Abstract
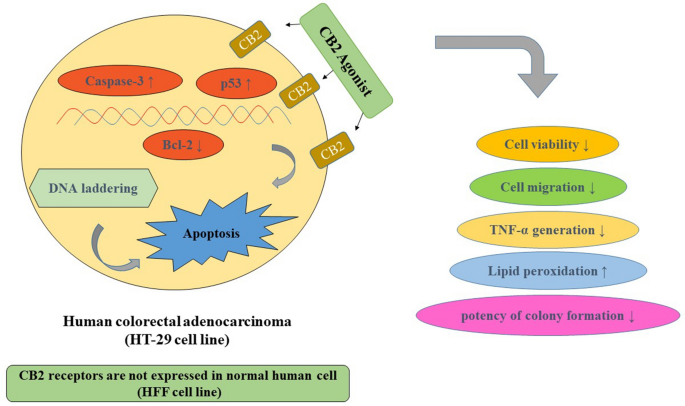
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is between the top three occurring cancers worldwide. The anticancer effects of Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) agonist (GW833972A) in the presence and absence of its inverse agonist (SR144528) on Human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells (HT-29) was investigated. Following cell viability assays on HT-29 and HFF cells, the molecular mechanism(s) of cytotoxicity and apoptotic pathways of cell death were analyzed. The anticancer effects of CB2 agonist were measured with tumor cell migration and colony-forming assays. Real-time PCR and Western blotting techniques were used to examine any alterations in the expression of apoptotic genes. A concentration and time-dependent cytotoxicity of CB2 agonist with IC50 value of 24.92 ± 6.99 μM was obtained. The rate of lipid peroxidation was elevated, while the TNF-α concentration was declined, significantly (p < 0.05). CB2 agonist (50 μM) reduced the colony-forming capability by 83% and tumor cell migration by 50%. Apoptotic effects of CB2 agonist were revealed with the increase of apoptotic cells in Acridine orange/Ethidium bromide staining, clear DNA fragmentation, pro-apoptotic genes and proteins upregulation (Caspase-3 and p53), and significant downregulation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2. All assessments demonstrated that CB2 agonist-induced effects were reversed by CB2 inverse agonist. These data suggest that CB2 agonists at micro-molar concentrations might be considered in the CRC treatment, and their effectiveness attributes to the apoptosis induction via upregulation of caspase-3 and p53 and downregulation of Bcl-2.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424
Grady WM, Markowitz SD (2015) The molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer and its potential application to colorectal cancer screening. Dig Dis Sci 60:762–772
Marco DJT, White VM (2019) The impact of cancer type, treatment, and distress on health-related quality of life: cross-sectional findings from a study of Australian cancer patients. Support Care Cancer 27:3421–3429
Gustavsson B, Carlsson G, Machover D, Petrelli N, Roth A, Schmoll HJ et al (2015) A review of the evolution of systemic chemotherapy in the management of colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 14:1–10
Abalo R, Uranga JA, Pérez-García I, de Andrés R, Girón R, Vera G et al (2017) May cannabinoids prevent the development of chemotherapy-induced diarrhea and intestinal mucositis? Experimental study in the rat. Neurogastroenterol Motil 29:e12952
Bar-Lev Schleider L, Mechoulam R, Lederman V, Hilou M, Lencovsky O, Betzalel O et al (2018) Prospective analysis of safety and efficacy of medical cannabis in large unselected population of patients with cancer. Eur J Intern Med 49:37–43
Fraguas-Sánchez AI, Fernández-Carballido A, Torres-Suárez AI (2016) Phyto-, endo- and synthetic cannabinoids: promising chemotherapeutic agents in the treatment of breast and prostate carcinomas. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 25:1311–1323
Javid FA, Phillips RM, Afshinjavid S, Verde R, Ligresti A (2016) Cannabinoid pharmacology in cancer research: A new hope for cancer patients? Eur J Pharmacol 775:1–14
Blázquez C, Carracedo A, Barrado L, Real PJ, Fernández-Luna JL, Velasco G et al (2006) Cannabinoid receptors as novel targets for the treatment of melanoma. FASEB j 20:2633–2635
Casanova ML, Blázquez C, Martínez-Palacio J, Villanueva C, Fernández-Aceñero MJ, Huffman JW et al (2003) Inhibition of skin tumor growth and angiogenesis in vivo by activation of cannabinoid receptors. J Clin Invest 111:43–50
Cianchi F, Papucci L, Schiavone N, Lulli M, Magnelli L, Vinci MC et al (2008) Cannabinoid receptor activation induces apoptosis through tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated ceramide de novo synthesis in colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 14:7691–7700
Galve-Roperh I, Sánchez C, Cortés ML, del Pulgar TG, Izquierdo M, Guzmán M (2000) Anti-tumoral action of cannabinoids: involvement of sustained ceramide accumulation and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Nat Med 6:313–319
Pacher P, Bátkai S, Kunos G (2006) The endocannabinoid system as an emerging target of pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Rev 58:389–462
Sánchez C, de Ceballos ML, del Pulgar TG, Rueda D, Corbacho C, Velasco G et al (2001) Inhibition of glioma growth in vivo by selective activation of the CB(2) cannabinoid receptor. Cancer Res 61:5784–5789
Chen L, Chen H, Li Y, Li L, Qiu Y, Ren J (2015) Endocannabinoid and ceramide levels are altered in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 34:447–454
Martínez-Martínez E, Gómez I, Martín P, Sánchez A, Román L, Tejerina E et al (2015) Cannabinoids receptor type 2, CB2, expression correlates with human colon cancer progression and predicts patient survival. Oncoscience 2:131–141
Wright K, Rooney N, Feeney M, Tate J, Robertson D, Welham M et al (2005) Differential expression of cannabinoid receptors in the human colon: cannabinoids promote epithelial wound healing. Gastroenterology 129:437–453
Martínez-Martínez E, Martín-Ruiz A, Martín P, Calvo V, Provencio M, García JM (2016) CB2 cannabinoid receptor activation promotes colon cancer progression via AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Oncotarget 7:68781–68791
Belvisi MG, Patel HJ, Freund-Michel V, Hele DJ, Crispino N, Birrell MA (2008) Inhibitory activity of the novel CB2 receptor agonist, GW833972A, on guinea-pig and human sensory nerve function in the airways. Br J Pharmacol 155:547–557
Tham M, Yilmaz O, Alaverdashvili M, Kelly MEM, Denovan-Wright EM, Laprairie RB (2019) Allosteric and orthosteric pharmacology of cannabidiol and cannabidiol-dimethylheptyl at the type 1 and type 2 cannabinoid receptors. Br J Pharmacol 176:1455–1469
Pyszniak M, Tabarkiewicz J, Łuszczki JJ (2016) Endocannabinoid system as a regulator of tumor cell malignancy - biological pathways and clinical significance. Onco Targets Ther 9:4323–4336
Niehaus WG Jr, Samuelsson B (1968) Formation of malonaldehyde from phospholipid arachidonate during microsomal lipid peroxidation. Eur J Biochem 6:126–130
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Liang CC, Park AY, Guan JL (2007) In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc 2:329–333
Franken NAP, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman J, van Bree C (2006) Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc 1:2315–2319
Gherghi ICh, Girousi ST, Voulgaropoulos AN, Tzimou-Tsitouridou R (2003) Study of interactions between DNA-ethidium bromide (EB) and DNA-acridine orange (AO), in solution, using hanging mercury drop electrode (HMDE). Talanta 61:103–112
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (2006) The single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction: twenty-something years on. Nat Protoc 1:581–585
Howlett AC, Barth F, Bonner TI, Cabral G, Casellas P, Devane WA et al (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors Pharmacol Rev 54:161–202
Greenhough A, Patsos HA, Williams AC, Paraskeva C (2007) The cannabinoid delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol inhibits RAS-MAPK and PI3K-AKT survival signalling and induces BAD-mediated apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer 121:2172–2180
Ihenetu K, Molleman A, Parsons ME, Whelan CJ (2003) Inhibition of interleukin-8 release in the human colonic epithelial cell line HT-29 by cannabinoids. Eur J Pharmacol 458:207–215
Ligresti A, Bisogno T, Matias I, De Petrocellis L, Cascio MG, Cosenza V et al (2003) Possible endocannabinoid control of colorectal cancer growth. Gastroenterology 125:677–687
Wright KL, Duncan M, Sharkey KA (2008) Cannabinoid CB2 receptors in the gastrointestinal tract: a regulatory system in states of inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 153:263–270
Khan MI, Sobocińska AA, Brodaczewska KK, Zielniok K, Gajewska M, Kieda C et al (2018) Involvement of the CB(2) cannabinoid receptor in cell growth inhibition and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest via the cannabinoid agonist WIN 55,212–2 in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 18:583
Wang F, Wang J, Zhao T, Zhang Y, Li Q (2019) CB2 receptor agonist JWH133 activates AMPK to inhibit growth of C6 glioma cells. Open Life Sci 14:363–375
Capozzi A, Mattei V, Martellucci S, Manganelli V, Saccomanni G, Garofalo T et al (2018) Anti-Proliferative Properties and Proapoptotic Function of New CB2 Selective Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist in Jurkat Leukemia Cells. Int J Mol Sci 19:1985
Ramer R, Hinz B (2008) Inhibition of cancer cell invasion by cannabinoids via increased expression of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases-1. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:59–69
Baram L, Peled E, Berman P, Yellin B, Besser E, Benami M et al (2019) The heterogeneity and complexity of Cannabis extracts as antitumor agents. Oncotarget 10:4091–4106
Jeong HJ, Kim SJ, Moon PD, Kim NH, Kim JS, Park RK et al (2007) Antiapoptotic mechanism of cannabinoid receptor 2 agonist on cisplatin-induced apoptosis in the HEI-OC1 auditory cell line. J Neurosci Res 85:896–905
Li Q, Wang F, Zhang YM, Zhou JJ, Zhang Y (2013) Activation of cannabinoid type 2 receptor by JWH133 protects heart against ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem 31:693–702
Rieder SA, Chauhan A, Singh U, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti P (2010) Cannabinoid-induced apoptosis in immune cells as a pathway to immunosuppression. Immunobiology 215:598–605
Sritharan S, Sivalingam N (2021) Curcumin induced apoptosis is mediated through oxidative stress in mutated p53 and wild type p53 colon adenocarcinoma cell lines. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 35:e22616
Jiang R, Lönnerdal B (2017) Bovine lactoferrin and lactoferricin exert antitumor activities on human colorectal cancer cells (HT-29) by activating various signaling pathways. Biochem Cell Biol 95:99–109
Turcotte C, Blanchet MR, Laviolette M, Flamand N (2016) The CB(2) receptor and its role as a regulator of inflammation. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:4449–4470
Becker WJ, Alrafas H, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti PS (2019) Cannabinoids decrease intestinal permeability and induce colonic CD103+ dendritic cells to increase T regulatory cells leading to decreased murine colitis-associated colon cancer. J Immunol 202(135):18
Ladin DA, Soliman E, Griffin L, Van Dross R (2016) Preclinical and Clinical Assessment of Cannabinoids as Anti-Cancer Agents. Front Pharmacol 7:361
Duncan M, Mouihate A, Mackie K, Keenan CM, Buckley NE, Davison JS et al (2008) Cannabinoid CB2 receptors in the enteric nervous system modulate gastrointestinal contractility in lipopolysaccharide-treated rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295:G78–G87
Snider NT, Nast JA, Tesmer LA, Hollenberg PF (2009) A cytochrome P450-derived epoxygenated metabolite of anandamide is a potent cannabinoid receptor 2-selective agonist. Mol Pharmacol 75:965–972
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to Miss. Shima Zeinali-Moghadam for her remarkable help and emotional support.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HM designed, performed the experiments, discussed the findings, and wrote the manuscript. AA performed the experiments, designed the schematic figures, and performed the statistical analyses.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We do confirm that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alenabi, A., Malekinejad, H. Cannabinoids pharmacological effects are beyond the palliative effects: CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells (HT-29). Mol Cell Biochem 476, 3285–3301 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04158-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04158-6