Abstract
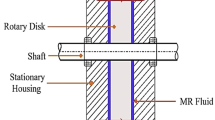
This paper proposes a new design for an automotive magnetorheological (MR) braking system using multiple rotary disks. We develop an analytical model to calculate the torque and validate our results using finite element analysis considering a non-linear relationship between magnetic field and magnetic flux. Using genetic algorithm, we optimize the system’s dimensions to generate maximum torque. The optimized geometry shows an improvement in output torque compared to existing systems. Moreover, our design directs higher flux onto the MR fluid and subsequently generates greater shear frictions. This design can be used in applications such as rehabilitation devices.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assadsangabi, B., Daneshmand, F., Vahdati, N., Eghtesad, M., Bazargan-Lari, Y.: Optimization and design of disk type MR brakes. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 12(6), 921–932 (2011)
Avraam, M., Horodinca, M., Letier, P., Preumont, A.: Portable smart wrist rehabilitation device driven by rotational MR fluid brake actuator for telemedecine applications. In: IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, IROS 2008, pp. 1441–1446. IEEE, Sept 2008
Avraam, M.T.: Magnetorehological fuid brake design and its application to a portable muscular rehabilitation device. Master’s thesis, Universite Libre de Bruxelles (2009)
Bucchi, F., Forte, P., Frendo, F.: Temperature effect on the torque characteristic of a magnetorheological clutch. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 22(1–2), 150–158 (2015)
Chi, Z., Zhang, D.: Multi-objective optimization of stiffness and workspace for a parallel kinematic machine. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 9(3), 281–293 (2013)
Du, G., Chen, X.: MEMS magnetometer based on magnetorheological elastomer measurement. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 45(1), 54–58 (2012)
Erol, O., Gurocak, H.: Interactive design optimization of magnetorheological brake actuators using the taguchi method. Smart Mater. Struct. 20(10), 105027 (2011)
Hong, S.R., Choi, S.B., Jung, W.J., Jeong, W.B.: Vibration isolation of structural systems using squeeze mode ER mounts. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 7(8), 421–424 (2002)
Huang, J., Zhang, J.Q., Yang, Y., Wei, Y.Q.: Analysis and design of a cylindrical magnetorheological fluid brake. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 129, 559–562 (2002)
Hung, N.Q., Bok, C.S.: Optimal design of a T-shaped drum-type brake for motorcycle utilizing magnetorheological fluid. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 40(2), 153–162 (2012)
Karakoc, K., Park, E.J., Suleman, A.: Design considerations for an automotive magnetorheological brake. Mechatronics 18(8), 434–447 (2008)
Kwan, A.K., Nam, T.H., Young, Y.: New approach to design MR brake using a small steel roller as a large size magnetic particle. In: International conference on control, automation and systems, ICCAS 2008, pp. 2640–2644. IEEE, Oct 2008
Li, W.H., Du, H.: Design and experimental evaluation of magnetorheological brake. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 21(7), 508–515 (2003)
Liu, G.P., Han, X., Jiang, C.: An efficient multi-objective optimization approach based on the micro genetic algorithm and its application. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 8(1), 37–49 (2012)
Lord Corporation, Technical Datasheet (2008)
Nam, T.H., Ahn, K.K.: A new structure of MR brake with the waveform boundary of rotary disk. In: ICCAS-SICE, 2009, pp. 2997–3002 (2009)
Nguyen, Q., Choi, S.: Optimal design of an automotive magnetorheological brake considering geometric dimensions and zero field friction heat. Smart Mater. Struct. 19(11), 115024 (2010)
Nguyen, Q., Choi, S.: Selection of magnetorheological brake types via optimal design considering maximum torque and constrained volume. Smart Mater. Struct. 21(1), 015012 (2012)
Nguyen, Q.H., Lang, V.T., Nguyen, N.D., Choi, S.B.: Geometric optimal design of a magneto-rheological brake considering different shapes for the brake envelope. Smart Mater. Struct. 23(1), 015020 (2014)
Niranjan, M., Jha, S., Kotnala, R.K.: Ball end magnetorheological finishing using bidisperse magnetorheological polishing fluid. Mater. Manuf. Process. 29(4), 487–492 (2014)
Park, E.J., Stoikov, D., da Luz, L.F., Suleman, A.: A performance evaluation of an automotive magnetorheological brake design with a sliding mode controller. Mechatronics 16(7), 405–416 (2006)
Park, E.J., da Luz, L.F., Suleman, A.: Multidisciplinary design optimization of an automotive magnetorheological brake design. Comput. Struct. 86(3), 207–216 (2008)
Rajamohan, V., Sedaghati, R., Rakheja, S.: Vibration analysis of a multi-layer beam containing magnetorheological fluid. Smart Mater. Struct. 19(1), 015013 (2010)
Rankin, P.J., Ginder, J.M., Klingenberg, D.J.: Electro- and magneto-rheology. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 3(4), 373–381 (1998)
Sarkar, C., Hirani, H.: Design of a squeeze film magnetorheological brake considering compression enhanced shear yield stress of magnetorheological fluid. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol. 412, p. 012045. IOP Publishing (2013)
Singh, A.K., Jha, S., Pandey, P.M.: Magnetorheological ball end finishing process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 27(4), 389–394 (2012)
Talbi, E.-G.: Metaheuristics: from design to implementation, vol. 74. Wiley, New York (2009)
Venkatachalam, R., Prabu, S.B., Raja, K.V.: Effect of constrained layers on vibrational characteristics of a composite sandwich system—a finite element based critical investigation. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 7(4), 291–298 (2011)
Weiss, K.D., Carlson, J.D., Nixon, D.A.: Viscoelastic properties of magneto- and electro-rheological fluids. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 5(6), 772–775 (1994)
Yang Jr, G., Carlson, D., Sain, K.: Large-scale MR fluid dampers: modeling and dynamic performance considerations. Eng. Struct. 24, 309–323 (2002)
Yao, G., Yap, F., Chen, G., Li, W., Yeo, S.: MR damper and its application for semi-active control of vehicle suspension system. Mechatronics 12(7), 963–973 (2002)
Yazid, I.I.M., Mazlan, S.A., Kikuchi, T., Zamzuri, H., Imaduddin, F.: Design of magnetorheological damper with a combination of shear and squeeze modes. Mater. Des. 54, 87–95 (2014)
Yeh, Z.F., Shih, Y.S.: Dynamic stability of a sandwich beam with magnetorheological core. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 34(2), 181–200 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hajiyan, M., Mahmud, S., Biglarbegian, M. et al. A new design of magnetorheological fluid based braking system using genetic algorithm optimization. Int J Mech Mater Des 12, 449–462 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-015-9322-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-015-9322-1