Abstract
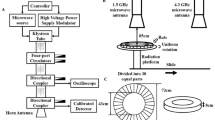
For decades, there has been an increasing concern about the potential hazards of non-ionizing electromagnetic fields that are present in the environment and alarming as a major pollutant or electro-pollutant for health risk and neuronal diseases. Therefore, the objective of the present study was to explore the effects of 10 GHz microwave radiation on developing mice brain. Two weeks old mice were selected and divided into two groups (i) sham-exposed and (ii) microwave-exposed groups. Animals were exposed for 2 h/day for 15 consecutive days. After the completion of exposure, within an hour, half of the animals were autopsied immediately and others were allowed to attain 6 weeks of age for the follow-up study. Thereafter results were recorded in terms of various biochemical, behavioral, and histopathological parameters. Body weight result showed significant changes immediately after treatment, whereas non-significant changes were observed in mice attaining 6 weeks of age. Several other endpoints like brain weight, lipid peroxidation, glutathione, protein, catalase, and superoxide dismutase were also found significantly (p < 0.05) altered in mice whole brain. These significant differences were found immediately after exposure and also in follow-up on attaining 6 weeks of age in microwave exposure group. Moreover, statistically significant (p < 0.001) effect was investigated in spatial memory of the animals, in learning to locate the position of platform in Morris water maze test. Although in probe trial test, sham-exposed animals spent more time in searching for platform into the target quadrant than in opposite or other quadrants. Significant alteration in histopathological parameters (qualitative and quantitative) was also observed in CA1 region of the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and ansiform lobule of cerebellum. Results from the present study concludes that the brain of 2 weeks aged mice was very sensitive to microwave exposure as observed immediately after exposure and during follow-up study at 6 weeks of age.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Çeliker M, Özgür A, Tümkaya L, Terzi S, Yılmaz M, Kalkan Y, Erdoğan E (2016) Effects of exposure to 2100 MHz GSM-like radiofrequency electromagnetic field on auditory system of rats. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol S1808–S8694:30222-1. doi:10.1016/j.bjorl.2016.10.004
Mugunthan N, Shanmugasamy K, Anbalagan J, Rajanarayanan S, Meenachi S (2016) Effects of long term exposure of 900-1800 MHz radiation emitted from 2G mobile phone on mice hippocampus—a histomorphometric study. J Clin Diagn Res 10:AF01–AF06. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2016/21630.8368
Kerimoğlu G, Hancı H, Baş O, Aslan A, Erol HS, Turgut A, Kaya H, Çankaya S, Sönmez OF, Odacı E (2016) Pernicious effects of long-term, continuous 900-MHz electromagnetic field throughout adolescence on hippocampus morphology, biochemistry and pyramidal neuron numbers in 60-day-old Sprague Dawley male rats. J Chem Neuroanat S0891–0618:30075–30078. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2016.07.004
Kim JY, Kim HJ, Kim N, Kwon JH, Park MJ (2016) Effects of radiofrequency field exposure on glutamate-induced oxidative stress in mouse hippocampal HT22 cells. Int J Radiat Biol 20:1–22
Chauhan P, Verma HN, Sisodia R, Kesari KK (2016) Microwave radiation (2.45 GHz) induced oxidative stress: whole body exposure effect on histopathology of Wistar rats. Electromagn Biol Med (in press). doi:10.3109/15368378.2016.1144063
Sharma A, Kesari KK, Saxena VK, Sisodia R (2016) The influence of prenatal 10 GHz microwave radiation exposure on a developing mice brain. Gen Physiol Biophys (in press)
Kesari KK, Behari J, Kumar S (2010) Mutagenic response of 2.45 GHz radiation exposure on rat brain. Int J Rad Biol 86:334–343
Kesari KK, Meena R, Nirala J, Kumar J, Verma HN (2014) Effect of 3G cell phone exposure with computer controlled 2-D stepper motor on non-thermal activation of the hsp27/p38MAPK stress pathway in rat brain. Cell Biochem Biophys 68:347–358
Kesari KK, Behari J (2009) Fifty GHz microwave exposure effect of radiations on rat brain. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 158:126–139
Lai H, Singh NP (1996) Single and double strand DNA breaks in rat brain cells after acute exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 69:513
Sharma A, Sisodia R, Bhatnagar D, Saxena VK (2014) Spatial memory and learning performance and its relationship to protein synthesis of Swiss albino mice exposed to 10 GHz microwaves. Int J Radiat Biol 90:29–35
Deshmukh PS, Megha K, Nasare N, Banerjee BD, Ahmed RS, Abegaonkar MP, Tripathi AK, Mediratta PK (2016) Effect of low level subchronic microwave radiation on rat brain. Biomed Environ Sci 29:858–867
Repacholi MH, Basten A, Gebski V, Noonan D, Finnie J, Harris AW (1997) Lymphomas in Eμ-Pim1 transgenic mice exposed to pulsed 900 MHz electromagnetic fields. Radiat Res 147:631
Baan R, Grosse Y, Lauby-Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Bouvard V et al (2011) Carcinogenicity of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. Lancet Oncol 12:624–626
Coureau G, Bouvier G, Lebailly P, Fabbro-Peray P, Gruber A et al (2014) Mobile phone use and brain tumours in the CERENAT case-control study. Occup Environ Med 71:514–522
Hardell L, Carlberg M (2013) Use of mobile and cordless phones and survival of patients with glioma. Neuroepidemiology 40:101–108
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Hansson Mild K (2013) Use of mobile phones and cordless phones is associated with increased risk for glioma and acoustic neuroma. Pathophysiology 20:85–110
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Soderqvist F, Mild KH (2013) Pooled analysis of case-control studies on acoustic neuroma diagnosed 1997–2003 and 2007–2009 and use of mobile and cordless phones. Int J Oncol 43:1036–1044
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Soderqvist F, Mild KH (2013) Case-control study of the association between malignant brain tumours diagnosed between 2007 and 2009 and mobile and cordless phone use. Int J Oncol 43:1833–1845
Mead N (2008) Strong signal for cell phone effects. Environ Health Perspect 116:422
Hao Y, Zhao L, Peng R (2015) Effects of microwave radiation on brain energy metabolism and related mechanisms. Mil Med Res 2:4. doi:10.1186/s40779-015-0033-6
Habash RW, Elwood JM, Krewski D, Lotz WG, McNamee JP, Prato FS (2009) Recent advances in research on radiofrequency fields and health: 2004-2007. Toxicol Environ Health B 12:250–288
Kaplan S, Erdem G, Altunkaynak BZ, Deniz OG, Kayhan E, Altunkaynak ME (2013) Histopathological examination of the Purkinje cells in the cerebellum of newborn rats following prenatal exposure to 900 MHz electromagnetic field. J Exp Clin Med 30:280
Walani S, Bhatnagar D, Sisodia R (2014) Biochemical alterations in cerebellum of Swiss albino mice after 10 GHz microwave exposure. Int J Adv Res 2:708–716
Kumar S, Kesari KK, Behari J (2011) Influence of microwave exposure on fertility of male rats. Fertil Steril 95:1500–1502
Kumar S, Behari J, Sisodia R (2012) Impact of microwave at X-band in the aetiology of male infertility. Electromagn Biol Med 31:223–232
Kumar S, Behari J, Sisodia R (2013) Influence of electromagnetic fields on reproductive system of male rats. Int J Radiat Biol 89:147–154
Zhang Y, Li Z, Gao Y, Zhang C (2015) Effects of fetal microwave radiation exposure on offspring behavior in mice. J Radiat Res 56:261–268
Rifat F, Sisodia R (2017) Modulation of 10 GHz microwaves induced biochemical changes in different organs of swiss albino mice by Prunus domestica fruit extract. Int J Pharm Sci Res 8:136–144
Paulraj R, Behari J (2012) Enzymatic alterations in developing rat brain cells exposed to a low-intensity 16.5 GHz microwave radiation. Electromagn Biol Med 31:233–242
Paulraj R, Behari J (2012) Biochemical changes in rat brain exposed to low intensity 9.9 GHz microwave radiation. Cell Biochem Biophys 63:97–102
Hamblin DL, Wood AW, Croft RJ, Stough C (2004) Examining the effects of electromagnetic fields emitted by GSM mobile phones on human event-related potentials and performance during an auditory task. Clin Neurophysiol 115:171–178
Sievert U, Eggert S, Pau HW (2005) Can mobile phone emissions affect auditory functions of cochlea or brain stem? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:451–455
Ferreri F, Curcio G, Pasqualetti P, De Gennaro L, Fini R, Rossini PM (2006) Mobile phone emissions and human brain excit- ability. Ann Neurol 60:188–196
Krause CM, Pesonen M, Haarala Björnberg C, Hämäläinen H (2007) Effects of pulsed and continuous wave 902 MHz mobile phone exposure on brain oscillatory activity during cognitive processing. Bioelectromagnetics 28:296–308
Kumlin T, Iivonen H, Miettinen P, Juvonen A, van Groen T, Puranen L, Pitkäaho R, Juutilainen J, Tanila H (2007) Mobile phone radiation and the developing brain: behavioral and morphological effects in juvenile rats. Radiat Res 168:471–479
Kang XK, LiLW Leong MS, Kooi PS (2001) A method of moments study of SAR inside spheroidal human head and current distribution among handset wireless antennas. J Electromag Waves Appl 15(1):61
Barnett J, Timotijevic L, Shepherd R, Senior V (2007) Public responses to precautionary information from the Department of Health (UK) about possible health risks from mobile phones. Health Policy 82:240–250
Rothman KJ, Chou CK, Morgan R, Balzano Q, Guy AW, Funch DP (1996) Assessment of cellular telephone and other radio frequency exposure for epidemiologic research. Epidemiology 7:291–298
Dimbylow PJ, Mann SM (1994) SAR calculations in an anatomically realistic model of the head for mobile communication transceivers at 900 MHz and 1.8 GHz. Phys Med Biol 39:1537–1544
Kheifets L, Repacholi M, Saunders R, van Deventer E (2005) The sensitivity of children to electromagnetic fields. Pediatrics 116:e303–e313
Dong J, Peng RY, Wang SM, Gao YB, Wang LF, Zhao L et al (2011) Effects on abilities of learning and memory and structural changes of brain in rats induced by microwave radiation under different conditions. Mil Med Sci 35:347–350
Rola R, Raber J, Rizk A, Otsuka S, VandenBerg SR, Morhardt DR, Fike JR (2004) Radiation-induced impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis is associated with cognitive deficits in young mice. Exp Neurol 188:316–330
Koivisto M, Krause CM, Revonsuo A, Laine M, Hämäläinen H (2000) The effects of electromagnetic field emitted by GSM phones on working memory. NeuroReport 11:1641–1643
Wang H, Peng R, Zhou H, Wang S, Gao Y, Wang L et al (2013) Impairment of long-term potentiation induction is essential for the disruption of spatial memory after microwave exposure. Int J Radiat Biol 89:1100–1107
Xu S, Ning W, Xu Z, Zhou S, Chiang H, Luo J (2006) Chronic exposure to GSM 1800 MHz microwaves reduces excitatory synaptic activity in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett 398:253–257
Zhao L, Peng RY, Wang SM, Wang LF, Gao YB, Dong J et al (2012) Relationship between cognition function and hippocampus structure after long-term microwave exposure. Biomed Environ Sci 25:182–188
Dasdag S, Bilgin HM, Akdag MZ, Celik H, Aksen F (2008) Effect of long term mobile phone exposure on oxidative-antioxidative processes and nitric oxide in rats. Biotech Biotechnolog Equip 22:992–997
Kesari KK, Kumar S, Behari J (2012) Evidence for mobile phone radiation exposure effects on reproductive pattern of male rats: role of ROS. Electromagn Biol Med 31:213–222
Kesari KK, Kumar S, Nirala J, Siddiqui MH, Behari J (2013) Biophysical evaluation of radiofrequency electromagnetic field effects on male reproductive pattern. Cell Biochem Biophys 65:85–96
Yakymenko I, Tsybulin O, Sidorik E, Henshel D, Kyrylenko O, Kyrylenko S (2015) Oxidative mechanisms of biological activity of low-intensity radiofrequency radiation. Electromagn Biol Med 19:1–16
Forman HJ, Ursini F, Maiorino M (2014) An overview of mechanisms of redox signaling. J Mol Cellul Cardiol 73:2–9
Jajte J, Grzegorczyk J, Zmyslony M, Rajkowska E (2002) Effect of 7 mT static magnetic field and iron ions on rat lymphocytes: apoptosis, necrosis and free radical processes. Bioelectrochem 57:107–111
Narayanan SN, Kumar RS, Karun KM, Nayak SB, Bhat PG (2015) Possible cause for altered spatial cognition of prepubescent rats exposed to chronic radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Metabol Brain Dis 30:1193–1206
Shehu A, Mohammed A, Magaji RA, Muhammad MS (2015) Exposure to mobile phone electromagnetic field radiation, ringtone and vibration affect anxiety-like behaviour and oxidative stress biomarkers in albino wistar rats. Metabol Brain Dis 31(2):355–362
Durney CH, Iskander MF, Massoudi H, Johnson CC (1984) An empirical formula for broad band SAR calculations of prolate spheroidal models of humans and animal. In: Osepchuk JM (ed) Biological effects of electromagnetic radiation. IEEE Press, New York, pp 85–90
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzym 52:302–310
Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B (1979) Levels of GSH, GR and GST activities in rat lung and liver. BBA 582:67–78
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxyde anion radical in the auto oxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxyde dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principal of protein by binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Fragopoulou AF, Miltiadous P, Stamatakis A, Stylianopoulou F, Koussoulakos SL, Margaritis LH (2010) Whole body exposure with GSM 900 MHz affects spatial memory in mice. Pathophysiology 17:179–187
Mallory FB (1994) In: Animal Tissue Techniques. 4th Eds. (Humason GL, Freeman WH) San Francisco p 150
Stead JDH, Chrales N, Fan M, Yongjia W, Simon E, Vazquez DM, Stanley JW, Huda A (2006) Transcriptional profiling of the developing rat brain reveals that the most dramatic regional differentiation in gene expression occurs postpartum. J Neurosci 26:345–353
Stringari J, Flavia C, Meotti DO, Souza ARS, Farina SM (2006) Postnatal methylmercury exposure induces hyperlocomotor activity and cerebellar oxidative stress in mice: dependence on the neurodevelopmental period. Neurochem Res 31:563–569
Subbarao KV, Richardson JS (1990) Iron dependent peroxidation of rat brain: a regional study. J Neurosci Res 26:224–232
Ogawa N (1994) Free radicals and neural cell damage. Rinsho Shinkeigake 34:1266–1268
Kesari KK, Kumar S, Behari J (2011) Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic waves exposure from cellular phone on reproductive pattern in male Wistar rats. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 164:546–559
Kesari KK, Kumar S, Behari J (2011) 900-MHz microwave radiation promotes oxidation in rat brain. Electromagn Biol Med 30:219–234
Cakatay U, Telci A, Kayali R, Tekeli F, Akcay T, Sivas A (2001) Relation of oxidative protein damage and nitrotyrosine levels in the aging rat brain. Exp Gerontol 36:221–229
Khan JY, Black SM (2003) Developmental changes in murine brain antioxidant enzymes. Pediatr Res 54:77–82
Kamal A, Biessels GJ, Duis SEJ, Gispen WH (2000) Learning and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: interaction of diabetes and ageing. Diabetologia 43:500–506
Jerusalinky D, Kornisiuk E, Izquierdo I (1997) Cholinergic neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity concerning memory processing. Neurochem Res 22:507–515
Liu R, Liu W, Doctrow SR, Baudry M (2003) Iron toxicity in organotypic cultures of hippocampal slices: role of reactive oxygen species. J Neurochem 85:492–502
Sakhnini L, Al-Ghareebb S, Khalilb S, Ahmedb R, Ameerb AA, Kamal A (2013) Effects of exposure to 50 Hz electromagnetic fields on Morris water-maze performance of prenatal and neonatal mice. J Assoc Arab Uni Basic Appl Sci 15:1–6
Sakhnini L, Ali HA, Qassab NA, Arab EA, Kamal A (2012) Subacute exposure to 50-Hz electromagnetic fields affect prenatal and neonatal mice’s motor coordination. J Appl Phys 111:307–314
Miranda RN, Blanco E, Begega A, SantiNLJ Arias JL (2006) Reversible changes in hippocampal CA1 synapses associated with water maze training in rats. Synapse 59:177–181
Nader K (2003) Memory traces unbound. Trends Neurosci 26:65–72
Dudai Y (2004) The neurobiology of consolidations, or, how stable is the engram. Annu Rev Psychol 55:51–86
Vago DR, Kesner RP (2005) Abstract Viewer/Itinerary Planner, Program No. 647.5. An electrophysiological and behavioral characterization of the temporoammonic pathway: Disruption produces deficits in retrieval and spatial mismatch. Society for Neuroscience, Washington, D.C
Jerman T, Kesner RP, Hunsaker MR (2006) Disconnection analysis of CA3 and DG in mediating encoding but not retrieval in a spatial maze learning task. Learn Mem 13:458–464
Rolls ET, Kesner RP (2006) A computational theory of hippocampal function, and empirical tests of the theory. Prog Neurobiol 79:1–48
Brun VH, Otnass MK, Molden S, Steffenach HA, Witter MP, Moser MB, Moser EI (2002) Place cells and place recognition maintained by direct entorhinal-hippocampal circuitry. Science 296:2243–2246
Hollup SA, Molden S, Donnett JG, Moser MB, Moser EI (2001) Accumulation of hippocampal place fields at the goal location in an annular water maze task. J Neurosci 21:1635–1644
Salford LG, Brun AE, Eberhardt JL, Malmgren L, Persson BRR (2003) Nerve cell damage in mammalian brain after exposure to microwaves from GSM mobile phones. Environ Health Perspect 111:881–883
D’Andrea JA, Adair ER, de Lorge JO (2003) Behavioral and cognitive effects of microwave exposure. Bioelectromagnetics Suppl 6:S39–S62
Sharma M (2001) Investigation on β-carotene vs radiation effect on mice cerebellum (Doctoral dissertation, PhD thesis, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur)
Albert EN, Sherif MF, Papadopoulos NJ, Slaby FJ, Monahan J (1981) Effect of non-ionizing radiation on the Purkinje cells of the rat cerebellum. Bioelectromagnetics 2:247–257
Rağbetl MC, Aydinlioğlu A, Koyun N, Rağbetl C, Bektas S, Ozdemır S (2010) The effect of mobile phone on the number of Purkinje cells: a stereological study. Int J Radiat Biol 86:548–554
Mausset AL, de Seze R, Montpeyroux F, Privat A (2001) Effects of radiofrequency exposure on the GABAergic system in the rat cerebellum: clues from semi-quantitative immunohistochemistry. Brain Res 912:33–46
Acknowledgement
The research group sincerely acknowledges the funding provided by University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi under the scheme of major research projects to accomplish the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A., Kesari, K.K., Saxena, V.K. et al. Ten gigahertz microwave radiation impairs spatial memory, enzymes activity, and histopathology of developing mice brain. Mol Cell Biochem 435, 1–13 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3051-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3051-8