Abstract
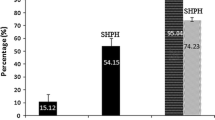
The current objective was framed on isolation of two angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from coastal trashes of squilla muscle (Harpiosquilla raphidea) prepared by enzymatic hydrolysis using alcalase, thermolysin and trypsin, which showed the highest degree of hydrolysate in 12th h hydrolysate 87.9 ± 1.6%, 63.1 ± 1.1% and 91.1 ± 2.7% respectively. Among these three hydrolysates, alcalase 5th h (64.8 ± 0.3) and thermolysin 6th h (68.4 ± 1.0) found to be maximum ACE-I inhibition activity. Initial separation was performed by ultra filtration (10–3 kDa) into three different fractions, alcalase (below 3 kDa) fraction observed maximum ACE-I inhibition activity with 75.2 ± 3.5% and thermolysin (3–10 kDa) with 79.5 ± 1.0% inhibition. Further, these two fractions have taken to ion exchange and gel filtration chromatography, the identified ACE-I inhibitory fractions (AC-A2 and TH-A2) also examined for its antioxidant properties. Further, these fractions were determined to be non-toxic against cell lines, functional activities by various assays and characterized into tri peptides MSN (Met-Ser-Asn) and MTH (Met-Thr-His) with a molecular weight of 350 Da and 388 Da respectively using LC–MS/MS. These low molecular weight peptides from natural sources may act as potential ingredient for nutraceutical and pharmaceutical industries.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aissaoui N, Abidi F, Hardouin J, Abdelkafi Z, Marrakchi N, Jouenne T, Marzouki MN (2017) ACE inhibitory and antioxidant activities of novel peptides from Scorpaena notata by-product protein hydrolysate. Int J Pept Res Therap 23:13–23
Amado IR, Vázquez JA, González P, Esteban-Fernández D, Carrera M, Piñeiro C (2014) Identification of the major ACE-inhibitory peptides produced by enzymatic hydrolysis of a protein concentrate from cuttlefish wastewater. Mar Drugs 12:1390–1405
Antonios TF, MacGregor GA (1995) Deleterious effects of salt intake other than effects on blood pressure. Clin Exp Pharm Physiol 22:180–184
Balti EV, Kengne AP, Fokouo JVF, Nouthé BE, Sobngwi E (2013) Metabolic syndrome and fatal outcomes in the post-stroke event: a 5-year cohort study in Cameroon. PLoS ONE 8:e60117
Balti R, Bougatef A, Sila A, Guillochon D, Dhulster P, Nedjar-Arroume N (2015) Nine novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) muscle protein hydrolysates and antihypertensive effect of the potent active peptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem 170:519–525
Bogard JR, Thilsted SH, Marks GC, Wahab MA, Hossain MA, Jakobsen J, Stangoulis J (2015) Nutrient composition of important fish species in Bangladesh and potential contribution to recommended nutrient intakes. J Food Compos Anal 42:120–133
Bordbar S, Ebrahimpour A, Abdul Hamid A, Abdul Manap MY, Anwar F, Saari N (2013) The improvement of the endogenous antioxidant property of stone fish (Actinopyga lecanora) tissue using enzymatic proteolysis. BioMed Res Int 2013:1–9
Bougatef A, Balti R, Nedjar-Arroume N, Ravallec R, Estelle A, Souissi N, Lassoued I, Guillochon D, Nasri M (2010) Evaluation of angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activities of smooth hound (Mustelus mustelus) muscle protein hydrolysates generated by gastrointestinal proteases: identification of the most potent active peptide. Eur Food Res Technol 23:127–135
Byun HG, Kim SK (2001) Purification and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) skin. Process Biochem 36:1155–1162
Carey RM, Siragy HM (2003) Newly recognized components of the renin-angiotensin system: potential roles in cardiovascular and renal regulation. Endocr Rev 24:261–271
Chi CF, Wang B, Wang YM, Zhang B, Deng SG (2015) Isolation and characterization of three antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of bluefin leatherjacket (Navodon septentrionalis) heads. J Funct Food 12:1–10
Cushman DW, Cheung HS (1971) Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem Pharm 20:1637–1648
Ferrero EA, Graziosi G, Marzari R, Mosco A (1983) Protein pattern variability of the hemolymph of mantis shrimp, Squilla mantis L. (crustacea, stomatopoda). J Exp Zool 225(2):341–345
Gauthier SF, Paquin P, Pouliot Y, Turgeon S (1993) Surface activity and related functional properties of peptides obtained from whey proteins1. J Dairy Sci 76:321–328
Gbogouri GA, Linder M, Fanni J, Parmentier M (2004) Influence of hydrolysis degree on the functional properties of salmon byproducts hydrolysates. J Food Sci 69:615–622
Geng X, Tian G, Zhang W, Zhao Y, Zhao L, Wang H, Ng TB (2016) A Tricholoma matsutake peptide with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory and antioxidative activities and antihypertensive effects in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci Rep 6:24130
Goupy P, Hugues M, Boivin P, Amiot MJ (1999) Antioxidant composition and activity of barley (Hordeum vulgare) and malt extracts and of isolated phenolic compounds. J Sci Food Agric 79:1625–1634
Hwang JS, Ko WC (2004) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of protein hydrolysates from tuna cooking juice. J Food Drug Anal 12:62–68
Jao CL, Ko WC (2002) 1, 1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging by protein hydrolyzates from tuna cooking juice. Fish Sci 68:430–435
Jing TY, Zhao XY (1995) The improved pyrogallol method by using termination agent for superoxide dismutase measurement. Prog Biochem Biophys 22:84–86
Joshi I, Sudhakar S, Nazeer RA (2016) Anti-inflammatory properties of bioactive peptide derived from gastropod influenced by enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 180:1128–1140
Kim SY, Park PS, Rhee KC (1990) Functional properties of proteolytic enzyme modified soy protein isolate. J Agric Food Chem 38:651–656
Kim SB, Yoon NY, Shim KB, Lim CW (2016) Antioxidant and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activities of northern shrimp (Pandalus borealis) by-products hydrolysate by enzymatic hydrolysis. Fish Aquat Sci 19:29
Klompong V, Benjakul S, Kantachote D, Shahidi F (2007) Antioxidative activity and functional properties of protein hydrolysate of yellow stripe trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as influenced by the degree of hydrolysis and enzyme type. Food Chem 102:1317–1327
Koehn FE, Carter GT (2005) The evolving role of natural products in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(3):206–220
Kohama Y, Matsumoto S, Oka H, Teramoto T, Okabe M, Mimura T (1988) Isolation of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor from tuna muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 155:332–337
Kristinsson HG, Rasco BA (2000) Fish protein hydrolysates: production, biochemical, and functional properties. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 40:43–81
Li Y, Jiang B, Zhang T, Mu W, Liu J (2008) Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of chickpea protein hydrolysate (CPH). Food Chem 106:444–450
Li R, Yang ZS, Sun Y, Li L, Wang JB, Ding G (2015) Purification and antioxidant property of antioxidative oligopeptide from short-necked clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) hydrolysate in vitro. J Aquat Food Prod Technol 24(6):556–565
Liu RL, Ge XL, Gao XY, Zhan HY, Shi T, Su N, Zhang ZQ (2016) Two angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides from almond protein and the protective action on vascular endothelial function. Food Funct 7:3733–3739
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mane S, Jamdar SN (2017) Purification and identification of Ace-inhibitory peptides from poultry viscera protein hydrolysate. J Food Biochem 41:1–10
Mohanty B, Mahanty A, Ganguly S, Sankar TV, Chakraborty K, Rangasamy A, Paul B, Sarma D, Mathew S, Asha KK, Behera B (2014) Amino acid composition of 27 food fishes and their importance in clinical nutrition. J Amino Acid 2014:7
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Method 65:55–63
Mutilangi WAM, Panyam D, Kilara A (1996) Functional properties of hydrolysates from proteolysis of heat-denatured whey protein isolate. J Food Sci 61:270–275
Ondetti MA, Rubin B, Cushman DW (1977) Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science 196:441–444
Paiva L, Lima E, Neto AI, Baptista J (2017) Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity, antioxidant properties, phenolic content and amino acid profiles of Fucus spiralis L. protein hydrolysate fractions. Mar Drugs 15:311
Patchett AA, Harris E, Tristram EW, Wyvratt MJ, Wu MT, Taub D, Peterson ER, Ikeler TJ, ten Broeke J, Payne LG, Ondeyka DL, Thorsett ED, Greenlee WJ, Lohr NS, Hoffsommer RD, Joshua H, Ruyle WV, Rothrock JW, Aster SD, Maycock AL, Robinson FM, Hirschmann R, Sweet CS, Ulm EH, Gross DM, Vassil TC, Stone CA (1980) A new class of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Nature 288:280–283
Pearce KN, Kinsella JE (1978) Emulsifying properties of proteins: evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J Agric Food Chem 26:716–723
Prieto P, Pineda M, Aguilar M (1999) Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: specific application to the determination of vitamin E. Anal Biochem 269:337–341
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med 26:1231–1237
Sachindra NM, Bhaskar N (2008) In vitro antioxidant activity of liquor from fermented shrimp biowaste. Bioresour Technol 99:9013–9016
Sathe SK, Salunkhe DK (1981) Functional properties of the great northern bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) proteins: emulsion, foaming, viscosity, and gelation properties. J Food Sci 46:71–81
Shabeena YN, Nazeer RA (2013) Antioxidant and functional properties of protein hydrolysates from pink perch (Nemipterus japonicus) muscle. J Food Sci Technol 50:972–978
Sorgentini DA, Wagner JR (2002) Comparative study of foaming properties of whey and isolate soybean proteins. Food Res Int 35:721–729
Souissi N, Bougatef A, Triki-Ellouz Y, Nasri M (2007) Biochemical and functional properties of sardinella (Sardinella aurita) by-product hydrolysates. Food Technol Biotechnol 45:187–194
Sudhakar S, Nazeer RA (2015) Preparation of potent antioxidant peptide from edible part of shortclub cuttlefish against radical mediated lipid and DNA damage. LWT Food Sci Technol 64:593–601
Wanasundara PJP, Ross AR, Amarowicz R, Ambrose SJ, Pegg RB, Shand PJ (2002) Peptides with angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity from defibrinated, hydrolyzed bovine plasma. J Agric Food Chem 50:6981–6988
Wang J, Hu J, Cui J, Bai X, Du Y, Miyaguchi Y, Lin B (2008) Purification and identification of a ACE inhibitory peptide from oyster proteins hydrolysate and the antihypertensive effect of hydrolysate in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem 111:302–308
World Health Organization Global Health Observatory (GHO) (2018) Data: raised blood pressure. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wu H, He HL, Chen XL, Sun CY, Zhang YZ, Zhou BC (2008) Purification and identification of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from shark meat hydrolysate. Process Biochem 43:457–461
Wu S, Feng X, Lan X, Xu Y, Liao D (2015) Purification and identification of Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from lizard fish (Saurida elongata) hydrolysate. J Funct Food 13:295–299
You SJ, Udenigwe CC, Aluko RE, Wu J (2010) Multifunctional peptides from egg white lysozyme. Food Res Int 43(3):848–855
Zhao Y, Li B, Dong S, Liu Z, Zhao X, Wang J, Zeng M (2009) A novel ACE inhibitory peptide isolated from Acaudina molpadioidea hydrolysate. Peptides 30:1028–1033
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant No: SB/YS/LS-328/2013 funded by the Department of Science and Technology (DST)—Science & Engineering Research Board (SERB) of the government of India. We extend our gratitude to the management and SRM Institute of Science and Technology for providing the facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Research Involving Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noorani, K.P.M., Nazeer, R.A. Enzymatic Production of Two Tri-peptides on ACE-I Inhibition and Antioxidant Activities. Int J Pept Res Ther 26, 2365–2377 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10037-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10037-3