Abstract
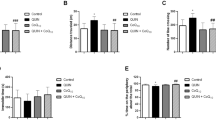
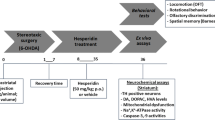
Quercetin, a polyphenolic compound found in a variety of plant products possesses various biological activities and beneficial effects on human health. Schizophrenia (SZ) is one of the neuropsychiatric disorders in human beings with rapid mortality and intense morbidity which can be treated with antipsychotics, but these commercial drugs exert adverse effects and have less efficacy to treat the full spectrum of SZ. The present study was conducted to evaluate neuroprotective effects of quercetin in the preventive and therapeutic treatment of SZ. Quercetin was administered as pre- and post-regimens at the dose of 50 mg/kg in dizocilpine-induced SZ rat model for two weeks. Rats were then subjected for the assessment of different behaviors followed by biochemical, neurochemical, and inflammatory marker analyses. The present findings revealed that quercetin significantly reverses the effects of dizocilpine-induced psychosis-like symptoms in all behavioral assessments as well as it also combats oxidative stress. This flavonoid also regulates dopaminergic, serotonergic, and glutamatergic neurotransmission. A profound effect on inflammatory cytokines and decreased %DNA fragmentation was also observed following the administration of quercetin. The findings suggest that quercetin can be considered as a preventive as well as therapeutic strategy to attenuate oxidative stress and cytokine toxicity, regulate neurotransmission, and prevent enhanced DNA fragmentation that can lead to the amelioration of psychosis-like symptoms in SZ.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are available in the manuscript.
References
Adell A (2020) Brain NMDA Receptors in Schizophrenia and Depression. Biomolecules 10(6):947
Aguirre-Hernandez AE, Gonzalez-Trujano ME, Martinez AL, Moreno J, Kite G, Terrazas T, Soto-Hernandez M (2010) HPLC/MS and anxiolytic-like effect of quercetin and kaemferol flavonoids from Tilia americana var maxicana. J Ethnopharmacol 127:91–97
Asevedo E, Gadelha A, Noto C, Mansur RB, Zugman A, Belangero SI, Berberian AA, Scarpato BS, Leclerc E, Teixeira AL, Gama CS, Bressan RA, Brietzke E (2013) Impact of peripheral levels of chemokines, BDNF and oxidative markers on cognition in individuals with schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 47:1376–1382
Aydın H, Tekin YK, Erşan S, Yavuz H, Erşan EE (2019) The apoptotic paradox in schizophrenia CMJ Original Research. Cumhuriyet Med J 41:256–262
Augustinsson KB (1957) Methods of biochemical analysis. Inter Sci NY 5:1–63
Barcelos GR, Grotto D, Serpeloni JM, Angeli JP, Rocha BA, de Oliveira Souza VC, Vicentini JT, Emanuelli T, Bastos JK, Antunes LM, Knasmüller S, Barbosa F Jr (2011) Protective properties of quercetin against DNA damage and oxidative stress induced by methylmercury in rats. Arch Toxicol 85(9):1151–1157
Batool Z, Agha F, Tabassum S, Batool TS, Siddiqui RA, Haider S (2019) Prevention of cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in rats by essential nutrients present in nuts. Acta Neurobiol Exp (wars) 79(2):169–183
Benros ME, Mortensen PB, Eaton WW (2012) Autoimmune diseases and infections as risk factors for schizophrenia. Ann NY Acad Sci 1262:56–66
Bernstein HG, Krause S, Krell D et al (2007) Strongly reduced number of parvalbumin-immunoreactive projection neurons in the mammillary bodies in schizophrenia: further evidence for limbic neuropathology. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1096:120–127
Bitanihirwe BK, Woo TU (2011) Oxidative stress in schizophrenia: an integrated approach. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35(3):878–893
Cabungcal JH, Steullet P, Kraftsik R, Cuenod M, Do KQ (2013) Early-life insults impair parvalbumin interneurons via oxidative stress: reversal by N-acetylcysteine. Biol Psychiatry 73:574–582
Chatterjee M, Rajkumar V, Surajit G, Gautam P (2012) Neurochemical and molecular characterization of ketamine-induced experimental psychosis model in mice. Neuropharmacology 63:1161–1171
Day AJ, Canada FJ, Diaz JC, Kroon PA, Mclauchlan R, Faulds CB, Plumb GW, Morgan MRA, Williamson G (2000) Dietary flavonoid and isoflavone glycosides are hydrolysed by the lactase site of lactase phlorizin hydrolase. FEBS Lett 468:166–170
de Oliveira L, Spiazzi CM, Bortolin T, Canever L, Petronilho F, Mina FG, Dal-Pizzol F, Quevedo J, Zugno AI (2009) Different subanesthetic doses of ketamine increase oxidative stress in the brain of rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:1003–1008
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulphydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Elmarakby AA, Pollock DM, Imig JD (2007) Renal Dysfunction in Hypertension and Obesity. Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry II 6:575–595
El-Nekeety AA, Abdel-Azeimb SH, Hassan AM, Hassand NS, Ayla SE, Abdel-Wahhab MA (2014) Quercetin inhibits the cytotoxicity and oxidative stress in liver of rats fed aflatoxin-contaminated diet. Toxicol Rep 1:319–329
Elfawy HA, Das B (2019) Crosstalk between mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and age related neurodegenerative disease: Etiologies and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci 218:165–184
Fiorani M, De Sanctis R, Menghinello P, Cucchiarini L, Cellini B, Dachà M (2001) Quercetin prevents glutathione depletion induced by dehydroascorbic acid in rabbit red blood cells. Free Radic Res 34:639–648
Ghosh A, Sarkar S, Mandal AK, Das N (2013) Neuroprotective role of nano encapsulated quercetin in combating ischemia-reperfusion induced neuronal damage in young and aged rats. PLoS ONE 8:e57735
Gu G, Zhang W, Li M, Ni J, Wang P (2015) Transplantation of NSC derived cholinergic neuron-like cells improves cognitive function in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neurosci 291:81–92
Gysin R, Kraftsik R, Sandell J, Bovet P, Chappuis C, Conus P, Deppen P, Preisig M, Ruiz V, Steullet P, Tosic M, Werge T, Cuénod M, Do KQ (2007) Impaired glutathione synthesis in schizophrenia: convergent genetic and functional evidence. PNAS 104:16621–16626
Hajizadeh MA, Valizadegan F (2017) Antidepressant effects of quercetin and its nanocrystal on schizophrenia animal model with using forced swimming test. Journal of Animal Research 30:3
Howes O, McCutcheon R, Stone J (2016) Glutamate and dopamine in schizophrenia: an update for the 21st century. J Psychopharmacol 29:97–115
Jakaria Azam S, Jo SH, Kim IS, Dash R (2019) Potential Therapeutic Targets of Quercetin and Its Derivatives: Its Role in the Therapy of Cognitive Impairment. J Clin Med 8:1789
Jarskog LF, Selinger ES, Lieberman JA, Gilmore JH (2004) Apoptotic proteins in the temporal cortex in schizophrenia: high Bax/Bcl-2 ratio without caspase-3 activation. Am J Psychiatry 161:109–115
Kahn RS, Sommer IE, Murray RM, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Weinberger DR, Cannon TD, O’Donovan M, Correll CU, Kane JM, van Os J, Insel TR (2015) Schizophrenia Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15067
Kantrowitz JT, Woods SW, Petkova E, Cornblatt B, Corcoran CM, Chen H, Silipo G, Javitt DC (2015) D-serine forthe treatment of negative symptoms in individuals at clinical high risk of schizophrenia: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised parallel group mechanistic proof-of-concept trial. Lancet Psychiatry 2:403–412
Lapi D, Vagnani S, Pignataro G, Esposito E, Paterni M, Colantuoni A (2012) Protective effects of Quercetin on Rat Pial micro artery occlusion and reperfusion. Front Physiol 3:32
Liu W, Wang D, Hong W, Yu Y, Tang J, Wang J, Liu F, Xu X, Tan L, Chen X (2017) Psychotomimetic effects of different doses of MK-801 and the underlying mechanisms in a selective memory impairment model. Behav Brain Res 320:517–525
Lu SC (2008) Regulation of glutathione synthesis. Mol Aspects Med 30:42–59
Lutz CK (2014) Stereotypic behavior in nonhuman primates as a model for the human condition. ILAR J 55(2):284–296
Obeng E (2021) Apoptosis (programmed cell death) and its signals - A review. Braz J Biol 81(4):1133–1143
Maas DA, Vallès A, Martens GJM (2017) Oxidative stress, prefrontal cortex hypomyelination and cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry 7:e1171
Maciel RM, Carvalho FB, Olabiyi AA, Schmatz R, Gutierres JM, Stefanello N, Zanini D, Rosa MM, Andrade CM, Rubin MA, Schetinger MR, Morsch VM, Danesi CC, Lopes STA (2016) Neuroprotective effects of quercetin on memory and anxiogenic-like behavior in diabetic rats: Role of ectonucleotidases and acetylcholinesterase activities. Biomed Pharmacother 84:559–568
Martínez-Cengotitabengoa M, Mac-Dowell KS, Leza JC, Micó JA, Fernandez M, Echevarría E, Sanjuan J, Elorza J, González-Pinto A (2012) Cognitive impairment is related to oxidative stress and chemokine levels in first psychotic episodes. Schizophr Res 137:66–72
Mazarati A, Shin D, Auvin S, Caplan R, Sankar R (2007) Kindling epileptogenesis in immature rats leads to persistent depressive behavior. Epilepsy Behav 3:377–383
McCutcheon RA, Krystal JH, Howes OD (2020) Dopamine and glutamate in schizophrenia: biology, symptoms and treatment. World Psychiatry 19:15–33
Meldrum BS (2000) Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the brain: review of physiology and pathology. J Nutr 130:1007S-1015S
Meneses A (2015) Serotonin, neural markers, and memory. Front Pharmacol 6:143
Mert DG, Turgut NH, Arslanbas E, Gungor H, Kara H (2019) The influence of quercetin on recognition memory and brain oxidative damage in a ketamine model of schizophrenia. Psychiatry and Clinical Psychopharmacology 29:1–7
Miyamoto S, Duncan GE, Marx CE, Lieberman JA (2005) Treatments for schizophrenia: A critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs. Mol Psychiatry 10:79–104
Nawaz A, Batool Z, Shazad S, Rafiq S, Afzal A, Haider S (2018) Physical enrichment enhances memory function by regulating stress hormone and brain acetylcholinesterase activity in rats exposed to restraint stress. Life Sci 207:42–49
Ramachandraih CT, Subramanyam N, Bar KJ, Baker G, Yeragani VK (2011) Antidepressants: from MAOIs to SSRIs and more. Indian J Psychiatry 53:180–182
Ravichandran R, Rajendran M, Devapiriam D (2014) Antioxidant study of quercetin and their metal complex and determination of stability constant by spectrophotometry method. Food Chem 146:472–478
Raza MU, Tufan T, Wang Y, Hill C, Zhu MY (2016) DNA Damage in Major Psychiatric Diseases. Neurotox Res 30(2):251–267
Rizk NN, Rafols JA, Dunbar JC (2006) Cerebral ischemia-induced apoptosis and necrosis in normal and diabetic rats: effects of insulin and C-peptide. Brain Res 1096:204–212
Roenker NL, Gudelsky GA, Ahlbrand R, Horn PS, Richtand NM (2012) Evidence for involvement of nitric oxide and GABA (B) receptors in MK-801- stimulated release of glutamate in rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 64:575–581
Samad N, Saleem A, Yasmin F, Shehzad MA (2018) Quercetin protects against stress-induced anxiety- and depression-like behavior and improves memory in male mice. Physiol Res 67:795–808
Sastry PS, Rao KS (2000) Apoptosis, and the nervous system. J Neurochem 74:1–20
Serafini M, Peluso I, Raguzzini A (2010) Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents. Proc Nutr Soc 69:273–278
Shahzad S, Batool Z, Tabassum S, Ahmad S, Kamil N, Khaliq S, Nawaz A, Haider S (2020) Blue-green algae: A miracle from sea combats the oxidative stress and improves behavioral deficits in an animal model of Schizophrenia. Pak J Pharm Sci 33:1847–1853
Shahzad S, Ahmad S, Madiha S, Khaliq S, Laraib Liaquat L, Sadir S, Rafiq S, Tabassum S, Batool Z, Haider S (2017) Dizocilpine induced psychosis-like behavior in rats: A possible animal model with full spectrum of schizophrenia. Pak J Pharm Sci 30:2423–2427
Song X, Fan X, Zhang J, Zheng H, Li X, Pang L, Chen X, Zhang W, Harrington A, Ziedonis D, Lv L (2014) Prolactin serum levels correlate with inflammatory status in drug-naïve first-episode schizophrenia. World J Biol Psychiatry 15:546–552
Song XQ, Lv LX, Li WQ, Hao YH, Zhao JP (2009) The interaction of nuclear factor-kappa B and cytokines is associated with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 65:481–488
Stojanovic A, Martorell L, Montalvo I, Ortega L, Monseny R, Vilella E, Labad J (2014) Increased serum interleukin-6 levels in early stages of psychosis: associations with at-risk mental states and the severity of psychotic symptoms. Psychoneuroendocrinology 41:23–32
Tosic M, Ott J, Barral S, Bovet P, Deppen P, Gheorghita F, Matthey ML, Parnas J, Preisig M, Saraga M, Solida A, Timm S, Wang AG, Werge T, Cuénod M, Do KQ (2006) Schizophrenia and oxidative stress: Glutamate cysteine ligase modifier as a susceptibility gene. Am J Hum Genet 79:586–592
Upthegrove R, Manzanares-Teson N, Barnes NM (2014) Cytokine function in medicationnaive first episode psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr Res 155:101–108
Wu B, Iwakiri R, Tsunada S, Utsumi H, Kojima M, Fujise T, Ootani A, Fujimoto K (2002) iNOS enhances rat intestinal apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion. Free Radic Biol Med 33:649–658
Yun J, Woo ER, Lee DG (2018) Effect of isoquercitrin on membrane dynamics and apoptosis-like death in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1860:357–363
Yan C, Lui SSY, Zou LQ, Wang CY, Zhou FC, Cheung EFC, Shum DHK, Chan RCK (2019) Anticipatory pleasure for future rewards is attenuated in patients with schizophrenia but not in individuals with schizotypal traits. Schizophr Res 206:118–126
Yousefian M, Shakour N, Hosseinzadeh H, Hayes AW, Hadizadeh F, Karimi G (2019) The natural phenolic compounds as modulators of NADPH oxidases in hypertension. Phytomedicine 55:200–213
Yousuf S, Atif F, Ahmad M (2009) Resveratrol exerts its neuroprotective effect by modulating mitochondrial dysfunctions and associated cell death during cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 1250:242–253
Zhang M, Zhao Z, He L, Wan C (2010) A meta-analysis of oxidative stress markers in Schizophrenia. Sci China Life Sci 53:112–124
Zhang XY, Tan YL, Cao LY, Wu GY, Xu Q, Shen Y, Zhou DF (2006) Antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in different forms of schizophrenia treated with typical and atypical antipsychotics. Schizophr Res 81:291–300
Zhou X, Li G, Yang B, Wu J (2019) Quercetin Enhances Inhibitory Synaptic Inputs and Reduces Excitatory Synaptic Inputs to OFF- and ON-Type Retinal Ganglion Cells in a Chronic Glaucoma Rat Model. Front Neurosci 13:672
Zhou Y, Danbolt NC (2014) Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the healthy brain. J Neural Transm (vienna) 121(8):799–817
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the University of Karachi for providing the research facility.
Funding
Haider S received financial support from Higher Education Commission, Pakistan (http://www.hec.gov.pk/english/pages/home.aspx), under the approved project NRPU-4480. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Sidrah Shahzad, Zehra Batool and Asia Afzal. Saida Haider supervised the research project. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Sidrah Shahzad, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The experimental work performed in this study was approved by the Advanced Studies and Research Board of Institute (ASRB/02926/Sc.).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shahzad, S., Batool, Z., Afzal, A. et al. Reversal of oxidative stress, cytokine toxicity and DNA fragmentation by quercetin in dizocilpine-induced animal model of Schizophrenia. Metab Brain Dis 37, 2793–2805 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01090-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01090-6