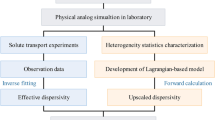
Abstract
Since 1963, radioactive waste has been injected in deep artesian aquifers of Cretaceous terrigenous deposits in western Siberia. It is well known that geologic heterogeneity strongly affects contaminant transport in unconsolidated formations. To predict the long-term migration of this radioactive waste the effective hydraulic and macrodispersion parameters are estimated by using a three-dimensional high-resolution hydraulic heterogeneity model. The heterogeneous model of the injection area is developed by applying transition probability geostatistics. This model is used to simulate local steady-state groundwater flow and advective transport, leading to numerical estimates of effective hydraulic conductivity and macrodispersion parameters. Mean seepage velocities and effective longitudinal macrodispersion are calculated from observed breakthrough curves for a conservative tracer. Results show that mean horizontal lengths exceed vertical lengths by a factor of more than 30. As a result, vertical effective hydraulic conductivity is two orders of magnitude less than the horizontal effective conductivity. Observed breakthrough curves exhibit long tails and appear to be non-Fickian. Estimated effective longitudinal macrodispersivity in the vertical direction is one order of magnitude less than that in the horizontal direction. Under a Fickian framework, this implies that dispersion modeling for regional transport simulations requires an anisotropic-media dispersion model.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkowitz B, Klafter J, Metzler R, Scher H (2002) Physical pictures of transport in heterogeneous media: advection-dispersion, random-walk, and fractional derivative formulations. Water Resour Res 38(10):1191–1203
Carle SF (1998) T-PROGS: transition probability geostatistical software. University of California, California
Carle SF, Fogg GE (1996) Transition probability-based indicator geostatistics. Math Geol 28(4):453–476
Carle SF, Fogg GE (1997) Modeling spatial variability with one- and multi-dimensional Markov chains. Math Geol 2(7):891–918
Chiang WH, Kinzelbach W (2001) 3D-groundwater modeling with PMWIN, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin, p 346
Dagan G, Indelman P (1993) Upscaling of permeability of anisotropic formations 2. General structure and small perturbation analysis. Water Resour Res 29(4):923–933
Danilov VV (2010) Mathematical modeling of deep disposal of liquid radioactive waste (for example, the Siberian chemical combine): Ph.D thesis, National Research Nuclear University MEPhI, Russia (in Russian)
De Marsily Gh, Delay F, Goncalves J, Renard Ph, Teles V (2005) Dealing with spatial heterogeneity. Hydrogeol J 13:161–183
Dell’Arciprete D, Vassena C, Baratelli M, Giudici M, Bersezio R, Felletti F (2014) Connectivity and single/dual domain transport models: tests on a point-bar/channel aquifer analogue. Hydrogeol J. doi:10.1007/s10040-014-1105-5
Desbarats AJ, Bachu S (1994) Geostatistical analysis of aquifer heterogeneity from the core scale to the basin-scale—a case-study. Water Resour Res 30(3):673–684
Detbarats AJ (1992) Spatial averaging of hydraulic conductivity in three dimensional heterogeneous porous medium. Math Geol 24(3):249–267
Deutsch C, Journel A (1992) GSLIB: geostatistical software library and usres guide. Oxford University Press, New York, 340 p
Engdahl N, Weissmann G (2010) Anisotropic transport rates in heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour Res 46. doi:10.1029/2009WR007910
Engdahl NB, Vogler ET, Weissmann GS (2010) Evaluation of aquifer heterogeneity effects on river flow loss using a transition probability framework. Water Resour Res 46. doi:10.1029/2009WR0079032010
Falivene O, Cabrera L, Munoz JA, Arbues P, Fernandez O, Saez A (2007) Statistical grid-based facies reconstruction and modeling for sedimentary bodies. Alluvial-palustrine and turbiditic examples. Geol Acta 5(3):199–230
Feehley CE, Zheng C, Molz FJ (2000) A dual-domain mass transfer approach for modeling solute transport in heterogeneous aquifers: application to the macrodispersion experiment (MADE) site. Water Resour Res 36(9):2501–2515
Fleckenstein JH, Fogg GE (2008) Efficient upscaling of hydraulic conductivity in heterogeneous alluvial aquifers. Hydrogeol J 16:1239–1250
Fogg GE, Carle SF, Green C (2000) Connected-network paradigm for the alluvial aquifer system. In: Zhang D, Winter CL (eds) Theory, modeling, and field investigation in hydrogeology: a special volume in honor of Shlomo P Neuman’s 60th Birthday: Boulder, Colorado. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 348:25–42
Foley MG, Bradley DG, Cole CR, Hanson JP, Hoover KA, Perkins WA, Williams MD (1995) Hydrogeology of West Siberian Basin and Tomsk region. PNL-10585. Pacific Northwest Laboratory, Richland
Gelhar LW (1993) Stochastic subsurface hydrology. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs 390 p
Glinskii ML, Pozdniakov SP, Chertkov LG, Zubkov AA, Danilov VV, Bakshevskaia VA, Samartsev VN (2014) Regional flow and transport simulation of liquid radioactive waste disposal at the Siberian chemical combine for long- and super-long-term postinjection periods. Radiochemistry 56(6):649–656
Gómez-Hernández JJ, Wen X-H (1998) To be or not to be multi-Gaussian? A reflection on stochastic hydrogeology. Adv Water Res 21(1):47–61
Harbaugh AW, Banta ER, Hill MC, McDonald MG (2000) MODFLOW-2000, the US geological survey modular ground-water model-user guide to modularization concepts and the ground-water flow process. Open-file report 00–92, U.S. Geological Survey Reston, p 130
Indelman P (1993) Upscaling of permeability of anisotropic heterogeneous formations: 3. Applications. Water Resour Res 29(4):935–943
Jury WA, Roth K (1990) Transfer functions and solute movement through soil: theory and applications. Birkhfiuser Verlag Basel, Boston 346 p
Knudby C, Carrera J (2005) On the relationship between indicators of geostatistical, flow and transport connectivity. Adv Water Resour 28:405–421
Koltermann CE, Gorelick SM (1996) Heterogeneity in sedimentary deposits: a review of structure-imitating, process-imitating, and descriptive approaches. Water Resour Res 32(9):2617–2658
Lee S-Y, Carl SF, Fogg GE (2007) Geologic heterogeneity and a comparison of two geostatistical models: sequential Gaussian and transition probability-based geostatistical simulation. Adv Water Resour 30:1914–1932
Li L, Zhou H, Gómez-Hernández JJ (2011) A comparative study of three-dimensional hydraulic conductivity upscaling at the macro-dispersion experiment (MADE) site, Columbus Air Force Base, Mississippi (USA). J Hydrol 404:278–293
Liu G, Zheng C, Gorelick SM (2004) Limits of applicability of the advection-dispersion model in aquifers containing connected high-conductivity channels. Water Resour Res, 40. doi:10.1029/2003WR002735
Maji R, Sudicky EA, Panday S, Teutsch G (2006) Transition probability/Markov chain analysis of DNAPL Source Zone and plumes. Ground Water 44(6):853–863
Neuman SP, Tartakovsky DM (2009) Perspective on theories of non-Fickian transport in heterogeneous media. Adv Water Resour 32:670–680
Pozdniakov S, Tsang CF (1999) A semianalytical approach to spatial averaging of hydraulic conductivity. J Hydrol 216(1–2):78–98
Pozdniakov SP, Bakshevskaya VA, Krohicheva IA, Danilov VV, Zubkov AA (2012) The influence of conceptual model of sedimentary formation hydraulic heterogeneity on contaminant transport simulation. Moscow Univ Geol Bull 67(1):43–51
Pozdniakov SP, Bakshevskaya VA, Zubkov AA, Danilov VV, Rybalchenko AI, Tsang C-F (2003) 3D modeling of injected waste transport in sandy-clay formation. Second international symposium “underground injection science and technology”, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. Berkeley, California, October 22–25, pp 51–52
Pozdniakov SP, Bakshevskaya VA, Zubkov AA, Danilov VV, Rybalchenko AI, Tsang C-F (2005) Modeling of waste injection in heterogeneous sandy-clay formation. In: Tsang C-F, Apps JA (eds) Underground injection science and technology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 203–219
Renard Ph, De Marsily G (1997) Calculating equivalent permeability: a review. Adv Water Resour 20(5):253–278
Renard Ph, Le Loc’h, Ledoux E, Marsily G, Mackay R (2000) A fast algorithm for the estimation of the equivalent hydraulic conductivity of heterogeneous media. Water Resour Res 36(12):3567–3580
Ritzi RW (2000) Behavior of indicator variograms and transition probabilities in relation to the variance in lengths of hydrofacies. Water Resour Res 36(11):3375–3381
Rybalchenko AI, Pimenov MK, Kostin PP, Balukova VD, Nosuckhin AV, Mikerin EI, Egorov NN, Kaimin EP, Kosareva IM, Kurochkin VM (1998) Deep injection disposal of liquid radioactive waste in Russia. In: Foley MG, Ballou L (eds) Battelle Press, Columbus Richland, p 205
Shestakov VM, Kuvaev AA, Lekhov AV, Pozdniakov SP, Rybalchenko AI, Zubkov AV, Davis PA, Kalinina EA (2002) Flow and transport modeling of liquid radioactive waste injection using data from the Siberian chemical plant injection site. Environ Geol 42(2–3):214–221
Sun AY, Ritzi RW, Sims DW (2008) Characterization and modeling of spatial variability in a complex alluvial aquifer: implications on solute transport. Water Resour Res 44. doi:10.1029/2007WR006119
Voss CI, Provost AM (2002) SUTRA, a model for saturated-unsaturated variable-density ground-water flow with solute or energy transport, U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations. Report 02–4231:291p
Weissmann GS, Fogg GE (1999) Multi-scale alluvial fan heterogeneity modeled with transition probability geostatistics in a sequence stratigraphic framework. J Hydrol 226:48–65
Ye M, Khaleel R (2008) A Markov chain model for characterizing media heterogeneity and sediment layering structure. Water Resour Res 44. doi:10.1029/2008WR006924
Yu C, Warrick AW, Conklin MH (1999) A moment method for analyzing breakthrough curves of step inputs. Water Resour Res 11:3567–3572
Zhang Y, Benson D, Baeumer B (2007) Predicting the tails of breakthrough curves in regional-scale alluvial systems. Ground Water 45(4):473–484
Zheng C, Gorelick SM (2003) Analysis of solute transport in flow fields influenced by preferential flowpaths at the decimeter scale. Ground Water 41(2):142–155
Zinn B, Harvey CF (2003) When good statistical models of aquifer heterogeneity go bad: a comparison of flow, dispersion, and mass transfer in connected and multivariate Gaussian hydraulic conductivity fields. Water Resour Res 39(3):1051–1068
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (projects 14-05-00409-a).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakshevskaia, V.A., Pozdniakov, S.P. Simulation of Hydraulic Heterogeneity and Upscaling Permeability and Dispersivity in Sandy-Clay Formations. Math Geosci 48, 45–64 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-015-9590-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-015-9590-1