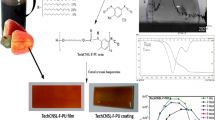
The fracture of guanidine-containing polymers and the chemical and physicomechanical properties of the synthesized materials under the influence of hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacteria (HOB) were studied. Scanning electron microscopy revealed the formation of a HOB biofilm on the surface of the studied materials. Such polymers inhibited catalase and lipolytic activity 1.3–3 times compared to the environment under control. According to the obtained data, the fracture of guanidine polymers was insignificant (4.4–6.53%). The physicomechanical properties of the materials – tensile strength and relative elongation practically did not change during 180 days of the experiment. These results are consistent with the results of IR microscopy. The method of thermogravimetric analysis showed that for the two studied materials, the initial temperature of decomposition did not decrease and their properties after exposure to the HOB did not change. It can be assumed that under the influence of bacteria on the surfaces of these polymers, minor surface biodegradation may have occurred. Therefore, the tested polyurethane-based material is promising for protecting various structures against biodamage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. I. Andreyuk, I. P. Kozlova, Zh. P. Kopteva, A. I. Pidlyashenko-Novokhatyi, V. V. Zanina, and L. M. Purish, Microbial Corrosion of Underground Structures [in Ukrainian], Naukova Dumka, Kyiv (2005).
K. S. Mohan, and T. Srivastava, “Microbial deterioration and degradation of polymeric materials,” J. Biochem Techn., 2, Is. 4, 210–215 (2010).
J.-G. Gu, and J.-D. Gu, “Methods currently used in testing microbiological degradation and deterioration of a wide range of polymeric materials with various degree of degradability: A review,” J. of Polymers and the Environment, 13, Is. 1, 65–74 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-004-1230-7
M. J. Larkin, L. A. Kulakov, and C. C. Allen, “Biodegradation and Rhodococcus – Masters of catabolic versatility,” Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 16, Spec. Is. 3, 282–290 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2005.04.007
M. Ya. Vortman, Yu. B. Pysmenna, A. I. Chuenko, D. R. Abdulina, Zh. P. Kopteva, A. E. Kopteva, A. V. Rudenko, V. V. Tretyak, V. N. Lemeshko, and V. V. Shevchenko, “Fungicidal and bactericidal activity of the alkyl-substituted guanidine-containing oligomers,” Mikrobiol. Zhurnal., 82, Is. 6, 54–63 (2020). https://doi.org/10.15407/microbiol82.06.054
Zh. P. Kopteva , and V. V. Zanina, “Microbial biofilms on protective layers of underground metal structures,” Mikrobiol. Zhurnal., 70, Is. 4, 71–85 (2008).
D. R. Abdulina, Zh. P. Kopteva, A. E. Kopteva, and M. Ya. Vortman, “Microbial destruction of polymeric materials: polyethylene foam, ethylene vinylacetate, and rubber,” Mater. Sci., 57, No. 4, 562–571 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-022-00579-w
S. Divjalakshmi, A. Subhashini, “Screening and isolation of polyethylene degrading bacteria from variouses soil enviroments,” J. of Environmental Sci. Toxicology and Food Techn., 10, 1–7 (2016).
G. O. Iutynska, N. Ya. Vortman, D. R. Abdulina, Zh. P. Kopteva, A. Ye. Kopteva, A. V. Rudenko, V. V. Tretyak, V. N. Lemeshko, and V. V. Shevchenko, “Biodegradation and antimicrobial activity of guanidine-containing polyethylene oxide hydrogel,” Biotechnologia Acta, 13, Is. 4, 60–70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.15407/biotech13.04.060
M. Ya. Vortman, Zh. P. Kopteva, A. E. Kopteva D. R. Abdulina, G. O. Iutynska, V. N. Lemeshko, and V. V. Shevchenko, “Microbial degradation of polyeterguanidinacrylates,” Functional Mater., 29, Is. 1, 107–117 (2022).
C. Belifore, M. V. Curia, and M. E. Farius, “Characterization of Rhodococcus sp. A5wh isolated from a high altitude Andean lake to unravel the survival strategy under lithium stress,” Rev. Argent. Microbiol., 50, Is. 3, 311–322 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ram.2017.07.005
A. Lugauskas, L. Levinskaite, and D. Peciulyte, “Micromycetes as deterioration agents of polymeric materials,” Int. Biodeterior and Biodegrad., 52, Is. 4, 233–242 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0964-8305(03)00110-0
J. Kyrikov, and E. D. Briassoulis, “Biodegradation of agricultural plastic films: A critical review,” J. Polymer and the Environment, 15, 125–150 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-007-0053-8
F. Ahimou, M. J. Semmens, G. Haugstad, and P. J. Novak, “Effect of protein, polysaccharide, and oxygen concentration profiles on biofilm cohesiveness,” Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,73, 2905–2910 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02420-06
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizyko-Khimichna Mekhanika Materialiv, Vol. 59, No. 4, 108–1116, July–August, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kopteva, Z.O., Vortman, M.Y., Iutynska, G.O. et al. Microbial Destruction of Guanidine-Containing Polymers. Mater Sci 59, 494–503 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-024-00803-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-024-00803-9