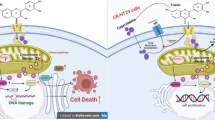
Abstract
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the world. About 18 milllion people were affected with cancer in 2018. Research in novel anti-cancer agents of bacterial origin thus gain importance. Azurin is a novel bacterial protein that has unique ability to specifically target cancer cells without any harmful effect to normal cells. In this study, cytotoxic effect of azurin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa SSj expressed in pET22b (+) vector and standard azurin (Sigma) were studied on (MCF7), (HCT15), and (VERO) cell lines by MTT assay. Apoptosis assay was performed using Hoechst staining and confirmed by FRET based assay on colon cancer cell lines (SW480). In vivo ascites antitumor model assay was also done to detect the in vivo cytotoxicity of azurin. Anti-hemolytic potential of purified azurin on human erythrocytes was also evaluated. Azurin induced cytotoxicity in both HCT15 and MCF7 cell lines, without having any adverse effect on the normal cells. Cell cycle analysis by Hoechst staining and FRET analysis, both showed evidence of apoptosis induced by azurin. In vivo ascites antitumor model proved that azurin treatment can increase the lifespan of tumor-bearing mice. Anti-hemolytic assay showed a significant increase of inhibition of hemolysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MCF7:
-
Michigan Cancer Foundation-7
- HCT 15:
-
Human colorectal carcinoma
- SW480:
-
Spectral karyotyping of the human colon cancer cell line
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-Yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- DLA:
-
Daltons lymphoma ascites
- EYFP:
-
Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein
- ECFP:
-
Enhanced cyan fluorescent protein
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- FSC:
-
Forward scatter
- SSC:
-
Side scatter
- FRET:
-
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- DEVD:
-
Aspartic acid–glutamic acid–valine–aspartic acid
References
Apiyo D, Wittung-Stafshede P (2005) Unique complex between bacterial azurin and tumor-suppressor protein p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 332(4):965–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.05.038
Chakrabarty AM (2003) Microorganisms and cancer: quest for a therapy. J Bacteriol 185(9):2683–2686
Chaudhari A, Fialho AM, Ratner D, Gupta P, Hong CS, Kahali S, Chakrabarty AM (2006) Azurin, Plasmodium falciparum malaria and HIV/AIDS: inhibition of parasitic and viral growth by Azurin. Cell Cycle 5(15):1642–1648. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.5.15.2992
Chaudhari A, Mahfouz M, Fialho AM, Yamada T, Granja AT, Zhu Y, Chakrabarty AM (2007) Cupredoxin-cancer interrelationship: azurin binding with EphB2, interference in EphB2 tyrosine phosphorylation, and inhibition of cancer growth. Biochemistry 46(7):1799–1810. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi061661x
da Rocha AB, Lopes RM, Schwartsmann G (2001) Natural products in anticancer therapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol 1(4):364–369
Elia MC, Storer RD, Harmon LS, Kraynak AR, McKelvey TW, Hertzog PR, Nichols WW (1993) Cytotoxicity as measured by trypan blue as a potentially confounding variable in the in vitro alkaline elution/rat hepatocyte assay. Mutat Res 291(3):193–205
Fialho A, Bernardes N, Chakrabarty AM (2016) Exploring the anticancer potential of the bacterial protein azurin. AIMS Microbiol 2(1):292–303. https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2016.3.292
Hashimoto W, Ochiai A, Hong CS, Murata K, Chakrabarty AM (2015) Structural studies on Laz, a promiscuous anticancer Neisserial protein. Bioengineered 6(3):141–148. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2015.1022303
Jose J, Dhanya AT, Haridas KR, Sumesh Kumar TM, Jayaraman S, Variyar EJ, Sudhakaran S (2016) Structural characterization of a novel derivative of myricetin from Mimosa pudica as an anti-proliferative agent for the treatment of cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 84:1067–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.020
Karpinski TM, Adamczak A (2018) Anticancer activity of bacterial proteins and peptides. Pharmaceutics. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020054
Lekshmi A, Varadarajan SN, Lupitha SS, Indira D, Mathew KA, Chandrasekharan Nair A, Santhoshkumar TR (2017) A quantitative real-time approach for discriminating apoptosis and necrosis. Cell Death Discov 3:16101. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2016.101
Mahfouz M, Hashimoto W, Das Gupta TK, Chakrabarty AM (2007) Bacterial proteins and CpG-rich extrachromosomal DNA in potential cancer therapy. Plasmid 57(1):4–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plasmid.2006.11.001
Mansoori GA, Mohazzabi P, McCormack P, Jabbari S (2007) Nanotechnology in cancer prevention, detection and treatment: bright future lies ahead. World Rev Sci Technol Sustain Dev 4(2):226–257. https://doi.org/10.1504/WRSTSD.2007.013584
Miyashita T, Reed JC (1995) Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell 80(2):293–299
Mohamed MS, Fattah SA, Mostafa HM (2010) Azurin as antitumor protein and its effect on the cancer cell lines. Curr Res J Biol Sci 2(6):396–401
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65(1–2):55–63
Nguyen C, Nguyen VD (2016) Discovery of Azurin-Like anticancer bacteriocins from human gut microbiome through homology modeling and molecular docking against the tumor suppressor p53. Biomed Res Int 2016:8490482. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8490482
Pasquale EB (2010) Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 10(3):165–180. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2806
Punj V, Das Gupta TK, Chakrabarty AM (2003) Bacterial cupredoxin azurin and its interactions with the tumor suppressor protein p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312(1):109–114
Punj V, Bhattacharyya S, Saint-Dic D, Vasu C, Cunningham EA, Graves J, Das Gupta TK (2004) Bacterial cupredoxin azurin as an inducer of apoptosis and regression in human breast cancer. Oncogene 23(13):2367–2378. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207376
Ramachandran S, Mandal M (2011) Induction of apoptosis of azurin synthesized from P. aeruginosa MTCC 2453 against Dalton’s lymphoma ascites model. Biomed Pharmacother 65(7):461–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2011.03.006
Ramachandran S, Sarkar S, Mazumadar A, Mandal M (2011) Azurin synthesis from Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 2453, properties, induction of reactive oxygen species, and p53 stimulated apoptosis in breast carcinoma cells. J Cancer Sci Ther. https://doi.org/10.4172/1948-5956.1000069
Sereena MC, Sebastian D (2018) Characterization of anticancer compound azurin from indigenous isolate Pseudomonas aeruginosa SSj. Int J Life Sci Res 6(4):174–179
Sobhan PK, Seervi M, Deb L, Varghese S, Soman A, Joseph J (2013) Calpain and reactive oxygen species targets Bax for mitochondrial permeabilisation and caspase activation in zerumbone induced apoptosis. PLoS ONE 8(4):e59350. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059350
Taylor BN, Mehta RR, Yamada T, Lekmine F, Christov K, Chakrabarty AM, Das Gupta TK (2009) Noncationic peptides obtained from azurin preferentially enter cancer cells. Cancer Res 69(2):537–546. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2932
Ulukaya E, Acilan C, Ari F, İkitimur E, Yilmaz Y (2011) A Glance at the methods for detection of apoptosis qualitatively and quantitatively. Turk J Biochem 36:261–269
Valli S (2018) Bioinformatic study of an antitumor protein, azurin. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 11(6):169. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11i6.23339
Yamada T, Goto M, Punj V, Zaborina O, Chen ML, Kimbara K, Chakrabarty AM (2002a) Bacterial redox protein azurin, tumor suppressor protein p53, and regression of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(22):14098–14103. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.222539699
Yamada T, Goto M, Punj V, Zaborina O, Kimbara K, Das Gupta TK, Chakrabarty AM (2002b) The bacterial redox protein azurin induces apoptosis in J774 macrophages through complex formation and stabilization of the tumor suppressor protein p53. Infect Immun 70(12):7054–7062
Yang DS, Miao XD, Ye ZM, Feng J, Xu RZ, Huang X, Ge FF (2005) Bacterial redox protein azurin induce apoptosis in human osteosarcoma U2OS cells. Pharmacol Res 52(5):413–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2005.06.002
Zaborina O, Dhiman N, Ling Chen M, Kostal J, Holder IA, Chakrabarty AM (2000) Secreted products of a nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain induce two modes of macrophage killing: external-ATP-dependent, P2Z-receptor-mediated necrosis and ATP-independent, caspase-mediated apoptosis. Microbiology 146:2521–2530. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-146-10-2521
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest regarding the publication of paper.
Research Involving Animal Rights
All applicable institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sereena, M.C., Sebastian, D. Evaluation of Anticancer and Anti-hemolytic Activity of Azurin, a Novel Bacterial Protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa SSj. Int J Pept Res Ther 26, 459–466 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-019-09851-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-019-09851-1