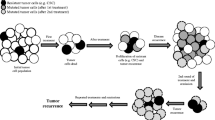
Abstract
Drug resistance developed towards conventional therapy is one of the important reasons for chemotherapy failure in cancer. The various underlying mechanism for drug resistance development in tumor includes tumor heterogeneity, some cellular levels changes, genetic factors, and others novel mechanisms which have been highlighted in the past few years. In the present scenario, researchers have to focus on these novel mechanisms and their tackling strategies. The small molecules, peptides, and nanotherapeutics have emerged to overcome the drug resistance in cancer. The drug delivery systems with targeting moiety enhance the site-specificity, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and increase the drug concentration inside the cells, thus minimizing drug resistance and improve their therapeutic efficacy. These therapeutic approaches work by modulating the different pathways responsible for drug resistance. This review focuses on the different mechanisms of drug resistance and the recent advancements in therapeutic approaches to improve the sensitivity and effectiveness of chemotherapeutics.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, Johnston PG. Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(10):714–26.
Haider T, Tiwari R, Vyas SP, Soni V. Molecular determinants as therapeutic targets in cancer chemotherapy: An update. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;200:85–109.
Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O’reilly MS. Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature. 1997;390(6658):404.
Sethi T, Rintoul RC, Moore SM, MacKinnon AC, Salter D, Choo C, et al. Extracellular matrix proteins protect small cell lung cancer cells against apoptosis: a mechanism for small cell lung cancer growth and drug resistance in vivo. Nat Med. 1999;5(6):662–8.
Housman G, Byler S, Heerboth S, Lapinska K, Longacre M, Snyder N, et al. Drug resistance in cancer: an overview. Cancers (Basel). 2014;6(3):1769–92.
Xue X, Liang XJ. Overcoming drug efflux-based multidrug resistance in cancer with nanotechnology. Chin J Cancer. 2012;31(2):100–9.
Gottesman MM, Pastan IH. The role of multidrug resistance efflux pumps in cancer: revisiting a JNCI publication exploring expression of the MDR1 (P-glycoprotein) Gene. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107(9):djv222.
Lahtz C, Pfeifer GP. Epigenetic changes of DNA repair genes in cancer. J Mol Cell Biol. 2011;3(1):51–8.
Wilson TR, Johnston PG, Longley DB. Anti-apoptotic mechanisms of drug resistance in cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009;9(3):307–19.
Nurwidya F, Takahashi F, Murakami A, Takahashi K. Epithelial mesenchymal transition in drug resistance and metastasis of lung cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2012;44(3):151–6.
Sun Y. Tumor microenvironment and cancer therapy resistance. Cancer Lett. 2016;380(1):205–15.
Wang Y, Cheetham AG, Angacian G, Su H, Xie L, Cui H. Peptide–drug conjugates as effective prodrug strategies for targeted delivery. Adv Drug Del Rev. 2017;110:112–26.
Wang M, Thanou M. Targeting nanoparticles to cancer. Pharmacol Res. 2010;62(2):90–9.
Yang Y, Jiang C, Yang Y, Guo L, Huang J, Liu X, et al. Silencing of LncRNA-HOTAIR decreases drug resistance of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer cells by inactivating autophagy via suppressing the phosphorylation of ULK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(4):1003–100.
Budden T, van der Westhuizen A, Bowden NA. Sequential decitabine and carboplatin treatment increases the DNA repair protein XPC, increases apoptosis and decreases proliferation in melanoma. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):100.
Roskoski R Jr. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGF receptor inhibitors in the treatment of renal cell carcinomas. Pharmacol Res. 2017;120:116–32.
Reinmuth N, Fan F, Liu W, Parikh AA, Stoeltzing O, Jung YD, et al. Impact of insulin-like growth factor receptor-I function on angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis of colon cancer. Lab Invest. 2002;82(10):1377–89.
Huijbers EJ, van Beijnum JR, Thijssen VL, Sabrkhany S, Nowak-Sliwinska P, Griffioen AW. Role of the tumor stroma in resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 2016;25:26–37.
Ma S, Pradeep S, Hu W, Zhang D, Coleman R, Sood A. The role of tumor microenvironment in resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. F1000Res. 2018;7:326.
Morin PJ. Drug resistance and the microenvironment: nature and nurture. Drug Resist Updat. 2003;6(4):169–72.
Tanaka K, Miyata H, Sugimura K, Fukuda S, Kanemura T, Yamashita K, et al. miR-27 is associated with chemoresistance in esophageal cancer through transformation of normal fibroblasts to cancer-associated fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36(8):894–903.
Xie X, Hu Y, Xu L, Fu Y, Tu J, Zhao H, et al. The role of miR-125b-mitochondria-caspase-3 pathway in doxorubicin resistance and therapy in human breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(9):7185–94.
Seguin L, Desgrosellier JS, Weis SM, Cheresh DA. Integrins and cancer: regulators of cancer stemness, metastasis, and drug resistance. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25(4):234–40.
Raghunand N, Mahoney BP, Gillies RJ. Tumor acidity, ion trapping and chemotherapeutics. II. pH-dependent partition coefficients predict importance of ion trapping on pharmacokinetics of weakly basic chemotherapeutic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;66(7):1219–29.
Pan ST, Li ZL, He ZX, Qiu JX, Zhou SF. Molecular mechanisms for tumour resistance to chemotherapy. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016;43(8):723–37.
Sharma A, Arambula JF, Koo S, Kumar R, Singh H, Sessler JL, et al. Hypoxia-targeted drug delivery. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(3):771–813.
Avril T, Vauleon E, Chevet E. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling and chemotherapy resistance in solid cancers. Oncogenesis. 2017;6(8):e373.
Gong T, Cui L, Wang H, Wang H, Han N. Knockdown of KLF5 suppresses hypoxia-induced resistance to cisplatin in NSCLC cells by regulating HIF-1α-dependent glycolysis through inactivation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):164.
Wojtkowiak JW, Verduzco D, Schramm KJ, Gillies RJ. Drug resistance and cellular adaptation to tumor acidic pH microenvironment. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(6):2032–8.
Gullotti E, Yeo Y. Extracellularly activated nanocarriers: a new paradigm of tumor targeted drug delivery. Mol Pharm. 2009;6(4):1041–51.
Zhao L, Liu W, Xiao J, Cao B. The role of exosomes and “exosomal shuttle microRNA” in tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Cancer Lett. 2015;356(2):339–46.
Shedden K, Xie XT, Chandaroy P, Chang YT, Rosania GR. Expulsion of small molecules in vesicles shed by cancer cells: association with gene expression and chemosensitivity profiles. Cancer Res. 2003;63(15):4331–7.
Song Z, Lin Y, Xia Zhang CF, Lu Y, Gao Y, Dong C. Cyclic RGD peptide-modified liposomal drug delivery system for targeted oral apatinib administration: enhanced cellular uptake and improved therapeutic effects. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:1941.
Yamamoto S, Kato A, Sakurai Y, Hada T, Harashima H. Modality of tumor endothelial VEGFR2 silencing-mediated improvement in intratumoral distribution of lipid nanoparticles. J Control Rel. 2017;251:1–10.
Mitamura T, Pradeep S, McGuire M, Wu SY, Ma S, Hatakeyama H, et al. Induction of anti-VEGF therapy resistance by upregulated expression of microseminoprotein (MSMP). Oncogene. 2018;37(6):722–31.
Smith BD, Kaufman MD, Leary CB, Turner BA, Wise SC, Ahn YM, et al. Altiratinib inhibits tumor growth, invasion, angiogenesis, and microenvironment-mediated drug resistance via balanced inhibition of MET, TIE2, and VEGFR2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14(9):2023–34.
Avril S, Dincer Y, Malinowsky K, Wolff C, Gundisch S, Hapfelmeier A, et al. Increased PDGFR-beta and VEGFR-2 protein levels are associated with resistance to platinum-based chemotherapy and adverse outcome of ovarian cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2017;8(58):97851–61.
Kim S-J, Uehara H, Yazici S, Busby JE, Nakamura T, He J, et al. Targeting platelet-derived growth factor receptor on endothelial cells of multidrug-resistant prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(11):783–93.
Min H-Y, Lee S-C, Woo JK, Jung HJ, Park KH, Jeong HM, et al. Essential role of DNA methyltransferase 1-mediated transcription of insulin-like growth factor 2 in resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(5):1299–311.
Eichten A, Su J, Adler AP, Zhang L, Ioffe E, Parveen AA, et al. Resistance to anti-VEGF therapy mediated by autocrine IL6/STAT3 signaling and overcome by IL6 blockade. Cancer Res. 2016;76(8):2327–39.
Scherbakov AM, Borunov AM, Buravchenko GI, Andreeva OE, Kudryavtsev IA, Dezhenkova LG, et al. Novel quinoxaline-2-carbonitrile-1,4-dioxide derivatives suppress HIF1alpha activity and circumvent MDR in cancer cells. Cancer Invest. 2018;36(3):199–209.
Dagogo-Jack I, Shaw AT. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15(2):81–94.
Marusyk A, Polyak K. Tumor heterogeneity: causes and consequences. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1805(1):105–17.
Makohon-Moore AP, Zhang M, Reiter JG, Bozic I, Allen B, Kundu D, et al. Limited heterogeneity of known driver gene mutations among the metastases of individual patients with pancreatic cancer. Nat Genet. 2017;49(3):358.
Negri T, Pavan GM, Virdis E, Greco A, Fermeglia M, Sandri M, et al. T670X KIT mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: making sense of missense. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101(3):194–204.
Kwak EL, Ahronian LG, Siravegna G, Mussolin B, Borger DR, Godfrey JT, et al. Molecular heterogeneity and receptor coamplification drive resistance to targeted therapy in MET-amplified esophagogastric cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015;5(12):1271–81.
Zhao BX, Wang J, Song B, Wei H, Lv WP, Tian LM, et al. Establishment and biological characteristics of acquired gefitinib resistance in cell line NCI-H1975/gefinitib-resistant with epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(4):2767–74.
Little AS, Balmanno K, Sale MJ, Newman S, Dry JR, Hampson M, et al. Amplification of the driving oncogene, KRAS or BRAF, underpins acquired resistance to MEK1/2 inhibitors in colorectal cancer cells. Sci Signal. 2011;4(166):ra17-ra.
Norquist B, Wurz KA, Pennil CC, Garcia R, Gross J, Sakai W, et al. Secondary somatic mutations restoring BRCA1/2 predict chemotherapy resistance in hereditary ovarian carcinomas. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(22):3008–155.
Kemper K, Krijgsman O, Cornelissen-Steijger P, Shahrabi A, Weeber F, Song JY, et al. Intra- and inter-tumor heterogeneity in a vemurafenib-resistant melanoma patient and derived xenografts. EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7(9):1104–18.
Oshimori N, Oristian D, Fuchs E. TGF-β promotes heterogeneity and drug resistance in squamous cell carcinoma. Cell. 2015;160(5):963–76.
Pestova TV, Kolupaeva VG, Lomakin IB, Pilipenko EV, Shatsky IN, Agol VI, et al. Molecular mechanisms of translation initiation in eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98(13):7029–36.
Bhat M, Robichaud N, Hulea L, Sonenberg N, Pelletier J, Topisirovic I. Targeting the translation machinery in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015;14(4):261–78.
Chu J, y Cajal SR, Sonenberg N, Pelletier J. Eukaryotic initiation factor 4F—sidestepping resistance mechanisms arising from expression heterogeneity. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018;48:89–96.
Campbell LL, Polyak K. Breast tumor heterogeneity: cancer stem cells or clonal evolution? Cell Cycle. 2007;6(19):2332–8.
Phi LTH, Sari IN, Yang YG, Lee SH, Jun N, Kim KS, et al. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) in drug resistance and their therapeutic implications in cancer treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:5416923.
Makena MR, Ranjan A, Thirumala V, Reddy AP. Cancer stem cells: road to therapeutic resistance and strategies to overcome resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(4):165339.
Boshuizen J, Koopman LA, Krijgsman O, Shahrabi A, van den Heuvel EG, Ligtenberg MA, et al. Cooperative targeting of melanoma heterogeneity with an AXL antibody-drug conjugate and BRAF/MEK inhibitors. Nat Med. 2018;24(2):203–12.
Russo M, Siravegna G, Blaszkowsky LS, Corti G, Crisafulli G, Ahronian LG, et al. Tumor heterogeneity and lesion-specific response to targeted therapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016;6(2):147–53.
Somasundaram R, Zhang G, Fukunaga-Kalabis M, Perego M, Krepler C, Xu X, et al. Tumor-associated B-cells induce tumor heterogeneity and therapy resistance. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):607.
Ahmed F, Haass NK. Microenvironment-driven dynamic heterogeneity and phenotypic plasticity as a mechanism of melanoma therapy resistance. Front Oncol. 2018;8:173.
Iwasaki S, Floor SN, Ingolia NT. Rocaglates convert DEAD-box protein eIF4A into a sequence-selective translational repressor. Nature. 2016;534(7608):558–61.
Bordeleau ME, Robert F, Gerard B, Lindqvist L, Chen SM, Wendel HG, et al. Therapeutic suppression of translation initiation modulates chemosensitivity in a mouse lymphoma model. J Clin Invest. 2008;118(7):2651–60.
Muntimadugu E, Kumar R, Saladi S, Rafeeqi TA, Khan W. CD44 targeted chemotherapy for co-eradication of breast cancer stem cells and cancer cells using polymeric nanoparticles of salinomycin and paclitaxel. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;143:532–46.
Jin C, Yang Z, Yang J, Li H, He Y, An J, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded nanoparticles decorated with anti-CD133 antibody: a targeted therapy for liver cancer stem cells. J Nanopart Res. 2013;16(1):2157.
Liu Q, Li RT, Qian HQ, Wei J, Xie L, Shen J, et al. Targeted delivery of miR-200c/DOC to inhibit cancer stem cells and cancer cells by the gelatinases-stimuli nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2013;34(29):7191–203.
Meijer C, Mulder NH, Timmer-Bosscha H, Sluiter WJ, Meersma GJ, de Vries EG. Relationship of cellular glutathione to the cytotoxicity and resistance of seven platinum compounds. Cancer Res. 1992;52(24):6885–9.
Longley DB, Johnston PG. Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance. J Pathol. 2005;205(2):275–92.
Hughes LR, Stephens TC, Boyle FT, Jackman AL. Raltitrexed (Tomudex TM), a highly polyglutamatable antifolate thymidylate synthase inhibitor. In: Jackman AL, editor. Antifolate drugs in cancer therapy Cancer Drug Discovery and Development. Totowa: Humana Press; 1999. p. 147–165.
Marin JJ, Al-Abdulla R, Lozano E, Briz O, Bujanda L, Banales JM, et al. Mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy in gastric cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2016;16(3):318–34.
Be H. Clinical pharmacology of 5-fluorouracil. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1989;16(4):215–37.
Zhao R, Babani S, Gao F, Liu L, Goldman ID. The mechanism of transport of the multitargeted antifolate (MTA) and its cross-resistance pattern in cells with markedly impaired transport of methotrexate. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6(9):3687–95.
Gagnon J-F, Bernard O, Villeneuve L, Têtu B, Guillemette C. Irinotecan inactivation is modulated by epigenetic silencing of UGT1A1 in colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(6):1850–8.
Saatci O, Borgoni S, Akbulut O, Durmus S, Raza U, Eyupoglu E, et al. Targeting PLK1 overcomes T-DM1 resistance via CDK1-dependent phosphorylation and inactivation of Bcl-2/xL in HER2-positive breast cancer. Oncogene. 2018;37(17):2251–69.
Du Z, Liu X, Chen T, Gao W, Wu Z, Hu Z, et al. Targeting a Sirt5-positive subpopulation overcomes multidrug resistance in wild-type kras colorectal carcinomas. Cell Rep. 2018;22(10):2677–89.
Schumacher D, Andrieux G, Boehnke K, Keil M, Silvestri A, Silvestrov M, et al. Heterogeneous pathway activation and drug response modelled in colorectal-tumor-derived 3D cultures. PLoS Genet. 2019;15(3):e1008076.
Shee K, Yang W, Hinds JW, Hampsch RA, Varn FS, Traphagen NA, et al. Therapeutically targeting tumor microenvironment-mediated drug resistance in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Exp Med. 2018;215(3):895–910.
Lippolis C, Refolo MG, D'Alessandro R, Carella N, Messa C, Cavallini A, et al. Resistance to multikinase inhibitor actions mediated by insulin like growth factor-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015;34(1):90.
Fox CA, Sapinoso LM, Zhang H, Zhang W, McLeod HL, Petroni GR, et al. Altered expression of TFF-1 and CES-2 in Barrett's Esophagus and associated adenocarcinomas. Neoplasia. 2005;7(4):407–16.
Boige V, Taïeb J, Hebbar M, Malka D, Debaere T, Hannoun L, et al. Irinotecan as first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter phase II study with dose adjustment according to baseline serum bilirubin level. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42(4):456–9.
Sampath D, Cortes J, Estrov Z, Du M, Shi Z, Andreeff M, et al. Pharmacodynamics of cytarabine alone and in combination with 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) in AML blasts in vitro and during a clinical trial. Blood. 2006;107(6):2517–24.
Shen D-w, Pastan I, Gottesman MM. Cross-resistance to methotrexate and metals in human cisplatin-resistant cell lines results from a pleiotropic defect in accumulation of these compounds associated with reduced plasma membrane binding proteins. Cancer Res. 1998;58(2):268–75.
Peterson RH, Biedler JL. Plasma membrane proteins and glycoproteins from Chinese hamster cells sensitive and resistant to actinomycin D. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(3):289–98.
Eichholtz-Wirth H, Hietel B. The relationship between cisplatin sensitivity and drug uptake into mammalian cells in vitro. Br J Cancer. 1986;54(2):239.
Kreitman RJ, Pastan I. Immunotoxins for targeted cancer therapy. Adv Drug Del Rev. 1998;31(1–2):53–88.
Zhang XW, Bu P, Liu L, Zhang XZ, Li J. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA PVT1 in gastric cancer cells promotes the development of multidrug resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;462(3):227–32.
Roundhill E, Fletcher J, Haber M, Norris M. Clinical relevance of multidrug-resistance-proteins (MRPs) for anticancer drug resistance and prognosis. In: Efferth T, editor. Resistance to targeted ABC transporters in cancer. Resistance to targeted anti-cancer therapeutics, vol. 4. Cham: Springer; 2015. p. 27–52.
Singh SK, Lillard JW Jr, Singh R. Reversal of drug resistance by planetary ball milled (PBM) nanoparticle loaded with resveratrol and docetaxel in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018;427:49–62.
Zhang Y, Wang Q. Sunitinib reverse multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells by modulating Stat3 and inhibiting P-gp function. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;67(2):575–81.
He L, Wang X, Liu K, Wu X, Yang X, Song G, et al. Integrative PDGF/PDGFR and focal adhesion pathways are downregulated in ERCC1-defective non-small cell lung cancer undergoing sodium glycididazole-sensitized cisplatin treatment. Gene. 2019;691:70–6.
Hahne JC, Valeri N. Non-coding RNAs and resistance to anticancer drugs in gastrointestinal tumours. Front Oncol. 2018;8:226.
Hegi ME, Liu L, Herman JG, Stupp R, Wick W, Weller M, et al. Correlation of O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation with clinical outcomes in glioblastoma and clinical strategies to modulate MGMT activity. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(25):4189–99.
Sun WL, Lan D, Gan TQ, Cai ZW. Autophagy facilitates multidrug resistance development through inhibition of apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Neoplasma. 2015;62(2):199–208.
Zhu W, Shan X, Wang T, Shu Y, Liu P. miR-181b modulates multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(11):2520–9.
Luan M, Chang J, Pan W, Chen Y, Li N, Tang B. Simultaneous fluorescence visualization of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and apoptosis processes in tumor cells for evaluating the impact of epithelial–mesenchymal transition on drug efficacy. Anal Chem. 2018;90(18):10951–7.
Tyler A, Johansson A, Karlsson T, Gudey SK, Brannstrom T, Grankvist K, et al. Targeting glucosylceramide synthase induction of cell surface globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) in acquired cisplatin-resistance of lung cancer and malignant pleural mesothelioma cells. Exp Cell Res. 2015;336(1):23–322.
Buckley D, Duke G, Heuer TS, O'Farrell M, Wagman AS, McCulloch W, et al. Fatty acid synthase—modern tumor cell biology insights into a classical oncology target. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;177:23–31.
Grunt TW. Interacting cancer machineries: cell signaling, lipid metabolism, and epigenetics. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018;29(2):86–988.
Shan L, Shan X, Zhang T, Zhai K, Gao G, Chen X, et al. Transferrin-conjugated paclitaxel prodrugs for targeted cancer therapy. RSC Adv. 2016;6(81):77987–98.
Huang XC, Huang RZ, Gou SH, Wang ZM, Liao ZX, Wang HS. Platinum(IV) complexes conjugated with phenstatin analogue as inhibitors of microtubule polymerization and reverser of multidrug resistance. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017;25(17):4686–700.
Xu Z, Hu W, Wang Z, Gou S. Platinum (IV) prodrugs multiply targeting genomic DNA, histone deacetylases and PARP-1. Eur J Med Chem. 2017;141:211–20.
Huang P, Wang D, Su Y, Huang W, Zhou Y, Cui D, et al. Combination of small molecule prodrug and nanodrug delivery: amphiphilic drug–drug conjugate for cancer therapy. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136(33):11748–56.
Zhao D, Zhang H, Tao W, Wei W, Sun J, He Z. A rapid albumin-binding 5-fluorouracil prodrug with a prolonged circulation time and enhanced antitumor activity. Biomater Sci. 2017;5(3):502–10.
Gao C, Tang F, Gong G, Zhang J, Hoi MP, Lee SM, et al. pH-responsive prodrug nanoparticles based on a sodium alginate derivative for selective co-release of doxorubicin and curcumin into tumor cells. Nanoscale. 2017;9(34):12533–42.
Gottesman MM. Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Annu Rev Med. 2002;53(1):615–27.
Marin JJ, Monte MJ, Blazquez AG, Macias RI, Serrano MA, Briz O. The role of reduced intracellular concentrations of active drugs in the lack of response to anticancer chemotherapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014;35(1):1–10.
Tiwari R, Jain P, Asati S, Haider T, Soni V, Pandey V. State-of-art based approaches for anticancer drug-targeting to nucleus. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2018;48:383–92.
Chauhan SS, Liang XJ, Su AW, Pai-Panandiker A, Shen DW, Hanover JA, et al. Reduced endocytosis and altered lysosome function in cisplatin-resistant cell lines. Br J Cancer. 2003;88(8):1327–34.
Loeffler M, Kruger JA, Niethammer AG, Reisfeld RA. Targeting tumor-associated fibroblasts improves cancer chemotherapy by increasing intratumoral drug uptake. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(7):1955–62.
Bar-Shavit R, Nag JK, Grisaru-Granovsky S, Uziely B. G-protein coupled receptor PAR(1) is overexpressed in glioma progenitor cells. Transl Cancer Res. 2016;5(6):S1185–S1188188.
Kübler E, Albrecht H. Large set data mining reveals overexpressed GPCRs in prostate and breast cancer: potential for active targeting with engineered anti-cancer nanomedicines. Oncotarget. 2018;9(38):24882.
Iqbal N, Iqbal N. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in cancers: overexpression and therapeutic implications. Mol Biol Int. 2014;2014:852748.
Pandey V, Gajbhiye KR, Soni V. Lactoferrin-appended solid lipid nanoparticles of paclitaxel for effective management of bronchogenic carcinoma. Drug Deliv. 2015;22(2):199–205.
Chen C, Zhao S, Karnad A, Freeman JW. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: therapeutic implications. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1):64.
Linja MJ, Savinainen KJ, Saramaki OR, Tammela TL, Vessella RL, Visakorpi T. Amplification and overexpression of androgen receptor gene in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61(9):3550–5.
Kapse-Mistry S, Govender T, Srivastava R, Yergeri M. Nanodrug delivery in reversing multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Front Pharmacol. 2014;5:159.
Lei M, Ma G, Sha S, Wang X, Feng H, Zhu Y, et al. Dual-functionalized liposome by co-delivery of paclitaxel with sorafenib for synergistic antitumor efficacy and reversion of multidrug resistance. Drug Deliv. 2019;26(1):262–72.
Bansal D, Yadav K, Pandey V, Ganeshpurkar A, Agnihotri A, Dubey N. Lactobionic acid coupled liposomes: an innovative strategy for targeting hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(1):140–6.
Hee Choi Y, Yu A-M. ABC transporters in multidrug resistance and pharmacokinetics, and strategies for drug development. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(5):793–807.
Binkhathlan Z, Lavasanifar A. P-glycoprotein inhibition as a therapeutic approach for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer: current status and future perspectives. Curr Cancer Drug Targ. 2013;13(3):326–46.
Allen J, Brinkhuis R, Wijnholds J, Schinkel AH. The mouse Bcrpl/Mxr/Abcp gene: amplification and overexpression in cell lines selected fbr resistance to topotecan, mitoxantrone, or doxorubicin. Cancer Res. 1999;59:4237–41.
Wang H, Gao Z, Liu X, Agarwal P, Zhao S, Conroy DW, et al. Targeted production of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria to overcome cancer drug resistance. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):562.
Orlando UD, Castillo AF, Medrano MAR, Solano AR, Maloberti PM, Podesta EJ. Acyl-CoA synthetase-4 is implicated in drug resistance in breast cancer cell lines involving the regulation of energy-dependent transporter expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;159:52–63.
Zheng X, Andruska N, Lambrecht MJ, He S, Parissenti A, Hergenrother PJ, et al. Targeting multidrug-resistant ovarian cancer through estrogen receptor α dependent ATP depletion caused by hyperactivation of the unfolded protein response. Oncotarget. 2018;9(19):14741.
Capranico G, De Isabella P, Castelli C, Supino R, Parmiani G, Zunino F. P-glycoprotein gene amplification and expression in multidrug-resistant murine P388 and B16 cell lines. Br J Cancer. 1989;59(5):682–5.
Zheng L-S, Wang F, Li Y-H, Zhang X, Chen L-M, Liang Y-J, et al. Vandetanib (Zactima, ZD6474) antagonizes ABCC1-and ABCG2-mediated multidrug resistance by inhibition of their transport function. PLoS ONE. 2009;4(4):e5172.
Fung SW, Cheung PF-Y, Yip CW, Ng LW-C, Cheung TT, Chong CC-N, et al. The ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCF1 is a hepatic oncofetal protein that promotes chemo-resistance, EMT and cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2019;457:98–109.
Amin ML. P-glycoprotein inhibition for optimal drug delivery. Drug Targ Insights. 2013;7:27–34.
Li PY, Lai PS, Hung WC, Syu WJ. Poly(L-lactide)-vitamin E TPGS nanoparticles enhanced the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin in drug-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biomacromol. 2010;11(10):2576–82.
Dintaman JM, Silverman JA. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein by D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS). Pharm Res. 1999;16(10):1550–6.
Negi LM, Talegaonkar S, Jaggi M, Verma AK. Hyaluronated imatinib liposomes with hybrid approach to target CD44 and P-gp overexpressing MDR cancer: an in-vitro, in-vivo and mechanistic investigation. J Drug Target. 2019;27(2):183–92.
Hartz A, Schulz J, Sokola B, Bauer B. CSIG-32 DUAL PI3K/Akt inhibition to overcome the P-gp/BCRP drug efflux system for improved drug delivery in glioblastoma therapy. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(suppl_6):vi50–vi51.
Zhang YK, Zhang XY, Zhang GN, Wang YJ, Xu H, Zhang D, et al. Selective reversal of BCRP-mediated MDR by VEGFR-2 inhibitor ZM323881. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;132:29–37.
Durmus S, Xu N, Sparidans RW, Wagenaar E, Beijnen JH, Schinkel AH. P-glycoprotein (MDR1/ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) restrict brain accumulation of the JAK1/2 inhibitor, CYT387. Pharmacol Res. 2013;76:9–16.
Susa M, Iyer AK, Ryu K, Choy E, Hornicek FJ, Mankin H, et al. Inhibition of ABCB1 (MDR1) expression by an siRNA nanoparticulate delivery system to overcome drug resistance in osteosarcoma. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(5):e10764.
Nourbakhsh M, Jaafari MR, Lage H, Abnous K, Mosaffa F, Badiee A, et al. Nanolipoparticles-mediated MDR1 siRNA delivery reduces doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells and silences MDR1 expression in xenograft model of human breast cancer. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(4):385–92.
Burg D, Wielinga P, Zelcer N, Saeki T, Mulder GJ, Borst P. Inhibition of the multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) by peptidomimetic glutathione-conjugate analogs. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;62(5):1160–6.
Tong WY, Alnakhli M, Bhardwaj R, Apostolou S, Sinha S, Fraser C, et al. Delivery of siRNA in vitro and in vivo using PEI-capped porous silicon nanoparticles to silence MRP1 and inhibit proliferation in glioblastoma. J Nanobiotechnol. 2018;16(1):38.
Lo Y-L, Liu Y. Reversing multidrug resistance in Caco-2 by silencing MDR1, MRP1, MRP2, and BCL-2/BCL-xL using liposomal antisense oligonucleotides. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(3):e90180.
Bouwman P, Jonkers J. The effects of deregulated DNA damage signalling on cancer chemotherapy response and resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(9):587–98.
Cummings M, Higginbottom K, McGurk CJ, Wong OG-W, Köberle B, Oliver RTD, et al. XPA versus ERCC1 as chemosensitising agents to cisplatin and mitomycin C in prostate cancer cells: role of ERCC1 in homologous recombination repair. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72(2):166–75.
Liu JL, Huang WS, Lee KC, Tung SY, Chen CN, Chang SF. Effect of 5-fluorouracil on excision repair cross-complementing 1 expression and consequent cytotoxicity regulation in human gastric cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(10):8472–80.
Tung SY, Lin CT, Chen CN, Huang WS. Effect of mitomycin C on X-ray repair cross complementing group 1 expression and consequent cytotoxicity regulation in human gastric cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(5):8333–422.
Valeri N, Gasparini P, Braconi C, Paone A, Lovat F, Fabbri M, et al. MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil by down-regulating human DNA MutS homolog 2 (hMSH2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(49):21098–103.
Ma P, Xu T, Huang M, Shu Y. Increased expression of LncRNA PANDAR predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;78:172–6.
Wang X, Li M, Wang Z, Han S, Tang X, Ge Y, et al. Silencing of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 by miR-101 and miR-217 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(7):3925–35.
Glasspool RM, Teodoridis JM, Brown R. Epigenetics as a mechanism driving polygenic clinical drug resistance. Br J Cancer. 2006;94(8):1087–92.
Gifford G, Paul J, Vasey PA, Kaye SB, Brown R. The acquisition of hMLH1 methylation in plasma DNA after chemotherapy predicts poor survival for ovarian cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(13):4420–6.
Si W, Shen J, Zheng H, Fan W. The role and mechanisms of action of microRNAs in cancer drug resistance. Clin Epigenet. 2019;11(1):25.
Xiong T, Wei H, Chen X, Xiao H. PJ34, a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, reverses melphalan-resistance and inhibits repair of DNA double-strand breaks by targeting the FA/BRCA pathway in multidrug resistant multiple myeloma cell line RPMI8226/R. Int J Oncol. 2015;46(1):223–32.
Tian H, Gao Z, Li H, Zhang B, Wang G, Zhang Q, et al. DNA damage response—a double-edged sword in cancer prevention and cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2015;358(1):8–16.
Nam AR, Jin MH, Park JE, Bang JH, Oh DY, Bang YJ. Therapeutic targeting of the DNA damage response using an ATR inhibitor in biliary tract cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2019;51(3):1167–79.
Chen P, Li J, Jiang HG, Lan T, Chen YC. Curcumin reverses cisplatin resistance in cisplatin-resistant lung caner cells by inhibiting FA/BRCA pathway. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(5):3591–9.
Song AL, Zhao L, Wang YW, He DQ, Li YM. Chemoresistance in gastric cancer is attributed to the overexpression of excision repair cross‐complementing 1 (ERCC1) caused by microRNA‐122 dysregulation. J Cell Comp Physiol. 2019;234(12):22485–92
He L, Liu K, Wang X, Chen H, Zhou J, Wu X, et al. NDRG1 disruption alleviates cisplatin/sodium glycididazole-induced DNA damage response and apoptosis in ERCC1-defective lung cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;100:54–60.
Ning J, Jiao Y, Xie X, Deng X, Zhang Y, Yang Y, et al. miR-138-5p modulates the expression of excision repair cross-complementing proteins ERCC1 and ERCC4, and regulates the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to cisplatin. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(2):1131–9.
Ju X, Yu H, Liang D, Jiang T, Liu Y, Chen L, et al. LDR reverses DDP resistance in ovarian cancer cells by affecting ERCC-1, Bcl-2, Survivin and Caspase-3 expressions. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;102:549–54.
Liu Y, Yue C, Li J, Wu J, Wang S, Sun D, et al. Enhancement of cisplatin cytotoxicity by Retigeric acid B involves blocking DNA repair and activating DR5 in prostate cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(3):2871–80.
Teng X, Fan XF, Li Q, Liu S, Wu DY, Wang SY, et al. XPC inhibition rescues cisplatin resistance via the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in A549/DDP lung adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(3):1875–82.
Han Z, Shi L. Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 modulates methotrexate resistance in osteosarcoma via miR-200c/ABCB1 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495(1):947–53.
Ge XS, Chen YB, Liao XY, Liu DQ, Li FF, Ruan HL, et al. Overexpression of long noncoding RNA PCAT-1 is a novel biomarker of poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Med Oncol. 2013;30(2):588.
Qiao L, Liu X, Tang Y, Zhao Z, Zhang J, Liu H. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA prostate cancer-associated ncRNA transcript 1 inhibits multidrug resistance and c-Myc-dependent aggressiveness in colorectal cancer Caco-2 and HT-29 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018;441(1–2):99–108.
Plumb JA, Strathdee G, Sludden J, Kaye SB, Brown R. Reversal of drug resistance in human tumor xenografts by 2'-deoxy-5-azacytidine-induced demethylation of the hMLH1 gene promoter. Cancer Res. 2000;60(21):6039–44.
Sabharwal A, Corrie PG, Midgley RS, Palmer C, Brady J, Mortimer P, et al. A phase I trial of lomeguatrib and irinotecan in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010;66(5):829–35.
Li YJ, Lei YH, Yao N, Wang CR, Hu N, Ye WC, et al. Autophagy and multidrug resistance in cancer. Chin J Cancer. 2017;36(1):52.
Huerta S, Heinzerling JH, Anguiano-Hernandez YM, Huerta-Yepez S, Lin J, Chen D, et al. Modification of gene products involved in resistance to apoptosis in metastatic colon cancer cells: roles of Fas, Apaf-1, NFkappaB, IAPs, Smac/DIABLO, and AIF. J Surg Res. 2007;142(1):184–94.
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, Pan Y, Zhao L, Sun S, et al. miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2008;123(2):372–9.
Teixeira C, Reed JC, Pratt MA. Estrogen promotes chemotherapeutic drug resistance by a mechanism involving Bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1995;55(17):3902–7.
Jeong SH, Lee HW, Han JH, Kang SY, Choi JH, Jung YM, et al. Low expression of Bax predicts poor prognosis in resected non-small cell lung cancer patients with non-squamous histology. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2008;38(10):661–9.
Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002;296(5573):1655–7.
Skalniak L, Kocik J, Polak J, Skalniak A, Rak M, Wolnicka-Glubisz A, Holak TA. Prolonged idasanutlin (RG7388) treatment leads to the generation of p53-mutated cells. Cancers. 2018;10(11):396.
Indran IR, Tufo G, Pervaiz S, Brenner C. Recent advances in apoptosis, mitochondria and drug resistance in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1807(6):735–45.
Wu CE, Koay TS, Ho YH, Lovat P, Lunec J. TP53 mutant cell lines selected for resistance to MDM2 inhibitors retain growth inhibition by MAPK pathway inhibitors but a reduced apoptotic response. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19(1):53.
Park J, Kim C, Gupta S. Differential transcriptional regulation of silencer of death domains in cord blood and peripheral blood lymphocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2000;6(3):289–93.
Greer YE, Gilbert SF, Gril B, Narwal R, Peacock Brooks DL, Tice DA, et al. MEDI3039, a novel highly potent tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor 2 agonist, causes regression of orthotopic tumors and inhibits outgrowth of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019;21(1):27.
Sun CY, Zhu Y, Li XF, Wang XQ, Tang LP, Su ZQ, et al. Scutellarin increases cisplatin-induced apoptosis and autophagy to overcome cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via ERK/p53 and c-met/AKT signaling pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:92.
Mohammad RM, Muqbil I, Lowe L, Yedjou C, Hsu H-Y, Lin L-T, et al. Broad targeting of resistance to apoptosis in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015;35:S78–S103.
van Staalduinen J, Baker D, ten Dijke P, van Dam H. Epithelial–mesenchymal-transition-inducing transcription factors: new targets for tackling chemoresistance in cancer? Oncogene. 2018; 37(48):6195–211.
Dongre A, Weinberg RA. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(2):69–84.
Song KA, Niederst MJ, Lochmann TL, Hata AN, Kitai H, Ham J, et al. Epithelial-to-MESENCHYMAL TRANSITION ANTAGONIZES RESPONSE TO TARGETED THERAPIES IN LUNG CANCER BY SUPPRESSINg BIM. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(1):197–208.
Xu J, Zhao X, He D, Wang J, Li W, Liu Y, et al. Loss of EGFR confers acquired resistance to AZD9291 in an EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer cell line with an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018;144(8):1413–22.
Yuan X, Wu H, Han N, Xu H, Chu Q, Yu S, et al. Notch signaling and EMT in non-small cell lung cancer: biological significance and therapeutic application. J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7(1):87.
Wilson C, Nicholes K, Bustos D, Lin E, Song Q, Stephan JP, et al. Overcoming EMT-associated resistance to anti-cancer drugs via Src/FAK pathway inhibition. Oncotarget. 2014;5(17):7328–41.
Bonnomet A, Syne L, Brysse A, Feyereisen E, Thompson E, Noël A, et al. A dynamic in vivo model of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions in circulating tumor cells and metastases of breast cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31(33):3741.
Davis FM, Stewart TA, Thompson EW, Monteith GR. Targeting EMT in cancer: opportunities for pharmacological intervention. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014;35(9):479–88.
Halder SK, Beauchamp RD, Datta PK. A specific inhibitor of TGF-β receptor kinase, SB-431542, as a potent antitumor agent for human cancers. Neoplasia. 2005;7(5):509–21.
Thaiparambil JT, Bender L, Ganesh T, Kline E, Patel P, Liu Y, et al. Withaferin A inhibits breast cancer invasion and metastasis at sub-cytotoxic doses by inducing vimentin disassembly and serine 56 phosphorylation. Int J Cancer. 2011;129(11):2744–55.
Guo Z, Li W, Yuan Y, Zheng K, Tang Y, Ma K, et al. Improvement of chemosensitivity and inhibition of migration via targeting tumor epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition cells by ADH-1-modified liposomes. Drug Deliv. 2018;25(1):112–21.
Hendrich A, Michalak K. Lipids as a target for drugs modulating multidrug resistance of cancer cells. Curr Drug Targets. 2003;4(1):23–30.
Merchant TE, Meneses P, Gierke LW, Den Otter W, Glonek T. 31 P Magnetic resonance phospholipid profiles of neoplastic human breast tissues. Br J Cancer. 1991;63(5):693.
Merchant TE, de Graaf PW, Minsky BD, Obertop H, Glonek T. Esophageal cancer phospholipid characterization by 31P NMR. NMR Biomed. 1993;6(3):187–93.
Raghavan V, Vijayaraghavalu S, Peetla C, Yamada M, Morisada M, Labhasetwar V. Sustained epigenetic drug delivery depletes cholesterol–sphingomyelin rafts from resistant breast cancer cells, influencing biophysical characteristics of membrane lipids. Langmuir. 2015;31(42):11564–73.
Wegner MS, Gruber L, Mattjus P, Geisslinger G, Grosch S. The UDP-glucose ceramide glycosyltransferase (UGCG) and the link to multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1). BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):153.
Jennemann R, Federico G, Mathow D, Rabionet M, Rampoldi F, Popovic ZV, et al. Inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma growth by blockade of glycosphingolipid synthesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(65):109201–166.
Wegner MS, Schomel N, Gruber L, Ortel SB, Kjellberg MA, Mattjus P, et al. UDP-glucose ceramide glucosyltransferase activates AKT, promoted proliferation, and doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(18):3393–410.
Liu Q, Luo Q, Halim A, Song G. Targeting lipid metabolism of cancer cells: a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;401:39–45.
Veigel D, Wagner R, Stubiger G, Wuczkowski M, Filipits M, Horvat R, et al. Fatty acid synthase is a metabolic marker of cell proliferation rather than malignancy in ovarian cancer and its precursor cells. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(9):2078–90.
Li CF, Fang FM, Chen YY, Liu TT, Chan TC, Yu SC, et al. Overexpressed fatty acid synthase in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: targeting a progression-associated metabolic driver enhances the antitumor effect of imatinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(16):4908–18.
Chatterjee S, Alsaeedi N, Hou J, Bandaru VV, Wu L, Halushka MK, et al. Use of a glycolipid inhibitor to ameliorate renal cancer in a mouse model. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(5):e63726.
Liu H, Wu X, Dong Z, Luo Z, Zhao Z, Xu Y, et al. Fatty acid synthase causes drug resistance by inhibiting TNF-alpha and ceramide production. J Lipid Res. 2013;54(3):776–85.
Wu S, Naar AM. SREBP1-dependent de novo fatty acid synthesis gene expression is elevated in malignant melanoma and represents a cellular survival trait. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):10369.
Bobba RK, Arya M, Benakanakere I, Johnson T, Freter C. Lipid cell membrane composition: a novel therapeutic target in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(15_suppl):7062.
Vijayaraghavalu S, Peetla C, Lu S, Labhasetwar V. Epigenetic modulation of the biophysical properties of drug-resistant cell lipids to restore drug transport and endocytic functions. Mol Pharm. 2012;9(9):2730–42.
Zhang RX, Li LY, Li J, Xu Z, Abbasi AZ, Lin L, et al. Coordinating biointeraction and bioreaction of a nanocarrier material and an anticancer drug to overcome membrane rigidity and target mitochondria in multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Adv Func Mater. 2017;27(39):1700804.
Hou TY, Davidson LA, Kim E, Fan YY, Fuentes NR, Triff K, et al. Nutrient-gene interaction in colon cancer, from the membrane to cellular physiology. Annu Rev Nutr. 2016;36:543–70.
Fuentes NR, Kim E, Fan YY, Chapkin RS. Omega-3 fatty acids, membrane remodeling and cancer prevention. Mol Aspects Med. 2018;64:79–91.
Poolsri WA, Phokrai P, Suwankulanan S, Phakdeeto N, Phunsomboon P, Pekthong D, et al. Combination of mitochondrial and plasma membrane citrate transporter inhibitors inhibits de novo lipogenesis pathway and triggers apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:3683026.
Wu X, Qin L, Fako V, Zhang JT. Molecular mechanisms of fatty acid synthase (FASN)-mediated resistance to anti-cancer treatments. Adv Biol Regul. 2014;54:214–21.
Stepanova DS, Semenova G, Kuo YM, Andrews AJ, Ammoun S, Hanemann CO, et al. An essential role for the tumor-suppressor merlin in regulating fatty acid synthesis. Cancer Res. 2017;77(18):5026–38.
Brandi J, Dando I, Pozza ED, Biondani G, Jenkins R, Elliott V, et al. Proteomic analysis of pancreatic cancer stem cells: Functional role of fatty acid synthesis and mevalonate pathways. J Proteom. 2017;150:310–22.
Chang L, Fang S, Chen Y, Yang Z, Yuan Y, Zhang J, et al. Inhibition of FASN suppresses the malignant biological behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells via deregulating glucose metabolism and AKT/ERK pathway. Lipids Health Dis. 2019;18(1):118.
Acknowledgements
The funding (Grant No. EMR/2017/001738) provided by Science & Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India, is gratefully acknowledged. Authors acknowledge to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi for financial support as SRF funding (Grant number for Haider T. 45/7/2018-Nan/BMS and for Pandey V. 45/01/2018-NAN/BMS) for research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haider, T., Pandey, V., Banjare, N. et al. Drug resistance in cancer: mechanisms and tackling strategies. Pharmacol. Rep 72, 1125–1151 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-020-00138-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-020-00138-7