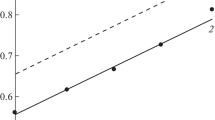
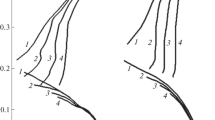
We study the corrosion behavior of electrode materials in the alkaline-water electrolysis within a broad range of electrolyte concentrations and for electrodes of different nature. It is discovered that the use of steel materials with low contents of chromium and vanadium impurities (0.1–0.3%) increases the corrosion resistance of the electrodes and weakens the dissolution of iron of steel anodes. The operation of anodes made of aluminum- and zinc-based alloys is accompanied by their dissolution. This fact makes it possible (due to the depolarization of the anodic process) to exclude the oxygen release by the mechanism of hydrogen depolarization, substantially simplify the technology of electrochemical synthesis of hydrogen, and to reduce the losses of materials and energy for the electrolysis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. M. Stepanenko, L. G. Reiter, V. M. Ledovs’kykh, and S. V. Ivanov, General and Inorganic Chemistry [in Ukrainian], Ped. Presa, Kiev (2000), Part 2.
A Handbook of a Chemist [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1964), Vol. 3.
A. N. Smirnov, “Investigation of the microstructure and the phase composition of 12Kh1MF steel after long-term operation,” Vestn. Kuzbass. Gos. Tekh. Univ., No. 2, 67–72 (2004).
B. I. Bairachnyi, G. G. Tul’s’kyi, V. V. Shtefan, and I. A. Tokareva, Industrial Electrochemistry: Chemical Current Sources, Electrolysis of the Melts, Electrosynthesis of Chemical Substances [in Ukrainian], Pidruchnyk NTU “KhPI”, Kharkiv (2016).
N. P. Zhuk, A Course of the Theory of Corrosion and Protection of Metals [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1976).
H. Nykyforchyn, E. Lunarska, O. Tsyrulnyk, et al., “Environmentally assisted “in-bulk” steel degradation of long-term service gas trunkline,” Eng. Failure Anal., 17, 624–632 (2010).
L. F. Kozin and S. V. Volkov, Contemporary Power Engineering and Ecology: Problems and Prospects [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (2006).
I. V. Gorynin and B. T. Timofeev, “Aging of materials of the equipment of nuclear power plants after designed service life,” Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mat., 42, No. 2, 13–27 (2006); English translation : Mater. Sci., 42, No. 2, 155–169 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizyko-Khimichna Mekhanika Materialiv, Vol. 53, No. 3, pp. 32–36, May–June, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bairachnyi, B.I., Zhelavs’kyi, S.G., Maizelis, A.O. et al. Corrosion Behavior of Electrode Materials in the Production of Hydrogen. Mater Sci 53, 324–329 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-017-0078-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-017-0078-7