Abstract
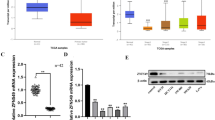
Receptor interacting protein serine/threonine kinase 4 (RIPK4) is widely involved in human cancer development. Nevertheless, its role in colon cancer (COAD) has not been elucidated till now. Our research aimed at exploring the function and underlying molecular mechanism of RIPK4 in COAD progression. Through bioinformatic analyses and RT-qPCR, RIPK4 was discovered to be increased in COAD cells and tissues, and its high level predicted poor prognosis. Loss-of-function assays revealed that RIPK4 silencing suppressed COAD cell growth, induced cell cycle arrest, and enhanced cell apoptosis. In vivo experiments also proved that tumor growth was inhibited by silencing of RIPK4. Luciferase reporter assay validated that RIPK4 was targeted and negatively regulated by miR-575. Western blotting demonstrated that Wnt3a, phosphorylated (p)-GSK-3β, and cytoplasmic and nuclear β-catenin protein levels, β-catenin nuclear translocation, and Cyclin D1, CDK4, Cyclin E, and c-Myc protein levels were reduced by RIPK4 knockdown, which however was reversed by treatment with LiCl, the Wnt/β-catenin pathway activator. LiCl also offset the influence of RIPK4 knockdown on COAD cell growth, cell cycle process, and apoptosis. Finally, RIPK4 downregulation reduced RUNX1 level, which was upregulated in COAD and its high level predicted poor prognosis. RIPK4 is positively associated with RUNX1 in COAD. Overexpressing RUNX1 antagonized the suppression of RIPK4 knockdown on RUNX1, Wnt3a, p-GSK-3β, cytoplasmic β-catenin, nuclear β-catenin, Cyclin D1, CDK4, Cyclin E, and c-Myc levels. Collectively, miR-575/RIPK4 axis repressed COAD progression via inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway through downregulating RUNX1.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sung H et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Riihimäki M et al (2016) Patterns of metastasis in colon and rectal cancer. Sci Rep 6:29765
Chiang AC, Massagué J (2008) Molecular basis of metastasis. N Engl J Med 359(26):2814–2823
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA (2011) Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 147(2):275–292
Shinji S et al (2022) Recent advances in the treatment of colorectal cancer: a review. J Nippon Med Sch 89(3):246–254
Tanghe G et al (2018) RIPK4 activity in keratinocytes is controlled by the SCF(β-TrCP) ubiquitin ligase to maintain cortical actin organization. Cell Mol Life Sci 75(15):2827–2841
Xu J, Wei Q, He Z (2020) Insight into the function of RIPK4 in keratinocyte differentiation and carcinogenesis. Front Oncol 10:1562
Liu S et al (2021) Overexpression of RIPK4 predicts poor prognosis and promotes metastasis in ovarian cancer. Biomed Res Int 2021:6622439
Qi ZH et al (2018) RIPK4/PEBP1 axis promotes pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion by activating RAF1/MEK/ERK signaling. Int J Oncol 52(4):1105–1116
Li H et al (2021) RIPK4 suppresses the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the phosphorylation of STAT3. Front Mol Biosci 8:654766
Wang X et al (2014) RIPK4 is downregulated in poorly differentiated tongue cancer and is associated with migration/invasion and cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Int J Biol Markers 29(2):e150–e159
Huang X et al (2013) Phosphorylation of Dishevelled by protein kinase RIPK4 regulates Wnt signaling. Science 339(6126):1441–1445
Nusse R, Clevers H (2017) Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 169(6):985–999
Steinhart Z, Angers S (2018) Wnt signaling in development and tissue homeostasis. Development 145(11):dev146589
Koni M, Pinnarò V, Brizzi MF (2020) The Wnt signalling pathway: a tailored target in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21(20):7697
Peng K et al (2015) Association between RIPK4 relative copy number and prognosis of colorectal cancer patient after oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi 18(11):1111–1114
Stuckel AJ et al (2022) Aberrant regulation of CXCR4 in cancer via deviant microRNA-targeted interactions. Epigenetics 17(13):2318–2331
Yang Y, Meng WJ, Wang ZQ (2020) MicroRNAs in colon and rectal cancer—novel biomarkers from diagnosis to therapy. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 20(8):1211–1226
Backes C, Meese E, Keller A (2016) Specific miRNA disease biomarkers in blood, serum and plasma: challenges and prospects. Mol Diagn Ther 20(6):509–518
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(3):203–222
Chen W et al (2019) miRNA-766 induces apoptosis of human colon cancer cells through the p53/Bax signaling pathway by MDM4. Exp Ther Med 17(5):4100–4108
Wei L et al (2022) miR-503-5p inhibits colon cancer tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, and lymphangiogenesis by directly downregulating VEGF-A. Gene Ther 29(1–2):28–40
Zhang W et al (2018) miRNA-185 serves as a prognostic factor and suppresses migration and invasion through Wnt1 in colon cancer. Eur J Pharmacol 825:75–84
Zhao J et al (2018) Overexpression of miRNA-143 inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting glucose uptake. Arch Med Res 49(7):497–503
Zhao X et al (2019) MiRNA-575 suppresses angiogenesis by targeting Rab5-MEK-ERK pathway in endothelial cells. Biosci Rep 39(1):BSR20181218
Wei G et al (2022) Altered expression of miR-575 in glioma is related to tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Neuromol Med 24(2):224–231
Gray A et al (2022) MicroRNA-575 acts as a novel oncogene via targeting multiple signaling pathways in glioblastoma. Exp Mol Pathol 128:104813
Feng W et al (2020) Long non-coding RNA LINC00115 contributes to the progression of colorectal cancer by targeting miR-489-3p via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Front Genet 11:567630
Li Q et al (2019) RUNX1 promotes tumour metastasis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and EMT in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):334
Liu JY et al (2018) RIPK4 promotes bladder urothelial carcinoma cell aggressiveness by upregulating VEGF-A through the NF-κB pathway. Br J Cancer 118(12):1617–1627
Liu DQ et al (2015) Increased RIPK4 expression is associated with progression and poor prognosis in cervical squamous cell carcinoma patients. Sci Rep 5:11955
Jin A et al (2022) Receptor interacting protein kinase 4 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in ovarian cancer via targeting protein kinase C delta. Drug Dev Res 83(2):407–415
Kopparam J et al (2017) RIP4 inhibits STAT3 signaling to sustain lung adenocarcinoma differentiation. Cell Death Differ 24(10):1761–1771
Poligone B et al (2015) PKK suppresses tumor growth and is decreased in squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. J Invest Dermatol 135(3):869–876
Lin S, Gregory RI (2015) MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 15(6):321–333
Cai L et al (2021) MicroRNA miR-330-3p suppresses the progression of ovarian cancer by targeting RIPK4. Bioengineered 12(1):440–449
Qin Y et al (2020) Downregulation of miR-575 inhibits the tumorigenesis of gallbladder cancer via targeting p27 Kip1. Onco Targets Ther 13:3667–3676
Liu SS et al (2020) The ERα-miR-575-p27 feedback loop regulates tamoxifen sensitivity in ER-positive breast cancer. Theranostics 10(23):10729–10742
Wang YN et al (2019) MicroRNA-575 regulates development of gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Biomed Pharmacother 113:108716
Yan S et al (2018) Long noncoding RNA MIR31HG inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by sponging microRNA-575 to modulate ST7L expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):214
Nakamura BN et al (2018) A20 regulates canonical Wnt-signaling through an interaction with RIPK4. PLoS ONE 13(5):e0195893
Zou L, Liu J, Lu H (2018) Influence of protein kinase RIPK4 expression on the apoptosis and proliferation of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep 17(2):3078–3084
Olmeda D et al (2003) Beta-catenin regulation during the cell cycle: implications in G2/M and apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 14(7):2844–2860
Kikuchi A, Kishida S, Yamamoto H (2006) Regulation of Wnt signaling by protein-protein interaction and post-translational modifications. Exp Mol Med 38(1):1–10
Polakis P (2012) Wnt signaling in cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4(5):a008052
Brabletz T et al (2000) Expression of nuclear beta-catenin and c-myc is correlated with tumor size but not with proliferative activity of colorectal adenomas. Am J Pathol 156(3):865–870
Wang J et al (2020) Cinobufacini inhibits colon cancer invasion and metastasis via suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and EMT. Am J Chin Med 48(3):703–718
Yu J et al (2019) CDX2 inhibits the proliferation and tumor formation of colon cancer cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling via transactivation of GSK-3β and Axin2 expression. Cell Death Dis 10(1):26
Yi Z et al (2020) Silencing of RIPK4 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition by inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in osteosarcoma. Mol Med Rep 21(3):1154–1162
Ito Y, Bae SC, Chuang LS (2015) The RUNX family: developmental regulators in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 15(2):81–95
Choi A et al (2017) RUNX1 is required for oncogenic Myb and Myc enhancer activity in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 130(15):1722–1733
Scheitz CJ et al (2012) Defining a tissue stem cell-driven Runx1/Stat3 signalling axis in epithelial cancer. Embo J 31(21):4124–4139
Keita M et al (2013) The RUNX1 transcription factor is expressed in serous epithelial ovarian carcinoma and contributes to cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Cell Cycle 12(6):972–986
Wu H et al (2015) LincRNA-uc002yug.2 involves in alternative splicing of RUNX1 and serves as a predictor for esophageal cancer and prognosis. Oncogene 34(36):4723–4734
Barutcu AR et al (2016) RUNX1 contributes to higher-order chromatin organization and gene regulation in breast cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1859(11):1389–1397
Mitsuda Y et al (2018) RUNX1 positively regulates the ErbB2/HER2 signaling pathway through modulating SOS1 expression in gastric cancer cells. Sci Rep 8(1):6423
Zhuang M et al (2014) The long non-coding RNA H19-derived miR-675 modulates human gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting tumor suppressor RUNX1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 448(3):315–322
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate all the participants providing supports for this study.
Funding
Our project was supported by Health commission of Hubei Province scientific Research Project: WJ2019H129; Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province: 2019CFB640; Research Projects of Biomedical Center of Hubei Cancer Hospital: 2022SWZX, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qun Wang was the main designer of this study. Qun Wang, Weijun Lu, Li Lu, and Dongde Wu performed the experiments and analyzed the data. Qun Wang, Weijun Lu, Ruopu Wu, and Dongde Wu drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hubei Cancer Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology. The animal studies were authorized by the Hubei Cancer Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology Animal Care and Use Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Lu, W., Lu, L. et al. miR-575/RIPK4 axis modulates cell cycle progression and proliferation by inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through inhibiting RUNX1 in colon cancer. Mol Cell Biochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-024-04938-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-024-04938-w