Abstract
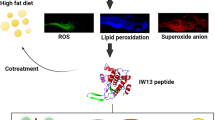
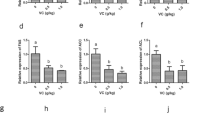
Obesity is one of the major contributing factors responsible for the onset of various metabolic syndrome. In obesity-related metabolic syndrome, increased oxidative stress in accumulated fat is a key pathogenic mechanism. The aim of this study is to investigate the lipid-lowering and antioxidant effects of RF13 peptide derived from vacuolar protein sorting associated protein 26B (VPS26B) in high fat diet (HFD) induced zebrafish larvae. Based on the arrangement, composition, and bioinformatics analysis of the VPS26B protein sequence, we predicted and synthesized a short peptide, 1RRGKGGRRVTMSF13 (RF13). In vitro analysis (DPPH, ABTS and nitric oxide assay) of RF13 on showed its potential antioxidant properties and radical scavenging capacity. Rat skeletal muscle cells (L6) and human erythrocyte cells are used for the evaluation of RF13 cytotoxicity at differing concentrations showed no cytotoxic effect. Zebrafish larvae feeding HFD, on day 4 post fertilization (dpf) to 6 dpf, there was an increase in production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid accumulation, which showed decreased expression of antioxidative enzymes such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), glutathione reductase (GR) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). However, RF13 treatment has significantly reduced the total cholesterol and triglycerides levels, enhanced antioxidant enzyme levels, and decreased lipid peroxidation. In addition, RF13 treatment has significantly decreased lipid accumulation, intracellular ROS and apoptosis in zebrafish larvae as compared to the HFD group. Furthermore, RF13 significantly downregulated the lipid metabolizing genes such as CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α (C/EBP-α), sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1) and fatty acid synthase (FAS), while they upregulated the antioxidant-related genes. These results suggests that RF13 peptides can be used as functional foods and natural drugs to enhance the antioxidant ability and also to alleviate lipid accumulation by regulating lipid metabolism.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- VPS26B:
-
Vacuolar protein sorting associated protein 26B
- HFD:
-
High fat diet
- FAS:
-
Fatty acid synthase
- LPL:
-
Lipoprotein lipase
- PPAR :
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- C/EBP-α:
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α
- SREBP1:
-
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- DPPH:
-
2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl
- ABTS:
-
2,2 -azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid
- HFD:
-
High fat diet
- DCFDA:
-
2’-7’-dichlorofluorescein diacetate
- DPPP:
-
Diphenyl-1-pyrenylphosphine
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
References
Ahmad O, Wang B, Ma K, Deng Y, Li M, Yang L, Yang Y, Zhao J, Cheng L, Zhou Q, Shang J (2019) Lipid modulating anti-oxidant stress activity of gastrodin on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease larval zebrafish model. Int J Mol Sci 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081984
Alam MA, Kauter K, Withers K, Sernia C, Brown L (2013) Chronic l-arginine treatment improves metabolic, cardiovascular and liver complications in diet-induced obesity in rats. Food Funct 4:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2fo30096f
Arockiaraj J, Gnanam AJ, Muthukrishnan D, Pasupuleti M, Milton J, Singh A (2013) An upstream initiator caspase 10 of snakehead murrel Channa striatus, containing DED, p20 and p10 subunits: Molecular cloning, gene expression and proteolytic activity. Fish Shellfish Immunol 34:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2012.11.040
Batista ÂG, Lenquiste SA, Cazarin CBB, da Silva JK, Luiz-Ferreira A, Bogusz S, Wang Hantao L, de Souza RN, Augusto F, Prado MA, Maróstica MR (2014) Intake of jaboticaba peel attenuates oxidative stress in tissues and reduces circulating saturated lipids of rats with high-fat diet-induced obesity. J Funct Foods 6:450–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2013.11.011
Belguith-Hadriche O, Ammar S, Contreras MdelM, Turki M, Segura-Carretero A, Feki E, Makni-Ayedi A, Bouaziz F, M (2016) Antihyperlipidemic and Antioxidant Activities of Edible Tunisian Ficus carica L. Fruits in High Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 71:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-016-0541-x
Birari RB, Bhutani KK (2007) Pancreatic lipase inhibitors from natural sources: unexplored potential. Drug Discov Today 12:879–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2007.07.024
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: A review. Ann Bot 91:179–194. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcf118
Braford MM, Rapid A (1976) and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding.Anal. Biochem.72,248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2017.04.003
Bray GA (2005) Drug treatment of obesity. Psychiatr Clin North Am 28:193–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psc.2004.09.009
Carmiel-Haggai M, Cederbaum AI, Nieto N (2005) A high-fat diet leads to the progression of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese rats. FASEB J 19:136–138. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-2291fje
Cha SH, Hwang Y, Heo SJ, Jun HS (2020) Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol attenuates palmitate-induced hepatic lipogenesis and inflammation. Mar Drugs 18:2–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18090475
Chang Y, Edeen K, Lu X, De Leon M, Mason RJ (2006) Keratinocyte growth factor induces lipogenesis in alveolar type II cells through a sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c-dependent pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 35:268–274. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2006-0037OC
Dandona P, Ghanim H, Chaudhuri A, Dhindsa S, Kim SS (2010) Macronutrient intake induces oxidative and inflammatory stress: Potential relevance to atherosclerosis and insulin resistance. Exp Mol Med 42:245–253. https://doi.org/10.3858/emm.2010.42.4.033
Dash P, Ghosh G (2017) Amino acid composition, antioxidant and functional properties of protein hydrolysates from Cucurbitaceae seeds. J Food Sci Technol 54:4162–4172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2855-6
Flynn EJ, Trent CM, Rawls JF (2009) Ontogeny and nutritional control of adipogenesis in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Lipid Res 50:1641–1652. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M800590-JLR200
Friedman JM, Obesity (2009) : Causes and control of excess body fat.Nature459,340–342. https://doi.org/10.1038/459340a
Gopinath P, Jesu A, Manjunathan T, Ajay G (2021) 6-Gingerol and semisynthetic 6‐Gingerdione counteract oxidative stress induced by ROS in zebrafish. Chem Biodivers 17:100374. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202100650
Guru A, Issac PK, Saraswathi NT, Seshadri VD, Gabr GA, Arockiaraj J (2021a) Deteriorating insulin resistance due to WL15 peptide from cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 in high glucose‐induced rat skeletal muscle L6 cells. Cell Biol Int 45:1698–1709. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11608
Guru A, Issac PK, Velayutham M, Saraswathi NT, Arshad A, Arockiaraj J (2021b) Molecular mechanism of down-regulating adipogenic transcription factors in 3T3-L1 adipocyte cells by bioactive anti-adipogenic compounds. Mol Biol Rep 48:743–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-06036-8
Guru A, Lite C, Freddy AJ, Issac PK, Pasupuleti M, Saraswathi NT, Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Arshad A, Arockiaraj J (2021c) Intracellular ROS scavenging and antioxidant regulation of WL15 from cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 demonstrated in zebrafish in vivo model. Dev Comp Immunol 114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2020.103863
Hachicho N, Reithel S, Miltner A, Heipieper HJ, Küster E, Luckenbach T (2015) Body mass parameters, lipid profiles and protein contents of zebrafish embryos and effects of 2,4-dinitrophenol exposure. PLoS ONE 10:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134755
Issac PK, Guru A, Chandrakumar SS, Lite C, Saraswathi NT, Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Arshad A, Arockiaraj J (2020) Molecular process of glucose uptake and glycogen storage due to hamamelitannin via insulin signalling cascade in glucose metabolism. Mol Biol Rep 47:6727–6740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05728-5
Issac PK, Guru A, Velayutham M, Pachaiappan R, Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Choi KC, Harikrishnan R, Arockiaraj J (2021a) Oxidative stress induced antioxidant and neurotoxicity demonstrated in vivo zebrafish embryo or larval model and their normalization due to morin showing therapeutic implications. Life Sci 283:119864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119864
Issac PK, Karan R, Guru A, Pachaiappan R, Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Choi KC, Harikrishnan R, Raj JA (2021b) Insulin signaling pathway assessment by enhancing antioxidant activity due to morin using in vitro rat skeletal muscle L6 myotubes cells. Mol Biol Rep 48:5857–5872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06580-x
Issac PK, Lite C, Guru A, Velayutham M, Kuppusamy G, Saraswathi NT, Olayan A, Aloufi EM, Elokaby AS, Elumalai MA, Arshad P, Arockiaraj A, J (2021c) Tryptophan-tagged peptide from serine threonine-protein kinase of Channa striatus improves antioxidant defence in L6 myotubes and attenuates caspase 3–dependent apoptotic response in zebrafish larvae. Fish Physiol Biochem 47:293–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00912-7
Jiang JF, Xu ZR, Wang YZ, Han XY, Wang L (2006) Postnatal expression pattern of the C/EBP alpha gene in porcine subcutaneous adipose tissue. J Anim Feed Sci 15:61–70. https://doi.org/10.22358/jafs/66841/2006
Kerr MC, Bennetts JS, Simpson F, Thomas EC, Flegg C, Gleeson PA, Wicking C, Teasdale RD, Traffic (2005) 6,991–1001. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00328.x
Kesh SB, Sarkar D, Manna K (2016) High-fat diet-induced oxidative stress and its impact on metabolic syndrome: A review. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 9:38–43
Koya-Miyata S, Arai N, Mizote A, Taniguchi Y, Ushio S, Iwaki K, Fukuda S (2009) Propolis prevents diet-induced hyperlipidemia and mitigates weight gain in diet-induced obesity in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 32:2022–2028. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.32.2022
Kumaresan V, Pasupuleti M, Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Arshad A, Amin SMN, Yusoff FM, Arockiaraj J (2018) A comparative transcriptome approach for identification of molecular changes in Aphanomyces invadans infected Channa striatus. Mol Biol Rep 45:2511–2523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4418-y
Lechleitner M, Koch T, Herold M, Dzien A, Hoppichler F (2000) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha plasma level in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and its association with glycaemic control and cardiovascular risk factors. J Intern Med 248:67–76
Lee D-Y, Kim E-H (2019) Therapeutic Effects of Amino Acids in Liver Diseases: Current Studies and Future Perspectives. J Cancer Prev 24:72–78. https://doi.org/10.15430/jcp.2019.24.2.72
Lee YJ, Choi HS, Seo MJ, Jeon HJ, Kim KJ, Lee BY (2015) Kaempferol suppresses lipid accumulation by inhibiting early adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and zebrafish. Food Funct 6:2824–2833. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5fo00481k
Liang X, Yu L, Gui W, Zhu G (2015) Exposure to difenoconazole causes changes of thyroid hormone and gene expression levels in zebrafish larvae. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:983–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.10.005
Lin H, Zhou Z, Zhong W, Huang P, Ma N, Zhang Y, Zhou C, Lai Y, Huang S, An H, Sun X, Gao L, Lv Z (2017) Naringenin inhibits alcoholic injury by improving lipid metabolism and reducing apoptosis in zebrafish larvae. Oncol Rep 38:2877–2884. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5965
Liu C, Shen YJ, Tu QB, Zhao YR, Guo H, Wang J, Zhang L, Shi HW, Sun Y (2018) Pedunculoside, a novel triterpene saponin extracted from Ilex rotunda, ameliorates high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 101:608–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.131
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the Superoxide Anion Radical in the Autoxidation of Pyrogallol and a Convenient Assay for Superoxide Dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03714.x
Mashmoul M, Azlan A, Khaza’Ai H, Yusof BNM, Noor SM (2013) Saffron: A natural potent antioxidant as a promising anti-obesity drug. Antioxidants 2:293–308. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox2040293
McGrath P, Li CQ (2008) Zebrafish: a predictive model for assessing drug-induced toxicity. Drug Discov Today 13:394–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2008.03.002
McKnight JR, Satterfield MC, Jobgen WS, Smith SB, Spencer TE, Meininger CJ, McNeal CJ, Wu G (2010) Beneficial effects of L-arginine on reducing obesity: Potential mechanisms and important implications for human health. Amino Acids 39:349–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0598-z
Ming G, feng, Xiao D, Gong W, Liu H, xia, Liu J, Zhou H, Liu Z, qian (2014) JAZF1 can regulate the expression of lipid metabolic genes and inhibit lipid accumulation in adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 445:673–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.02.088
Misselbeck K, Parolo S, Lorenzini F, Savoca V, Leonardelli L, Bora P, Morine MJ, Mione MC, Domenici E, Priami C (2019) A network-based approach to identify deregulated pathways and drug effects in metabolic syndrome. Nat Commun 10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13208-z
Moon YJ, Soh JR, Yu JJ, Sohn HS, Cha YS, Oh SH (2012) Intracellular lipid accumulation inhibitory effect of Weissella koreensis OK1-6 isolated from Kimchi on differentiating adipocyte. J Appl Microbiol 113:652–658. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05348.x
Moro CO, Basile G (2000) Obesity and medicinal plants. Fitoterapia 71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0367-326X(00)00177-5
Muthu BHD, Guru A, Sudhakaran G, Murugan R, Arshad A, Arockiaraj J (2021) Double-edged sword role of shrimp miRNA explains an evolutionary language between shrimp‐pathogen interactions that unties the knot of shrimp infection. Rev Aquac 0–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12613
Noeman SA, Hamooda HE, Baalash AA (2011) Biochemical study of oxidative stress markers in the liver, kidney and heart of high fat diet induced obesity in rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr 3:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-5996-3-17
Pacher P, Beckman JS, Liaudet L (2007) Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol Rev 87:315–424. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00029.2006
Petra S, Bojan D, Samo K, Mojca L, Damjan J, Borut S (2009) Screening of Selected Food and Medicinal Plant Extracts for Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition. Phyther Res 23:874–877. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr
Rajapakse N, Mendis E, Byun HG, Kim SK (2005) Purification and in vitro antioxidative effects of giant squid muscle peptides on free radical-mediated oxidative systems. J Nutr Biochem 16:562–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.02.005
Ramachandran R, Krishnaraj C, Sivakumar AS, Prasannakumar P, Abhay Kumar VK, Shim KS, Song CG, Yun S, Il (2017) Anticancer activity of biologically synthesized silver and gold nanoparticles on mouse myoblast cancer cells and their toxicity against embryonic zebrafish. Mater Sci Eng C 73:674–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.12.110
Razak MA, Begum PS, Viswanath B, Rajagopal S (2017) Multifarious Beneficial Effect of Nonessential Amino Acid, Glycine: A Review. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1716701
Savini I (2015) Disordered eating in Obesity. Obes. A Pract. Guid. 65–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19821-7
Seaman MNJ (2004) Cargo-selective endosomal sorting for retrieval to the Golgi requires retromer. J Cell Biol 165:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200312034
Shieh YS, Chang YS, Hong JR, Chen LJ, Jou LK, Hsu CC, Her GM (2010) Increase of hepatic fat accumulation by liver specific expression of Hepatitis B virus X protein in zebrafish. Biochim Biophys Acta—Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1801:721–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.04.008
Sinha AK (1972) Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem 47:389–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(72)90132-7
Sonklin C, Laohakunjit N, Kerdchoechuen O (2018) Assessment of antioxidant properties of membrane ultrafiltration peptides from mungbean meal protein hydrolysates. PeerJ 2018. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5337
Sung YY, Yoon T, Kim SJ, Yang WK, Kim HK (2011) Anti-obesity activity of Allium fistulosum L. extract by down-regulation of the expression of lipogenic genes in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Mol Med Rep 4:431–435. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2011.451
Timme-Laragy AR, Van Tiem LA, Linney EA, Di Giulio RT (2009) Antioxidant responses and NRF2 in synergistic developmental toxicity of PAHs in Zebrafish. Toxicol Sci 109:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfp038
Türkoğlu M, Baran A, Sulukan E, Ghosigharehagaji A, Yildirim S, Ceyhun HA, Bolat İ, Arslan M, Ceyhun SB (2021) The potential effect mechanism of high-fat and high-carbohydrate diet-induced obesity on anxiety and offspring of zebrafish. Eat Weight Disord. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-021-01140-5
Udenigwe CC, Lu YL, Han CH, Hou WC, Aluko RE (2009) Flaxseed protein-derived peptide fractions: Antioxidant properties and inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in murine macrophages. Food Chem 116:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.02.046
Vargas R, Vásquez IC (2017) Effects of overfeeding and high-fat diet on cardiosomatic parameters and cardiac structures in young and adult zebrafish. Fish Physiol Biochem 43:1761–1773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-017-0407-7
Velayutham M, Guru A, Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Choi KC, Elumalai P, Harikrishnan R, Arshad A, Arockiaraj J (2021a) GR15 peptide of S-adenosylmethionine synthase (SAMe) from Arthrospira platensis demonstrated antioxidant mechanism against H2O2 induced oxidative stress in in-vitro MDCK cells and in-vivo zebrafish larvae model. J. Biotechnol. 342, 79–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.10.010
Velayutham M, Ojha B, Issac PK, Lite C, Guru A, Pasupuleti M, Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Arockiaraj J (2021b) NV14 from serine O ‐acetyltransferase of cyanobacteria influences the antioxidant enzymes in vitro cells, gene expression against H 2 O 2 and other responses in vivo zebrafish larval model. Cell Biol Int. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11680
Wang L, Jayawardena TU, Yang HW, Lee HG, Kang MC, Sanjeewa KKA, Oh JY, Jeon YJ (2020) Isolation, characterization, and antioxidant activity evaluation of a fucoidan from an enzymatic digest of the edible seaweed, hizikia fusiforme. Antioxidants 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050363
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dr. Kanchana K. Mala for providing necessary help in performing haemolytic assay and associated ethical clearance (885/IEC/2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis and investigation Writing-original draft preparation: AJ, MV; Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Supervision: JA.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Human and Animal Participants
This research does not involve any human or animal objects; however, we have collected human blood from healthy volunteers for the hemolytic assay performed in this study. The blood from the healthy individuals was collected as per the guidelines of the Institutional Ethical Committee regulation (Ethical Clearance No. 885/IEC/2015). For blood collection, informed consent was obtained from all the participated adults in written form. All authors are aware of the details of their research work that are presented in the current manuscript and gave their consent to publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guru, A., Velayutham, M. & Arockiaraj, J. Lipid-Lowering and Antioxidant Activity of RF13 Peptide From Vacuolar Protein Sorting-Associated Protein 26B (VPS26B) by Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in HFD Induced Obesity in Zebrafish Larvae. Int J Pept Res Ther 28, 74 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-022-10376-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-022-10376-3