Abstract
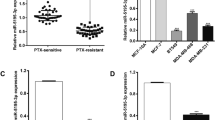
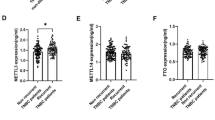
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most lethal subtype of BC, with unfavorable treatment outcomes. Evidence suggests the engagement of lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 in BC development. This study investigated the action of MCM3AP-AS1 in chemoresistance of TNBC cells. Drug-resistant TNBC cell lines SUM159PTR and MDA-MB-231R were constructed by exposure to increasing concentrations of doxorubicin/docetaxel (DOX/DXL). MCM3AP-AS1 and miR-524-5p expression levels were determined by RT-qPCR. RNA binding motif 39 (RBM39) level was measured using Western blot. Cell viability and apoptosis were assessed by CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry. The targeted binding of miR-524-5p with MCM3AP-AS1 or RBM39 was predicted by ECORI database and validated by dual-luciferase assays. The gain-and-loss of function assays were conducted in cells to investigate the interactions among MCM3AP-AS1, miR-524-5p, and RBM39. TNBC xenograft mouse models were established through subcutaneous injection of MCM3AP-AS1-silencing MDA-MB-231R cells and intraperitoneally administrated with DOX/DXL to verify the role of MCM3AP-AS1 in vivo. MCM3AP-AS1 was upregulated in drug-resistant TNBC cells, and MCM3AP-AS1 silencing could sensitize drug-resistant TNBC cells to chemotherapeutic drugs by promoting apoptosis. MCM3AP-AS1 targeted miR-524-5p. After DOX/DXL treatment, miR-524-5p inhibition partially reversed the effect of MCM3AP-AS1 silencing on inhibiting chemoresistance and promoting apoptosis of drug-resistant TNBC cells. miR-524-5p targeted RBM39. Silencing MCM3AP-AS1 promoted apoptosis via the miR-524-5p/RBM39 axis, thereby enhancing chemosensitivity of drug-resistant TNBC cells. MCM3AP-AS1 knockdown upregulated miR-524-5p, downregulated RBM39, and restrained tumor development in vivo. MCM3AP-AS1 silencing potentiates apoptosis of drug-resistant TNBC cells by upregulating miR-524-5p and downregulating RBM39, thereby suppressing chemoresistance in TNBC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Waks AG, Winer EP (2019) Breast cancer treatment: a review. JAMA 321:288–300. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.19323
da Silva JL, Cardoso Nunes NC, Izetti P, de Mesquita GG, de Melo AC (2020) Triple negative breast cancer: a thorough review of biomarkers. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 145:102855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.102855
Nedeljkovic M, Damjanovic A (2019) Mechanisms of chemotherapy resistance in triple-negative breast cancer-how we can rise to the challenge. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8090957
Garrido-Castro AC, Lin NU, Polyak K (2019) Insights into molecular classifications of triple-negative breast cancer: improving patient selection for treatment. Cancer Discov 9:176–198. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1177
Bridges MC, Daulagala AC, Kourtidis A (2021) LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function. J Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202009045
Tan YT, Lin JF, Li T, Li JJ, Xu RH, Ju HQ (2021) LncRNA-mediated posttranslational modifications and reprogramming of energy metabolism in cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond) 41:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1002/cac2.12108
Zhang W, Guan X, Tang J (2021) The long non-coding RNA landscape in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Prolif 54:e12966. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12966
Azizidoost S, Ghaedrahmati F, Sheykhi-Sabzehpoush M, Uddin S, Ghafourian M, Mousavi Salehi A, Keivan M, Cheraghzadeh M, Nazeri Z, Farzaneh M, Khoshnam SE (2023) The role of LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 in human cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 25:33–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02904-w
Xu S, Kong D, Chen Q, Ping Y, Pang D (2017) Oncogenic long noncoding RNA landscape in breast cancer. Mol Cancer 16:129. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0696-6
Thomson DW, Dinger ME (2016) Endogenous microRNA sponges: evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet 17:272–283. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.20
Venkatesh J, Wasson MD, Brown JM, Fernando W, Marcato P (2021) LncRNA-miRNA axes in breast cancer: novel points of interaction for strategic attack. Cancer Lett 509:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2021.04.002
Jin T, Zhang Y, Zhang T (2020) MiR-524-5p suppresses migration, invasion, and EMT progression in breast cancer cells through targeting FSTL1. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 35:789–801. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2019.3046
Tian Q, Lu Y, Yan B, Wu C (2022) Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals that miR-524-5p/MEF2C regulates bone metastasis in prostate cancer and breast cancer. Comput Math Methods Med 2022:5211329. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5211329
Xu Y, Nijhuis A, Keun HC (2022) RNA-binding motif protein 39 (RBM39): an emerging cancer target. Br J Pharmacol 179:2795–2812. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15331
Puvvula PK, Yu Y, Sullivan KR, Eyob H, Rosenberg J, Welm A, Huff C, Moon AM (2021) Inhibiting an RBM39/MLL1 epigenomic regulatory complex with dominant-negative peptides disrupts cancer cell transcription and proliferation. Cell Rep 35:109156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109156
Ogbu SC, Rojas S, Weaver J, Musich PR, Zhang J, Yao ZQ, Jiang Y (2021) DSTYK enhances chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010097
Pan X, Hong X, Li S, Meng P, Xiao F (2021) METTL3 promotes adriamycin resistance in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by accelerating pri-microRNA-221-3p maturation in a m6A-dependent manner. Exp Mol Med 53:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-00510-w
Xia M, Zu X, Chen Z, Wen G, Zhong J (2021) Noncoding RNAs in triple negative breast cancer: mechanisms for chemoresistance. Cancer Lett 523:100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2021.09.038
Hermawan A, Putri H (2020) Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals miR-494 and its target genes as predictive biomarkers of trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 32:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43046-020-00028-2
Derakhshan F, Reis-Filho JS (2022) Pathogenesis of triple-negative breast cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 17:181–204. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-042420-093238
Barzaman K, Karami J, Zarei Z, Hosseinzadeh A, Kazemi MH, Moradi-Kalbolandi S, Safari E, Farahmand L (2020) Breast cancer: biology, biomarkers, and treatments. Int Immunopharmacol 84:106535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106535
Liu Y, Teng L, Fu S, Wang G, Li Z, Ding C, Wang H, Bi L (2021) Highly heterogeneous-related genes of triple-negative breast cancer: potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. BMC Cancer 21:644. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-021-08318-1
Zhang X, Xie K, Zhou H, Wu Y, Li C, Liu Y, Liu Z, Xu Q, Liu S, Xiao D, Tao Y (2020) Role of non-coding RNAs and RNA modifiers in cancer therapy resistance. Mol Cancer 19:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01171-z
Qiao Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Tang Y, Feng R, Pang W (2022) Tamoxifen resistance-related ceRNA network for breast cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:1023079. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.1023079
Tang TP, Qin CX, Yu H (2021) MCM3AP-AS1 regulates proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells via binding with ZFP36. Transl Cancer Res 10:4478–4488. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr-21-1940
Riahi A, Hosseinpour-Feizi M, Rajabi A, Akbarzadeh M, Montazeri V, Safaralizadeh R (2021) Overexpression of long non-coding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 in breast cancer tissues compared to adjacent non-tumour tissues. Br J Biomed Sci 78:53–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/09674845.2020.1798058
Ren G, Han G, Song Z, Zang A, Liu B, Hu L, Jia L, Hong D, Yang L, Qie S (2021) LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 downregulates LncRNA MEG3 in triple negative breast cancer to inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 31:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2021038296
Taheri M, Shoorei H, Tondro Anamag F, Ghafouri-Fard S, Dinger ME (2021) LncRNAs and miRNAs participate in determination of sensitivity of cancer cells to cisplatin. Exp Mol Pathol 123:104602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2021.104602
Sun H, Wu P, Zhang B, Wu X, Chen W (2021) MCM3AP-AS1 promotes cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells via the miR-138/FOXC1 axis. Oncol Lett 21:211. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2021.12472
Guo C, Gong M, Li Z (2020) Knockdown of lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 attenuates chemoresistance of burkitt lymphoma to doxorubicin treatment via targeting the miR-15a/EIF4E axis. Cancer Manag Res 12:5845–5855. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S248698
Thakur KK, Kumar A, Banik K, Verma E, Khatoon E, Harsha C, Sethi G, Gupta SC, Kunnumakkara AB (2021) Long noncoding RNAs in triple-negative breast cancer: a new frontier in the regulation of tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol 236:7938–7965. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30463
Han J, Han B, Wu X, Hao J, Dong X, Shen Q, Pang H (2018) Knockdown of lncRNA H19 restores chemo-sensitivity in paclitaxel-resistant triple-negative breast cancer through triggering apoptosis and regulating Akt signaling pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 359:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.09.018
Adorno-Cruz V, Hoffmann AD, Liu X, Dashzeveg NK, Taftaf R, Wray B, Keri RA, Liu H (2021) ITGA2 promotes expression of ACLY and CCND1 in enhancing breast cancer stemness and metastasis. Genes Dis 8:493–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2020.01.015
Miyamoto M, Sawada K, Nakamura K, Yoshimura A, Ishida K, Kobayashi M, Shimizu A, Yamamoto M, Kodama M, Hashimoto K, Kimura T (2020) Paclitaxel exposure downregulates miR-522 expression and its downregulation induces paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep 10:16755. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73785-8
Bai X, Zhang S, Qiao J, Xing X, Li W, Zhang H, Xie J (2021) Long non-coding RNA SChLAP1 regulates the proliferation of triple negative breast cancer cells via the miR-524-5p/HMGA2 axis. Mol Med Rep. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.12085
Xie H, Yao J, Wang Y, Ni B (2022) Exosome-transmitted circVMP1 facilitates the progression and cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-524-5p-METTL3/SOX2 axis. Drug Deliv 29:1257–1271. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2022.2057617
Yin H, Cui X (2021) Knockdown of circHIPK3 facilitates temozolomide sensitivity in glioma by regulating cellular behaviors through miR-524-5p/KIF2A-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 36:556–567. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2020.3575
Li Z, Li Y, Wang X, Liang Y, Luo D, Han D, Li C, Chen T, Zhang H, Liu Y, Wang Z, Chen B, Wang L, Zhao W, Yang Q (2021) LINC01977 promotes breast cancer progression and chemoresistance to doxorubicin by targeting miR-212-3p/GOLM1 axis. Front Oncol 11:657094. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.657094
Zhang L, Zheng X, Shen A, Hua D, Zhu P, Li C, Han Z (2022) Long noncoding RNA RP11-70C1.3 confers chemoresistance of breast cancer cells through miR-6736-3p/NRP-1 axis. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 22:87–99. https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2021.5803
Chilewski SD, Bhosale D, Dees S, Hutchinson I, Trimble R, Pontiggia L, Mercier I, Jasmin JF (2020) Development of CAPER peptides for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Cell Cycle 19:432–447. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2020.1711579
Lemaitre F, Chakrama F, O’Grady T, Peulen O, Rademaker G, Deward A, Chabot B, Piette J, Colige A, Lambert C, Dequiedt F, Habraken Y (2022) The transcription factor c-Jun inhibits RBM39 to reprogram pre-mRNA splicing during genotoxic stress. Nucleic Acids Res 50:12768–12789. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1130
Pogacar Z, Groot K, Jochems F, Dos Santos Dias M, Mulero-Sanchez A, Morris B, Roosen M, Wardak L, De Conti G, Velds A, Lieftink C, Thijssen B, Beijersbergen RL, Bernards R, Leite de Oliveira R (2022) Genetic and compound screens uncover factors modulating cancer cell response to indisulam. Life Sci Alliance. https://doi.org/10.26508/lsa.202101348
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was partially supported by grants from the Major Project in Natural Science Research in Higher Education Institutions of Anhui Province, Grant/Award Number: 2023AH040393.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YPW is the guarantor of integrity of the entire study and contributed to the statistical analysis; YPW, HYS contributed to the study concepts, manuscript editing; XDW contributed to the study design, literature research, manuscript review; ZYZ, HYS contributed to the definition of intellectual content; ZYZ, JG contributed to the experimental studies, manuscript preparation; JG, XDW contributed to the data acquisition; YPW, ZYZ contributed to the data analysis; All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interests in this study.
Ethical approval
All animal experimental procedures were ratified by the Research Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University and conducted in strict accordance with the National Guide for Laboratory Animals(Approval number: LLSC20220982). Considerable efforts were made to minimize the animal amount and their suffering.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2023_4908_MOESM1_ESM.tiff
Figure S1 Knockdown of miR-524-5p increased the drug resistance of SUM159PT and MDA-MB-231. RT-qPCR to determine miR-524-5p expression in A SUM159PT and B MDA-MB-231 cells; Flow cytometry to assess apoptosis in C SUM159PT and D MDA-MB-231 cells with or without DOX/DXL treatment; CCK-8 to evaluate E SUM159PT and F MDA-MB-231 cell viability. The cellular experiments were repeated three times. Data were expressed as mean ± SD, and one-way ANOVA was utilized for comparisons among multiple groups, followed by Tukey’s test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01
Supplementary file1 (TIFF 9940 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, X., Sun, H. et al. LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer through the miR-524-5p/RBM39 axis. Mol Cell Biochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04908-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04908-8