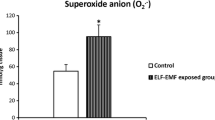
Abstract
Research on the effects of Mobile phone radio frequency emissions on biological systems has been focused on noise and vibrations as auditory stressors. This study investigated the potential effects of exposure to mobile phone electromagnetic field radiation, ringtone and vibration on anxiety-like behaviour and oxidative stress biomarkers in albino wistar rats. Twenty five male wistar rats were randomly divided into five groups of 5 animals each: group I: exposed to mobile phone in switched off mode (control), group II: exposed to mobile phone in silent mode, group III: exposed to mobile phone in vibration mode, group IV: exposed to mobile phone in ringtone mode, group V: exposed to mobile phone in vibration and ringtone mode. The animals in group II to V were exposed to 10 min call (30 missed calls for 20 s each) per day for 4 weeks. Neurobehavioural studies for assessing anxiety were carried out 24 h after the last exposure and the animals were sacrificed. Brain samples were collected for biochemical evaluation immediately. Results obtained showed a significant decrease (P < 0.05) in open arm duration in all the experimental groups when compared to the control. A significant decrease (P < 0.05) was also observed in catalase activity in group IV and V when compared to the control. In conclusion, the results of the present study indicates that 4 weeks exposure to electromagnetic radiation, vibration, ringtone or both produced a significant effect on anxiety-like behavior and oxidative stress in young wistar rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbate C, Micali E, Giorgianni C, Munao F, Brecciaroli R, Salmaso L, Germano D (2004) Affective correlates of occupational exposure to whole-body vibration-A case-control study. Psychother Psychosom 73:375–379
Agarwal A, Desai NR, Makker K, Varghese A, Mouradi R, Sabanegh E, Sharma R (2009) Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic waves (RF-EMW) from cellular phones on human ejaculated semen: an in vitro pilot study. Fertil Steril 92(4):1318–1325
Ahlbom A, Green A, Kheifets L (2004) Epidemiology of health effects of radiofrequency exposure. Environ Health Perspect 112:1741–1754
Aydogan F, Unlu I, Aydin E, Yumusak N, Devrim E, Samim EE, Ozgur E, et al. (2015) The effect of 2100 MHz radiofrequency radiation of a 3G mobile phone on the parotid gland of rats. Am J Otolaryngol Head Neck Med Surg 36:39–46
Balci M, Devrim E, Durak I (2007) Effects of mobile phones on oxidant/antioxidant balance in cornea and lens of rats. Curr Eye Res 32(1):21–25
Beers Jr RF, Sizer IW (1952) A Spectrophotomeric Method for Meassuring the Breakdown of Hydrogen Peroxide by Catalase. J Biol Chem 195:133–140
Berglund B, Hassmén P (1996) Sources and effects of low-frequency noise. J Acoust 26(3):307–314
Brookes T (2012) A Brief History of mobile Phones. Available at: http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/history-mobile-phones/ Retrieved on Dec 11,
Brown RE, Corey SC, Moore AK (1999) Differences in measures of exploration and fear in MHC-congenic C57BL/6 J and B6-H2K mice. Behav Genet 26:263–271
Clark C, Sörqvist P (2012) A 3 year update on the influence of noise on performance and behavior. Noise Health 14(61):292–296
Das DK, Maulik N (2006) Resveratrol in Cadioprotection: A therapeutic Potential in Alternative Medicine. Mol Interv 6(1):36–47
Dasdag S, Zulkuf AM, Aksen F, Yilmaz F, Bashan M, Mutlu DM, Salih CM (2003) Whole body exposure of rats to microwaves emitted from a cell phone does not affect the testes. Bioelectromagnetics 24(3):182–188
De Iuliis GN, Newey RJ, King BV, Aitken RJ (2009) Mobile phone radiation induces reactive oxygen species production and DNA damage in human spermatozoa in vitro. PLoS One 4(7):6446
de Kloet ER (2003) Hormones, brain and stress. Endocr Regul 37:51–68
de Kloet ER, Joels M, Holsboer F (2005) Stress and the brain: from adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:463–475
Devrim E, Ergüder IB, Kılıçoğlu B, et al. (2008) Effects of electromagnetic radiation use on oxidant/antioxidant status and DNA turn-over enzyme activities in erythrocytes and heart, kidney, liver, and ovary tissues from rats: Possible protective role of vitamin C. Toxicol Mech Methods 18:679–683
Di S, Maxson MM, Franco A, Tasker JG (2009) Glucocorticoids regulate glutamate and GABA synapse-specific retrograde transmission via divergent nongenomic signaling pathways. J Neurosci 29:393–401
Dormolen VM, Hertog C (1994) Combined workload, methodological considerations on recent research. In: Manninen O (ed) Recent Advances in Researches on the Combined Effects of Environmental Factors. Tampere, Finland, Pk-Paino, pp. 25–39
Eyad I (2012) Charts of GSM/3GSM coverage and frequency usage for the world, Europe, Asia and the Americas. Available at: www.coveragemaps.com Retrieved on 2/12/2012.
Faravelli C, Lo Sauro C, Godini L, Lelli L, Benni L, Pietrini F, Lazzeretti L, et al. (2012) Childhood stressful events, HPA axis and anxiety disorders. World J Psychiatr 2(1):13–25
Griffin MJ (1990) Handbook of Human Vibration. London: San Diego. Academic Press, p. 1008
Guney M, Ozguner F, Oral B, Karahan N, Mungan T (2007) 900 MHz radiofrequency-induced histopathologic changes and oxidative stress in rat endometrium: protection by vitamins E and C. Toxicol Ind Health 23(7):411–420
Herman JP, Mueller NK, Figueiredo H (2004) Role of GABA and glutamate circuitry in hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical stress integration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1018:35–45
Hirose H, Sakuma N, Kaji N, Suhara T, Sekijima M, Nojima T, Miyakohi J (2006) Phosphorylation and gene expression of p53 are not affected in human cells exposed to 2.1425 GHz band CW or W=CDMA modulated radiation allocated to radio base stations. Bioelectomagnetics 27:494–504
Hovatta I, Tennant RS, Helton R, Marr RA, Singer O, Redwine JM, Ellison JA, et al. (2005) Glyoxalase 1 and glutathione reductase 1 regulate anxiety in mice. Nature 438:662–666
Hung CS, Anderson C, Horne JA, McEvoy P (2007) Mobile phone 'talk-mode' signal delays EEG-determined sleep onset. Neurosci Lett 421(1):82–86
ICNRP (1998) Guidelines For Limiting Exposure To Time-Varying Electric, Magnetic, And Electromagnetic Fields (up to 300 GHz). Int Comm Non-Ionizing Radiat Prot Health Phys 74(4):494–505
Imge EB, Kiliçoğlu B, Devrim E, et al. (2010) Effects of mobile phone use on brain tissue from the rat and a possible protective role of vitamin C – a preliminary study. Int J Radiat Biol 86:1044–1049
Janero DR (1990) Malondialdehyde and thiobarbituric acid-reactivity as diagnostic indices of lipid peroxidation and peroxidative tissue injury. Free Radic Biol Med 9:515–540
Janet P (2011) Triple GSM SIM Phone comes from Japan via AKAI". MobileSmug Available at: http://mobilesmug.com/news/1-phones/732-triple-gsm-sim-phone-comes-from-japan-via-akai. Retrieved 19 January 2012
Khirazova EE, Baizhumanov AA, Trofimova LK, Maslova DMV, Sokolova NA, Kudryashova NY (2012) Effects of GSM-Frequency Electromagnetic Radiation on some Physiological and Biochemical Parameters in Rats. Bull of Exp Biol and Med 153(6)
Lister RG (1987) The use of a plus-maze to measure anxiety in the mouse. Psychopharmacology 92:180–185
Liebel F, Kaur S, Ruvolo E, Kollias N, Southall MD (2012) Irradiation of skin with visible light induces reactive oxygen species and matrix-degrading enzymes. J Invest Dermatol 132(7):1901–1907
Makoto A, Akira O (1983) Effect of whole body vibration on the rat brain content of serotonin and plasma corticosterone. Eur J Appl Physiol 52:15–19
Marco C (2002) The effects of vibration on human performance and hormonal profile. Empirical and Theoretical issues in Sport Sciences Budapest Pp 23-32
Martin JP, Dailey M, Sugar E (1987) Negative and Positive Assays of Superoxide Dismutase Based on Hematoxylin Autoxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 255:329–336
Masood A, Nadeem A, Mustafa SJ, O’Donnell JM (2008) Reversal of oxidative stress-induced anxiety by inhibition of phosphodiesterase-2 in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326:369–379
Mausset-Bonnefont AL, Hirbec H, Bonnefont X, Privat A, Vignon J, de Seze R (2004) Acute exposure to GSM 900-MHz electromagnetic fields induces glial reactivity and biochemical modifications in the rat brain. Neurobiolical Discussion 17(3):445–54
Meral I, Mert H, Mert N, Deger Y, Yoruk I, Yektin A, Keskin S (2007) Effects of 900-MHz electromagnetic field emitted from cellular phone on brain oxidative stress and some vitamin levels of guinea pigs. Brain Res 1169:120–124
Narayanan SN, Kumar RS, Kedage V, Nalini K, Nayak S, Bhat PG (2014) Evaluation of oxidant stress and antioxidant defense in discrete brain regions of rats exposed to 900 MHz radiation. Bratisl Lek Listy 115(5):260–266
NCC (2012) National Communication Council. http://www.ncc.gov.ng/industry-statistics/subscriber-data.html. Retrieved on 13/12/2012
Nittby H, Grafström G, Tian DP, Malmgren L, Brun A, Persson BR, Salford LG, Eberhardt J (2008) Cognitive impairment in rats after long-term exposure to GSM-900 mobile phone radiation. Bioelectromagnetics 29(3):219–232
Okhawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay of lipid peroxides in animals’ tissue by thiobarbituraic acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Oktem F, Ozguner F, Mollaoglu H, Koyu A, Uz E (2005) Oxidative damage in the kidney induced by 900-MHz-emitted mobile phone: protection by melatonin. Arch Med Res 36(4):350–355
Oral B, Guney M, Ozguner F, Karahan N, Mungan T, Comlekci S, Cesur G (2006) Endometrial apoptosis induced by a 900-MHz mobile phone: preventive effects of vitamins E and C. Adv Ther 23(6):957–973
Polat N, Kilinc A, Yalcin AS (2013) Oxidative stress parameters in blood and urine of metal-shelf factory workers. Mar Med J 26:25–29
Raju SK, Sareesh NN, Satheesha N, Maneesh M (2009) Hypoactivity Of Wistar Rats Exposed To Mobile Phone On Elevated Plus Maze. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 53(3):283–286
Salama N, Kishimoto T, Kanayama HO (2009) The mobile phone decreases fructose but not citrate in rabbit semen: a longitudinal study. Syst Biol Reprod Me 55(5–6):181–187
Salim S (2011) Oxidative Stress in Anxiety: Implications for Pharmacotherapy. Am J of Integr Med 1(1):11–21
Sapolsky RM, Romero LM, Munck AU (2000) How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr Rev 21:55–89
Sareesh NN, Raju SK, Bhagath KP, Satheesha N, Maneesh M (2009) Spatial Memory Perfomance of Wistar Rats Exposed to Mobile Phone. Clinics 64(3):231–234
Smith A, Thomas M, Brockman P (1993) Noise respiratory virus infections and performance. In: Vallet M (ed) Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Noise as a Public Health Problem, vol 2. Nice, France, INRETS, pp. 311–314
Talbott E, Thompson SJ (1995) Health effects from environmental noise exposure. In: Introduction to Environmental Epidemiology. Lewis Publishers, New York, pp. 209–219
Tekebe G (2002) A comparative study on the hydroperoxide and thiol specificity of the glutathione peroxidase family and selenoprotein P. J Biol Chem 277(43):41254–41258
Trullas R, Skolnick P (1993) Differences in fear motivated behaviors among inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology 111:323–331
van Kempen EE, van Kamp I, Stellato RK, Lopez-Barrio I, Haines MM, Nilsson ME, Clark C, Houthuijs D, Brunekreef B, Berglund B, Stansfeld SA (2009) Children's annoyance reactions to aircraft and road traffic noise. J Acoust Soc Am 125(2):895–904
Yurekli AI, Ozkan M, Kalkan T, Saybasili H, Atukeren P, Pinar K, Gumustas K, Seker S (2006) GSM base station electromagnetic radiation and oxidative stress in rats. Electomag Biol Med 25:177
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Malam Isa Ahmed-Sherif of the Department of Human Physiology, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria, for his assistance in training and handling of the animals, Mr. Olu Aiyegbuisi of the Department of Chemical Pathology, Ahmadu Bello University Teaching Hospital Zaria, Nigeria for biochemical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental protocols were in accordance with the Ahmadu Bello University Research policy; and ethic and regulations governing the care and use of experimental animals (NIH Publication no. 85–23, revised 1996).
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shehu, A., Mohammed, A., Magaji, R.A. et al. Exposure to mobile phone electromagnetic field radiation, ringtone and vibration affects anxiety-like behaviour and oxidative stress biomarkers in albino wistar rats. Metab Brain Dis 31, 355–362 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9758-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9758-x