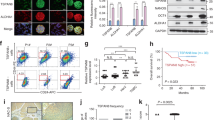
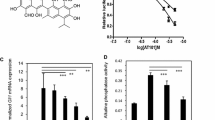
Abstract
Since PI3K/Akt/mTOR and sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathways are highly activated in glioblastoma-initiating cells (GICs), we examined the effects of inhibiting these pathways on GIC characteristics and tumor growth in mice. NVP-LDE-225 (inhibitor of Smoothened) inhibited the expression of Gli1, Gli2, Smoothened, Patched1, and Patched2, and induced the expression of SuFu, whereas NVP-BEZ-235 (dual inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR) inhibited the expression of p-PI3K, p-Akt, p-mTOR, and p-p70S6K. NVP-LDE-225 co-operated with NVP-BEZ-235 in inhibiting the self-renewal capacity of GICs, expression of pluripotency maintaining factors (Nanog, c-Myc, Oct4, and Sox2), Musashi1, cyclin D1, and Bcl-2, and transcription and expression of Gli, and in inducing the expression of cleaved caspase-3, cleaved PARP and Bim. Additionally, NVP-LDE-225 co-operated with NVP-BEZ-235 in inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Finally, the combination of NVP-LDE-225 and NVP-BEZ-235 was superior in inhibiting tumor growth, regulating the expression of pluripotency promoting factors, stem cell markers, cell cycle, and cell proliferation, and modulating EMT compared to single agent alone. In conclusion, the combined inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR and SHH pathways was superior to single pathway inhibition in suppressing glioblastoma growth by targeting GICs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2017) Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67:7–30
Louis DNOH, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW, Kleihues P (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114(2):97–109
Stupp R, WPMWea (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Ruiz I Altaba AMC, Stecca B (2007) The Gli code: an information nexus regulating cell fate, stemness, and cancer. Trends Cell Biol 17:438–447
Jia JJJ (2006) Decoding the Hedgehog signal in animal development. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1249–1265
Vorechovsky ITO, Hartman M, Stromberg B, Nister M, Collins VP et al (1997) Somatic mutations in the human homolog of patched in primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Oncogene 15:361–366
Becher OJ, Hambardzumyan D, Fomchenko EI, Momota H, Mainwaring L, Bleau AM, Katz AM, Edgar M, Kenney AM, Cordon-Cardo C, Blasberg RG, Holland EC(2008) Gli activity correlates with tumor grade in platelet-derived growth factor-induced gliomas. Cancer Res 68:2241–2249
Chandra V, Das T, Gulati P, Biswas NK, Rote S, Chatterjee U, Ghosh SN, Deb S, Saha SK, Chowdhury AK, Ghosh S, Rudin CM, Mukherjee A, Basu A, Dhara S (2015) Hedgehog signaling pathway is active in GBM with GLI1 mRNA expression showing a single continuous distribution rather than discrete high/low clusters. PLoS One 10:e0116390
Clement V, Sanchez P, de Tribolet N, Radovanovic I, Ruiz I Altaba A (2007) HEDGEHOG-GLI1 signaling regulates human glioma growth, cancer stem cell self-renewal, and tumorigenicity. Curr Biol 17:165–172
Xu Q, Yuan X, Liu G, Black KL, Yu JS (2008) Hedgehog signaling regulates brain tumor-initiating cell proliferation and portends shorter survival for patients with PTEN-coexpressing glioblastomas. Stem Cells 26:3018–3026
Becher OJHD, Fomchenko EI, Momota H, Mainwaring L, Bleau AM et al (2008) Gli activity correlates with tumor grade in platelet-derived growth factor-induced gliomas. Cancer Res 68:2241–2249
Kenney AMWH, Rowitch DH (2004) Hedgehog and PI-3 kinase signaling converge on Nmyc1 to promote cell cycle progression in cerebellar neuronal precursors. Development 131:217–228
Knobbe CBRG (2003) Genetic alterations and aberrant expression of genes related to the phosphatidyl-inositol-3′-kinase/protein kinase B (Akt) signal transduction pathway in glioblastomas. Brain Pathol 13:507–518
Wiencke JKZS, Jelluma N, Tihan T, Vandenberg S, Tamgüney T, Baumber R, Parsons R et al (2007) Methylation of the PTEN promoter defines low-grade gliomas and secondary glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 9:271–279
Medema RHKG, Bos JL, Burgering BM (2000) AFX-like Forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle regulation by Ras and PKB through p27kip1. Nature 404: 782–787
Fayard ETL, Baudry A, Hemmings BA (2005) Protein kinase B/Akt at a glance. J Cell Sci 118:5675–5678
Inoki KLY, Zhu T, Wu J, Guan KL (2002) TSC2 phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signaling. Nat Cell Biol 4:648–657
Fan QWWW (2006) Isoform specific inhibitors of PI3 kinase in glioma. Cell Cycle 20:2301–2305
Pan SWX, Jiang J et al (2010) Discovery of NVP-LDE225, a potent and selective smoothened antagonist ACS. Med Chem Lett 1:130–134
Maira SMSF, Brueggen J, Furet P, Schnell C, Fritsch C, Brachmann S, Chène P, De Pover A, Schoemaker K, Fabbro D, Gabriel D, Simonen M, Murphy L, Finan P, Sellers W, García-Echeverría C (2008) Identification and characterization of NVP-BEZ235, a new orally available dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1851–1863
Bier A, Giladi N, Kronfeld N, Lee HK, Cazacu S, Finniss S, Xiang C, Poisson L, deCarvalho AC, Slavin S, Jacoby E, Yalon M, Toren A, Mikkelsen T, Brodie C (2013) MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits the stemness of glioma stem cells by targeting RTVP-1. Oncotarget 4:665–676
Fu J, Rodova M, Nanta R, Meeker D, Van Veldhuizen PJ, Srivastava RK, Shankar S (2013) NPV-LDE-225 (Erismodegib) inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition and self-renewal of glioblastoma-initiating cells by regulating miR-21, miR-128, and miR-200. Neuro Oncol 15:691–706
Shankar SND, Tang SN, Meeker D, Passarini J, Sharma J, Srivastava RK (2011) Resveratrol inhibits pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics in human and KrasG12D transgenic mice by inhibiting pluripotency maintaining factors and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS ONE 6:16530
RJ J (2009) Cancer stem cells: clinical relevance. J Mol Med (Berl) 87:1105–1110
Chen QGS, Singh KP, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2010) Resveratrol induces growth arrest and apoptosis through activation of FOXO transcription factors in prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 5:15228–15234, 2010
Kenney AMCM, Rowitch DH (2003) Nmyc upregulation by sonic hedgehog signaling promotes proliferation in developing cerebellar granule neuron precursors. Development 130:15–28
Sharma N, Nanta R, Sharma J, Gunewardena S, Singh KP, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2015) PI3K/AKT/mTOR and sonic hedgehog pathways cooperate together to inhibit human pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics and tumor growth. Oncotarget 6:32039–32060
Ricci-Vitiani LLD, Pilozzi E, Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C, De Maria R (2007) Identification and expansion of human colon cancer-initiating cells. Nature 445:111–115
Malanchi IPH, Kassen D, Hussenet T, Metzger D, Chambon P, Huber M, Hohl D, Cano A, Birchmeier W, Huelsken J (2008) Cutaneous cancer stem cell maintenance is dependent on beta-catenin signalling. Nature 452:650–653
Braun S, Oppermann H, Mueller A, Renner C, Hovhannisyan A, Baran-Schmidt R, Gebhardt R, Hipkiss A, Thiery J, Meixensberger J, Gaunitz F (2012) Hedgehog signaling in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Biol Ther 13:487–495
Filbin MG, Dabral SK, Pazyra-Murphy MF, Ramkissoon S, Kung AL, Pak E, Chung J, Theisen MA, Sun Y, Franchetti Y, Sun Y, Shulman DS, Redjal N, Tabak B, Beroukhim R, Wang Q, Zhao J, Dorsch M, Buonamici S, Ligon KL, Kelleher JF, Segal RA (2013) Coordinate activation of Shh and PI3K signaling in PTEN-deficient glioblastoma: new therapeutic opportunities. Nat Med 19:1518–1523
Lima FR, Kahn SA, Soletti RC, Biasoli D, Alves T, da Fonseca AC, Garcia C, Romao L, Brito J, Holanda-Afonso R, Faria J, Borges H, Moura-Neto V (2012) Glioblastoma: therapeutic challenges, what lies ahead. Biochim Biophys Acta 1826:338–349
Xu QYX, Liu G, Black KL, Yu JS (2008) Hedgehog signaling regulates brain tumor-initiating cell proliferation and portends shorter survival for patients with PTEN-coexpressing glioblastomas. Stem Cells 26:3018–3026
Varjosalo MTJ (2008) Hedgehog: functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev 22:2454–2472
Ho KSSM (2002) Hedgehog in the nervous system: functions, modifications and mechanisms. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:57–63
Hooper JESM (2005) Communicating with Hedgehogs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:306–317
Cowan RHP, Kelsey A, Birch JM, Gattamaneni R et al (1997) The gene for the basal cell carcinoma syndrome acts as a tumour-suppressor gene in medulloblastoma. Br J Cancer 76:141–145
Goodrich LVML, Higgins KM (1997) Scott MP Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants. Science 277:1109–1113
Rudin CMHC, Laterra J, Yauch RL, Callahan CA et al (2009) Treatment of medulloblastoma with hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449. N Engl J Med 361:1173–1178
Bar EECA, Farah MH, Eberhart CG (2007) Hedgehog signaling promotes medulloblastoma survival via BclII. Am J Pathol 170:347–355
Kaneko YSS, Imai T, Suzuki A, Nakamura Y, Sawamoto K, Ogawa Y, Toyama Y, Miyata T, Okano H (2002) Musashi1: an evolutionally conserved marker for CNS progenitor cells including neural stem cells. Dev Neurosci 22:139–153
Sakakibara SOH (1997) Expression of neural RNA-binding proteins in the postnatal CNS: implications of their roles in neuronal and glial cell development. J Neurosci Res 17:8300–8312
Toda MIY, Yu W, Imai T, Ikeda E, Yoshida K, Kawase T, Kawakami Y, Okano H, Uyemura K (2001) Expression of the neural RNA-binding protein Musashi1 in human gliomas. Glia 34:1–7
Ma YHMR, Knerlich F, Kruse ML, Mehdorn HM, Held-Feindt J (2008) Expression of stem cell markers in human astrocytomas of different WHO grades. J Neurooncol 86:31–45
Xu X, Zhou Y, Xie C, Wei SM, Gan H, He S, Wang F, Xu L, Lu J, Dai W, He L, Chen P, Wang X, Guo C (2012) Genome-wide screening reveals an EMT molecular network mediated by Sonic hedgehog-Gli1 signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS ONE 7:e43119
Ke Z, Caiping S, Qing Z, Xiaojing W (2015) Sonic hedgehog-Gli1 signals promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer by mediating PI3K/AKT pathway. Med Oncol 32:368
Srivastava RK, Kaylani SZ, Edrees N, Li C, Talwelkar SS, Xu J, Palle K, Pressey JG, Athar M (2014) GLI inhibitor GANT-61 diminishes embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma growth by inhibiting Shh/AKT-mTOR axis. Oncotarget 5:12151–12165
Hao K, Tian XD, Qin CF, Xie XH, Yang YM (2013) Hedgehog signaling pathway regulates human pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. Oncol Rep 29:1124–1132
Yoo YA, Kang MH, Lee HJ, Kim BH, Park JK, Kim HK, Kim JS, Oh SC (2011) Sonic hedgehog pathway promotes metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via activation of Akt, EMT, and MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Res 71:7061–7070
Wang YDQ, Yen CJ, Xia W, Izzo JG, Lang JY, Li CW et al (2012) The crosstalk of mTOR/S6K1 and hedgehog pathways. Cancer cell 21:374–387
Acknowledgements
We thank all the lab members for critical reading of the manuscript and technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS, AS, JS, and RKS conceived the ideas and designed the study. RN carried out the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. All the authors have approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors of this article have declared ‘‘no conflict of interest”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nanta, R., Shrivastava, A., Sharma, J. et al. Inhibition of sonic hedgehog and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways cooperate in suppressing survival, self-renewal and tumorigenic potential of glioblastoma-initiating cells. Mol Cell Biochem 454, 11–23 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3448-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3448-z