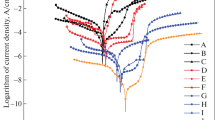
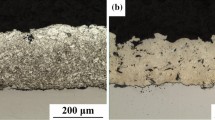
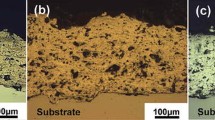
We study the corrosion of a hot-dip zinc coating and arc-sprayed aluminum and zinc coatings in chloride- acetate solutions and model seawater saturated with hydrogen sulfide. It is shown that, in chloride–acetate solutions, hydrogen sulfide promotes an increase in the corrosion rate of 20 steel by more than an order of magnitude. For the hot-dip zinc coatings, hydrogen sulfide does not change the corrosion rate, whereas for the arc-sprayed coatings, it decreases the corrosion rate by a factor of ∼ 5. The saturation of model seawater with hydrogen sulfide decreases the corrosion rate of 20 steel by a factor of ∼ 7 and the corrosion rate of the hot-dip zinc coating by a factor of ∼ 1.4 but does not affect the corrosion rate of the arc-sprayed coating. The insoluble corrosion product of zinc, namely, its sulfide, does not passivate these coatings. Hydrogen sulfide leads to an insignificant increase in the corrosion rate of the arc-sprayed aluminum coating both in a chloride–acetate solution and in model seawater. Its values are 3–7 times lower than for 20 steel, which indicates the possibility of application of the coatings based on aluminum for the corrosion protection of steels in hydrogen-sulfide-containing media.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. М. Zharskii, N. P. Ivanova, D. V. Kuis, and N. А. Svidunovich, Corrosion and Protection of Metalworks and Equipment: A Textbook [in Russian], Vysshaya Shkola, Minsk (2012).
E. Bardal, Corrosion and Protection, Springer, London–New York (2004).
A. Philip and P. E. Schweitzer, Paint and Coatings: Applications and Corrosion Resistance, CRC Press, Taylor & Francis (2006).
E. I. Kryzhanivs’kyi, M. K. Il’nyts’kyi, and R. S. Yaremiichuk, Marine Stationary Platforms: A Handbook for Students [in Ukrainian], Ivano-Frankivs'k State Technical University of Oil and Gas, Ivano-Frankivs'k (1996).
E. I. Kryzhanivs’kyi and L. Ya. Poberezhnyi, “Corrosion of marine hydroengineering installations,” in: Proc. of the 8th Int. Conf. “Problems of Corrosion and Corrosion Protection of Structural Materials” [in Ukrainian], No. 5, Vol. 1 (2006), pp. 155–159.
P. Maass and P. Peissker, Handbook of Hot-Dip Galvanization, Wiley, New York (2011).
E. V. Proskurkin and D. A. Sukhomlin, “Influence of the galvanizing method on the physicomechanical, electrochemical, and protective properties of zinc coatings,” Korroz.: Mater., Zashch., No. 5, 34–42 (2006).
E. V. Proskurkin, “Protective zinc coatings for severe corrosion-erosion conditions of operation,” Teor. Neftegaz, No. 9, 42–51 (2009).
Z. Ahmad, Principles of Corrosion Engineering and Corrosion Control, Elsevier, Boston, (2006).
C. Vargel, Corrosion of Aluminum, Elsevier, Amsterdam–Boston (2004).
V. І. Pokhmurs’kyi, М. М. Student, V. М. Dovhunyk, H. V. Pokhmurs’ka, and I. I. Sydorak, Electric-Arc Restoring and Protective Coatings [in Ukrainian], Karpenko Physicomechanical Institute, Ukrainian National Academy of Sciences, Lviv (2005).
NACE Standard TM 0284-90. Standard Test Method. Evaluation of Pipeline Steels for Resistance to Stepwise Cracking, National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE), Houston, TX (1990).
I. A. Kuz’mina, Content of Dissolved Oxygen in Water: Methodical Guidelines [in Russian], Novgorod State University, Velikii Novgorod (2007).
H. Ma, X. Cheng, G. Li, S. Chen, Z. Quan, S. Zhao, and L. Niu, “The influence of hydrogen sulfide on corrosion of iron under different conditions,” Corros. Sci., 42, No. 10, 1669–1683 (2000).
R. A. Lidin, V. A. Molochko, and L. L. Andreeva, Chemical Properties of Inorganic Substances: A Tutorial for Higher Educational Institutions [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (2000).
R. A. Kiper, Physicochemical Properties of Substances: A Handbook of Chemistry [in Russian], Khabarovsk (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizyko-Khimichna Mekhanika Materialiv, Vol. 54, No. 3, pp. 136–141, May–June, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoma, М.S., Ivashkiv, V.R., Datsko, B.М. et al. Influence of Hydrogen Sulfide on the Corrosion-Electrochemical Properties of 20 Steel with Coatings Based on Zinc and Aluminum. Mater Sci 54, 438–443 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-018-0203-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-018-0203-2