Abstract
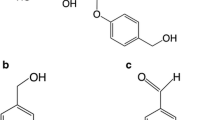
The lifetime prevalence rate for major depressive disorder (MDD) is approximately 17 % for most developed countries around the world. Dietary polyphenols are currently used as an adjuvant therapy to accelerate the therapeutic efficacy on depression. Ferulic acid (FA) or 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-cinnamic acid (Fig. 1a) is a main polyphenolic component of Chinese herb Radix Angelicae Sinensis, which is found to have antidepressant-like effects through regulating serotonergic and noradrenergic function. The present study examined the synergistic effect of low doses of FA combined with subthreshold dose of piperine, a bioavailability enhancer, on depression-like behaviors in mice, and investigated the possible mechanism. The administration of FA, even in the highest dose tested, reduced immobility time by 60 % in the tail suspension and forced swimming tests (TST and FST) in mice when compared to control. The maximal antidepressant-like effect of FA was obtained with 200 mg/kg. In addition, piperine only produced a weak antidepressant-like effect in the TST and FST. However, the evidence from the interaction analysis suggested a synergistic effect when low doses of FA were combined with a subthreshold dose of piperine. Further neurochemical evidence such as monoamine levels in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, and hypothalamus and measurements of monoamine oxidase activity also supported a synergistic effect of FA and piperine in the enhancement of monoaminergic function. This finding supports the concept that the combination strategy might be an alternative therapy in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with high efficacy and low side effects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atal CK, Dubey RK, Singh JJ (1985) Biochemical basis of enhanced drug bioavailability by piperine: evidence that piperine is a potent inhibitor of drug metabolism. Pharmacol Exp Ther 232:258–262
Awad AS, El-Sharif AA (2011) Curcumin immune-mediated and anti-apoptotic mechanisms protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion and distant organ induced injuries. Int Immunopharmacol 11:992–996
Bhutani MK1, Bishnoi M, Kulkarni SK (2009) Anti-depressant like effect of curcumin and its combination with piperine in unpredictable chronic stress-induced behavioral, biochemical and neurochemical changes. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:39–43
Bourin M, Mocaër E, Porsolt R (2004) Antidepressant-like activity of S 20098 (agomelatine) in the forced swimming test in rodents: involvement of melatonin and serotonin receptors. J Psychiatr Neurosci 29:126–133
Butterweck V, Böckers T, Korte B, et al (2002) Long-term effects of St. John's wort and hypericin on monoamine levels in rat hypothalamus and hippocampus. Brain Res 930:21–29
Chakrabarti SK, Loua KM, Bai CJ, Durham H, Panisset JC (1998) Modulation of monoamine oxidase activity in different brain regions and platelets following exposure of rats to methylmercury. Neurotoxicol Teratol 20:161–168
Das U, Manna K, Sinha M, Datta S, Das DK, Chakraborty A, Ghosh M, Saha KD, Dey S (2014) Role of ferulic acid in the amelioration of ionizing radiation induced inflammation: a murine model. PLoS One 9:e97599
Elliott PJ, Jirousek M (2008) Sirtuins: novel targets for metabolic disease. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 9:371–378
Hamon M, Blier P (2013) Monoamine neurocircuitry in depression and strategies for new treatments. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 45:54–63
Huang W, Chen Z, Wang Q, Lin M, Wu S, Yan Q, Wu F, Yu X, Xie X, Li G, Xu Y, Pan J (2013) Piperine potentiates the antidepressant-like effect of trans-resveratrol: involvement of monoaminergic system. Metab Brain Dis 28:585–595
Johnson JJ, Nihal M, Siddiqui IA, Scariett CO, Bailey HH, Mukhtar H, Ahmad N (2011) Enhancing the bioavailability of resveratrol by combining it with piperine. Nutr Food Res 55:169–176
Kwon S, Lee B, KimM LH, Park HJ, Hahm DH (2010) Antidepressant like effect of the methanolic extract from bupleurum falcatum in the tail suspension test. Progr Neuro Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 34:265–270
Lam RW, Wan DD, Cohen NL, Kennedy SH (2002) Cobining antidepressants for treatment-resistant depression: a review. J Clin Psychiatr 63:685–693
Lopez JP, Lim R, Cruceanu C, Crapper L, Fasano C, Labonte B, Maussion G, Yang JP, Yerko V, Vigneault E, El Mestikawy S, Mechawar N, Pavlidis P, Turecki G (2014) miR-1202 is a primate-specific and brain-enriched microRNA involved in major depression andantidepressant treatment. Nat Med In press
Muralidhara KMDJ (2014) Neuroprotective efficacy of a combination of fish oil and ferulic acid against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in rats: behavioural and biochemical evidence. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 39:487–496
Ogiwara T, Satoh K, Kadoma Y, Murakami Y, Unten S, Atsumi T, Sakagami H, Fujisawa S (2002) Radical scavenging activity and cytotoxicity of ferulic acid. Anticancer Res 22:2711–2717
Ota KT, Liu RJ, Voleti B, Maldonado-Aviles JG, Duric V, Iwata M, Dutheil S, Duman C, Boikess S, Lewis DA, Stockmeier CA, Dileone RJ, Rex C, Aghajanian GK, Duman RS (2014) REDD1 is essential for stress-induced synaptic loss and depressive behavior. Nat Med 20:531–535
Rinwa P, Kumar A, Garg S (2013) Suppression of neuroinflammatory andapoptotic signaling cascade by curcumin alone and in combination with piperine in rat model of olfactory bulbectomy induced depression. PLoS One 8:e61052
Rubio G, San L, Lopez-Munoz F, Alamo C (2004) Reboxetine adjunct for partial or nonresponders to antidepressant treatment. J Affect Disord 81:67–72
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P (1985) The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 85:367–370
Wang BH, Ou-Yang JP (2005) Pharmacological actions of sodium ferulate in cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 23:161–172
Xu Y, Ku BS, Yao HY, Lin YH, Ma X, Zhang YH, Li XJ (2005) Antidepressant effects of curcumin in the forced swim test and olfactory bulbectomy models of depression in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82:200–206
Xu Y, Li S, Chen RJ, Li GW, Barish PA, You WT, Chen L, Lin MM, Ku BS, Pan JC, Ogle W (2010) Antidepressant-like effect of low molecular proanthocyanidin in mice: involvement of monoaminergic system. Pharm. Biochem. Behav 94:447–453
Xu Y, Zhang L, Shao T, Ruan L, Wang L, Sun J, Li JX, Zhu X, O’Donnell JM, Pan JC (2013) Ferulic acid increases pain threshold and ameliorates depression-like behaviors in reserpine-treated mice: behavioral and neurobiological analyses. Metab Brain Dis 28:571–583
Yu YL, Wang R, Chen C, Du X, Ruan L, Sun J, Li JX, Zhang L, O’Donnell JM, Pan JC, Xu Y (2013) Antidepressant-like effect of trans-resveratrol in chronic stress model: behavioral and neurochemical evidences. J. Psychia. Res 47:315–322
Zhang L, Wang QD, Shi HM, Pan JC (2013) Influence of ferulic acid on the pain-depression dyad induced by reserpine. Yao Xue Xue Bao 48:32–37
Zhang Y, Huang X, Wang Y, Xie Y, Qiu X (2011) Ferulic acid-induced anti-depression and prokinetics similar to chaihu-shugan-San via polypharmacology. Brain Res Bull 86:222–228
Acknowledgments
G.W. Li, L.N. Ruan, R.J. Chen and R.Y. Wang contributed equally to this work. This work was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo (No. 2012A610256; 2014A610256), 2015 Zhejiang provincial Public Welfare Technology Application Research Plan (2015C33297), and Ministry of Science and Technology Spark Plan (2014GA701011) for G.W. Li.; The Natural Science Foundation of Changzhou (No. ZD2O1413) for Dr. W. Huang; The National Institute of General Medical Sciences (Reed - U54GM104942) for Dr. M. Reed. Zhejiang Province Extremely Key Subject Building Funding “Pharmacology and Biochemical Pharmaceutics 2008”, Latitudinal project of Wenzhou Medical University (No. 95012011) and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. Y14H310034) for Professor J. C. Pan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Ruan, L., Chen, R. et al. Synergistic antidepressant-like effect of ferulic acid in combination with piperine: involvement of monoaminergic system. Metab Brain Dis 30, 1505–1514 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9704-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9704-y