proteins caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 on cerebral ischemia rats. Biomedical Reports 1:861–867. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2013.153
Liu Z, Shi Q, Song X, Wang Y, Wang Y, Song E, Song Y (2016) Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4)-ATF3-C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) cascade shows an essential role in the ER stress-induced sensitization of tetrachlorobenzoquinone-challenged PC12 cells to ROS-mediated apoptosis via death receptor 5 (DR5) signaling. Chem Res Toxicol 29:1510–1518. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00181
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.20.1.84
Madden E, Logue SE, Healy SJ, Manie S, Samali A (2019) The role of the unfolded protein response in cancer progression: from oncogenesis to chemoresistance. Biol Cell 111:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/boc.201800050
Manaenko A, Chen H, Kammer J, Zhang JH, Tang J (2011) Comparison Evans blue injection routes: intravenous versus intraperitoneal, for measurement of blood–brain barrier in a mice hemorrhage model. J Neurosci Methods 195:206–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.12.013
Mercado G, Castillo V, Soto P, López N, Axten JM, Sardi SP, Hoozemans JJM, Hetz C (2018) Targeting PERK signaling with the small molecule GSK2606414 prevents neurodegeneration in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 112:136–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.01.004
Moreno JA, Halliday M, Molloy C, Radford H, Verity N, Axten JM, Ortori CA, Willis AE, Fischer PM, Barrett DA, Mallucci GR (2013) Oral treatment targeting the unfolded protein response prevents neurodegeneration and clinical disease in prion-infected mice. Sci Transl Med 5:206ra138. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3006767
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(84)90007-4
Nakka VP, Gusain A, Raghubir R (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays critical role in brain damage after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Neurotox Res 17:189–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9110-5
Nakka VP, Prakash-Babu P, Vemuganti R (2016) Crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative stress, and autophagy: potential therapeutic targets for acute CNS injuries. Mol Neurobiol 53:532–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9029-6
Owen CR, Kumar R, Zhang P, McGrath BC, Cavener DR, Krause GS (2005) PERK is responsible for the increased phosphorylation of eIF2α and the severe inhibition of protein synthesis after transient global brain ischemia. J Neurochem 94:1235–1242. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03276.x
Pemberton JM, Pogmore JP, Andrews DW (2021) Neuronal cell life, death, and axonal degeneration as regulated by the BCL-2 family proteins. Cell Death Differ 28:108–122. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00654-2
Pomierny-Chamioło L, Moniczewski A, Wydra K, Suder A, Filip M (2013) Oxidative stress biomarkers in some rat brain structures and peripheral organs underwent cocaine. Neurotox Res 23:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-012-9335-6
Qin C, Zhou L-Q, Ma X-T, Hu Z-W, Yang S, Chen M, Bosco DB, Wu L-J, Tian D-S (2019) Dual functions of microglia in ischemic stroke. Neurosci Bull 35:921–933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-019-00388-3
Radford H, Moreno JA, Verity N, Halliday M, Mallucci GR (2015) PERK inhibition prevents tau-mediated neurodegeneration in a mouse model of frontotemporal dementia. Acta Neuropathol 130:633–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1487-z
Sano R, Reed JC (2013) ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:3460–3470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.028
Scheper W, Hoozemans JJM (2015) The unfolded protein response in neurodegenerative diseases: a neuropathological perspective. Acta Neuropathol 130:315–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1462-8
Shacham T, Patel C, Lederkremer GZ (2021) PERK pathway and neurodegenerative disease: to inhibit or to activate? Biomolecules 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11030354
Shi K, Tian D-C, Li Z-G, Ducruet AF, Lawton MT, Shi F-D (2019) Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet Neurol 18:1058–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30078-X
Smedley GD, Walker KE, Yuan SH (2021) The role of PERK in understanding development of neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158146
Taalab YM, Ibrahim N, Maher A, Hassan M, Mohamed W, Moustafa AA, Salama M, Johar D, Bernstein L (2018) Mechanisms of disordered neurodegenerative function: concepts and facts about the different roles of the protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK). Rev Neurosci 29:387–415. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2017-0071
Walter P, Ron D (2011) The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334:1081–1086. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1209038
Wang W, Li M, Wang Y, Wang Z, Zhang W, Guan F, Chen Q, Wang J (2017) GSK-3β as a target for protection against transient cerebral ischemia. Int J Med Sci 14:333–339. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.17514
Wei J, Wu X, Luo P, Yue K, Yu Y, Pu J, Zhang L, Dai S, Han D, Fei Z (2019) Homer1a attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced mitochondrial stress after ischemic reperfusion injury by inhibiting the PERK pathway. Front Cell Neurosci 13:101. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00101
Wicha P, Tocharus J, Janyou A, Jittiwat J, Changtam C, Suksamrarn A, Tocharus C (2017) Hexahydrocurcumin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, attenuates inflammation, and improves antioxidant defenses in a rat stroke model. PLoS One 12:e0189211. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189211
Yan F, Cao S, Li J, Dixon B, Yu X, Chen J, Gu C, Lin W, Chen G (2017) Pharmacological inhibition of PERK attenuates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats through the activation of Akt. Mol Neurobiol 54:1808–1817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9790-9
Yang W, Paschen W (2016) Unfolded protein response in brain ischemia: a timely update. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:2044–2050. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X16674488
Zhu Y, Yu J, Gong J, Shen J, Ye D, Cheng D, Xie Z, Zeng J, Xu K, Shen J, Zhou H, Weng Y, Pan J, Zhan R (2021) PTP1B inhibitor alleviates deleterious microglial activation and neuronal injury after ischemic stroke by modulating the ER stress-autophagy axis via PERK signaling in microglia. Aging 13:3405–3427. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202272
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Department of Health Research (DHR), under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India for awarding the Young Scientist fellowship to Ms. Neha Dhir. Also, the authors gratefully appreciate GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) Pharmaceuticals Ltd. for providing the drug (GSK260414) to conduct this study. Authors also acknowledge PGIMER, Chandigarh, India for providing the facilities and resources to conduct this study.
Funding
The project was funded by the Department of Health Research (DHR), under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. (Grant No. R 12014/18/2018-HR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Neha Dhir, Biksah Medhi and Ajay Prakash have designed the study protocol and experiments. Neha Dhir, Ashish Jain and Amit Raj Sharma performed the experimental and molecular experiments. Bishan Das Radotra helped in analysing histopathological data. All authors have analysed the data. Neha Dhir has written the manuscript. All authors have read, corrected and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) at the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India, approved the study protocol. (IAEC Approval No. 93/IAEC/653).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest either financial or personal in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dhir, N., Jain, A., Sharma, A.R. et al. PERK inhibitor, GSK2606414, ameliorates neuropathological damage, memory and motor functional impairments in cerebral ischemia via PERK/p-eIF2ɑ/ATF4/CHOP signaling. Metab Brain Dis 38, 1177–1192 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01183-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01183-w