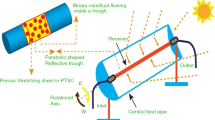
Abstract
In this work, the performance of an inline dimpled-based absorber plate solar air heater (IDPSAH) is studied in relation to pitch, a system parameter, and air flow rate (Mair), an operating parameter. In this regard, two alternative IDPSAH with pitch ratios 0.88 and 1.33 have been experimentally evaluated on alternative days by altering the Mair from 0.010 to 0.053 kg s-1 (Proportional Re range: 1971.66–11,113.24) and the result are compared with flat plate solar air heater (FPSAH). For performance evaluation and comparative research, various parameters have been studied, including air temperature difference, efficiencies (ηinst, ηeff, ηdaily), global heat loss coefficient, heat removal factor, collector efficiency, top loss, area averaged Nusselt number (Nuavg), and friction factor (favg), among others. The effective efficiency reaches its maximum at a particular Mair and then begins to decline, but the instantaneous and daily efficiency of IDPSAH and FPSAH increases continuously. Due to a decrease top loss, the efficiency of IDPSAH is higher than FPSAH. The instantaneous efficiency of IDPSAH at pitch ratio 0.88 is 1.13–1.53 times greater than the instantaneous efficiency of IDPSAH at pitch ratio 1.33 and it is 1.21–1.86 times higher than FPSAH. With an increase in Re, the favg value decreases; while, the Nuavg of both the FPSAH and IDPSAH increases. In comparison with IDPSAH with pitch ratio 1.33, the Nuavg of IDPSAH at pitch ratio 0.88 is 1.23–1.41 times higher, and it is 1.68–2.12 times higher than FPSAH. In comparison with IDPSAH at pitch ratio 1.33 and FPSAH, the favg of IDPSAH at pitch ratio 0.88 is higher. However, there is a significant enhancement in overall performance of IDPSAH than the FPSAH.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FPSAH:
-
Flat absorber plate Solar air heater or Flat absorber plate Solar air collector
- IDPSAH:
-
Inline Dimpled absorber Plate Solar air heater or Inline Dimple absorber Plate Solar air collector
- D p :
-
Print or imprint diameter of dimple, m
- d h :
-
Indention depth of dimple, m
- S T , S L :
-
Span wise and Stream wise dimple pitch, m
- D h :
-
Equivalent diameter of SAH duct, m
- W, H :
-
Width and height of SAH duct, m
- W/H :
-
Aspect ratio of SAH duct
- A pl :
-
Surface area of plate (glass or absorber), m2
- N gl :
-
Number of glazing (tempered glass)
- t gl :
-
Thickness of glazing (tempered glass), m
- tins :
-
Insulation thickness, m
- \({\overline{T}}_{{\text{airin}}} ,{\overline{T}}_{{\text{airout}}}\) :
-
Mean temperature of inlet air and outlet air in a SAH, K
- \({M}_{{\text{air}}}\) :
-
Air flow rate in SAH, kg s-1
- \({\overline{V}}_{{\text{i}}},{\overline{V}}_{0}\) :
-
Mean air flow velocity at inlet and outlet of the SAH, m s-1
- \({A}_{{\text{i}}}{,A}_{0}\) :
-
Inlet and outlet area of solar duct, m2
- \({Q}_{{\text{ext}}}\) :
-
Amount of useful heat extracted rate for air type solar collector, W
- \({Q}_{{\text{rec}}}\) :
-
Amount of heat received rate by the collector surface (absorber plate) in air type solar collector, W
- \({\eta }_{{\text{inst}}}\) :
-
SAH instantaneous (or thermal) efficiency
- I :
-
Solar irradiation or net global irradiation fall on solar collector plane, W m-2
- α:
-
Absorber plate’s absorptivity
- τ:
-
Glass’s transmissivity
- \({C}_{{\text{pair}}}\) :
-
Air specific heat, J kg-1 K-1
- \({Q}_{{\text{eff}}}\) :
-
Effective heat transfer rate, W
- \({P}_{{\text{bl}}}\) :
-
Pumping energy required by the blower, W
- \({\eta }_{{\text{eff}}}\) :
-
SAH effective Efficiency
- Nuavg :
-
Area averaged Nusselt number
- h avg :
-
The area averaged convective heat transfer coefficient, W m−2 K-1
- ka :
-
The fluid (air) thermal conductivity W m-1 K-1
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- μa :
-
The air viscosity, N s m-2
- ρ a :
-
The air density, kg m-3
- f avg :
-
Area averaged friction factor
- \(\Delta {P}_{{\text{d}}}\) :
-
Pressure drop, Pa
- L :
-
Absorber plate’s length, m
- \({F}_{0}, {F}_{{\text{R}}}\) :
-
SAH heat removal factor based on air outlet and inlet temperature
- F/ :
-
The collector efficiency or SAH efficiency factor of SAH
- \({\eta }_{{\text{daily}}}\) :
-
SAH daily Efficienc
- \({Q}_{{\text{top}}}\) :
-
Amount of heat loss rate from the top of the tempered glass, W
- \({T}_{{\text{gl}}}\) :
-
Tempered glass temperature, K
- \({T}_{{\text{amb}}}\) :
-
Ambient (surrounding air) temperature, K
- \({h}_{{\text{w}}}\) :
-
Wind heat transfer coefficient (because of convection), W m−2 K-1
- \({h}_{{\text{r}}}\) :
-
Radiative heat transfer Coefficient, W m−2 K-1
- \({V}_{{\text{w}}}\) :
-
Wind velocity, m s-1
- σ:
-
Stefan–Boltzmann Constant, W m−2 K-4
- \({\epsilon }_{{\text{g}}}\) :
-
Glass covers emissivity
- \({T}_{{\text{s}}}\) :
-
Temperature of the sky, K
- \({U}_{{\text{L}}}\) :
-
SAH global heat loss (total heat loss) coefficient, W m−2 K-1
- p/e :
-
Ratio of roughness pitch to roughness height
References
Debnath S, Das B, Randive PR, Pandey KM. Performance analysis of solar air collector in the climatic condition of North Eastern India. Energy. 2018;165:281–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.09.038.
Yadav AS, Bhagoria JL. A CFD based thermo-hydraulic performance analysis of an artificially roughened solar air heater having equilateral triangular sectioned rib roughness on the absorber plate. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;70:1016–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.11.074.
Gawande VB, Dhoble AS, Zodpe DB, Chamoli S. A review of CFD methodology used in literature for predicting thermo-hydraulic performance of a roughened solar air heater. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2016;54:550–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.025.
Hosseini SS, Ramiar A, Ranjbar AA. Numerical investigation of natural convection solar air heater with different fins shape. Renew Energy. 2018;117:488–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.10.052.
Chamoli S, Lu R, Xu D, Yu P. Thermal performance improvement of a solar air heater fitted with winglet vortex generators. Sol Energy. 2018;159:966–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.11.046.
Karwa R, Chauhan K. Performance evaluation of solar air heaters having v-down discrete rib roughness on the absorber plate. Energy. 2009;35:398–409.
Panda S, Kumar R. Combined effect of solar intensity and air mass flow rate on inline spherical dimple based solar air heater during summer season. Sol Energy. 2023;258:156–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2023.05.002.
Panda S, Kumar R. Flow friction and thermal performance of dimple imprinted based solar air-heater: A numerical study. Numer Heat Transf Part A Appl. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/10407782.2022.2105066.
Panda S, Kumar R. A review on heat transfer enhancement of solar air heater using various artificial roughed geometries. J Adv Res Fluid Mech Therm Sci. 2021;89:92–133.
Pandey NK, Bajpai VK. Experimental investigation of heat transfer and friction characteristics of arc-shaped roughness elements having central gaps on the absorber plate of solar air heater. J Sol Energy Eng. 2016;138:041005.
Sun W, Ji J, He W. Influence of channel depth on the performance of solar air heaters. Energy. 2010;35:4201–7.
Karim MA, Hawlader MNA. Development of solar air collectors for drying applications. Energy Convers Manag. 2004;45:329–44.
Karsli S. Performance analysis of new-design solar air collectors for drying applications. Renew Energy. 2007;32:1645–60.
Gupta D, Solanki SC, Saini JS. Heat and fluid flow in rectangular solar air heater ducts having transverse rib roughness on absorber plates. Sol Energy. 1993;51:31–7.
Saini RP, Verma J. Heat transfer and friction factor correlations for a duct having dimple-shape artificial roughness for solar air heaters. Energy. 2008;33:1277–87.
Raj AK, Vinay CN, Srinivas M, Jayaraj S. Experimental investigation on solar thermal air heater with a combination of roughness elements for heat transfer improvement. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;146:1453–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10097-z.
Hassan H, Abo-Elfadl S, El-Dosoky MF. An experimental investigation of the performance of new design of solar air heater (tubular). Renew Energy. 2020;151:1055–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.11.112.
Abo-Elfadl S, Hassan H, El-Dosoky MF. Study of the performance of double pass solar air heater of a new designed absorber: an experimental work. Sol Energy. 2020;198:479–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2020.01.091.
Das B, Mondol JD, Debnath S, Pugsley A, Smyth M, Zacharopoulos A. Effect of the absorber surface roughness on the performance of a solar air collector: an experimental investigation. Renew Energy. 2020;152:567–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.01.056.
Kumar R, Chand P. Performance enhancement of solar air heater using herringbone corrugated fins. Energy. 2017;127:271–9.
Priyam A, Chand P. Thermal and thermohydraulic performance of wavy finned absorber solar air heater. Sol Energy. 2016;130:250–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.02.030.
Alam T, Kim MH. Heat transfer enhancement in solar air heater duct with conical protrusion roughness ribs. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;126:458–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.07.181.
Sheelam S, Velayudhan PC. Solar air collector with right-angle triangle corrugations for an indirect type solar dryer for enhancement in performance. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2024;149:311–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12680-6.
Aharwal KR, Gandhi BK, Saini JS. Heat transfer and friction characteristics of solar air heater ducts having integral inclined discrete ribs on absorber plate. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2009;52:5970–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2009.05.032.
Bhagoria JL, Saini JS, Solanki SC. Heat transfer coefficient and friction factor correlations for rectangular solar air heater duct having transverse wedge shaped rib roughness on the absorber plate. Renew Energy. 2002;25:341–69.
Bopche SB, Tandale MS. Experimental investigations on heat transfer and frictional characteristics of a turbulator roughened solar air heater duct. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2009;52:2834–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2008.09.039.
Gawande VB, Dhoble AS, Zodpe DB, Chamoli S. Experimental and CFD investigation of convection heat transfer in solar air heater with reverse L-shaped ribs. Sol Energy. 2016;131:275–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.02.040.
Sawhney JS, Maithani R, Chamoli S. Experimental investigation of heat transfer and friction factor characteristics of solar air heater using wavy delta winglets. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;117:740–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.01.113.
Singh S, Chander S, Saini JS. Heat transfer and friction factor correlations of solar air heater ducts artificially roughened with discrete V-down ribs. Energy. 2011;36:5053–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.05.052.
Yadav S, Kaushal M, Varun S. Nusselt number and friction factor correlations for solar air heater duct having protrusions as roughness elements on absorber plate. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2013;44:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2012.05.011.
Sahu MM, Bhagoria JL. Augmentation of heat transfer coefficient by using 90° broken transverse ribs on absorber plate of solar air heater. Renew Energy. 2005;30:2057–73.
Lanjewar A, Bhagoria JL, Sarviya RM. Experimental study of augmented heat transfer and friction in solar air heater with different orientations of W-Rib roughness. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2011;35:986–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2011.01.019.
Jaurker AR, Saini JS, Gandhi BK. Heat transfer and friction characteristics of rectangular solar air heater duct using rib-grooved artificial roughness. Sol Energy. 2006;80:895–907.
Karwa R, Chitoshiya G. Performance study of solar air heater having v-down discrete ribs onabsorber plate. Energy. 2013;55:939–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.03.068.
Skullong S, Kwankaomeng S, Thianpong C, Promvonge P. Thermal performance of turbulent flow in a solar air heater channel with rib-groove turbulators. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2014;50:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2013.11.001.
Ravi RK, Saini RP. Effect of roughness elements on thermal and thermohydraulic performance of double pass solar air heater duct having discrete multi V-shaped and staggered rib roughness on both sides of the absorber plate. Exp Heat Transf. 2018;31:47–67.
Promvonge P, Khanoknaiyakarn C, Kwankaomeng S, Thianpong C. Thermal behavior in solar air heater channel fitted with combined rib and delta-winglet. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2011;38:749–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2011.03.014.
Chabane F, Moummi N, Benramache S. Experimental study of heat transfer and thermal performance with longitudinal fins of solar air heater. J Adv Res. 2014;5:183–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2013.03.001.
Akpinar EK, Koçyiǧit F. Experimental investigation of thermal performance of solar air heater having different obstacles on absorber plates. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37:416–21.
Omojaro AP, Aldabbagh LBY. Experimental performance of single and double pass solar air heater with fins and steel wire mesh as absorber. Appl Energy. 2010;87:3759–65.
Gill RS, Singh S, Singh PP. Low cost solar air heater. Energy Convers Manag. 2012;57:131–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2011.12.019.
Mahboub C, Moummi N, Brima A, Moummi A. Experimental study of new solar air heater design. Int J Green Energy. 2016;13:521–9.
Kabeel AE, Khalil A, Shalaby SM, Zayed ME. Investigation of the thermal performances of flat, finned, and v-corrugated plate solar air heaters. J Sol Energy Eng. 2016;138:051004.
Şevik S, Abuşka M. Thermal performance of flexible air duct using a new absorber construction in a solar air collector. Appl Therm Eng. 2019;146:123–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.09.100.
Kumar A, Layek A. Thermo-hydraulic performance of solar air heater having winglet type roughness element. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2022;147:10481–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11286-8.
Sethi M, Varun, Thakur NS. Correlations for solar air heater duct with dimpled shape roughness elements on absorber plate. Sol Energy. 2012;86:2852–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2012.06.024.
Şevik S, Özdilli Ö, Abuşka M. Experimental investigation of relative roughness height effect in solar air collector with convex dimples. Renew Energy. 2022;194:100–16.
Kumar V. Nusselt number and friction factor correlations of three sides concave dimple roughened solar air heater. Renew Energy. 2019;135:355–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.12.002.
Kumar V, Prasad L. Thermal performance investigation of three sides concave dimple roughened solar air heaters. Sol Energy. 2019;188:361–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.06.008.
Panda S, Kumar R. A review on effect of various artificial roughness on heat transfer enhancement in a channel flow. J Therm Eng. 2021;7:1267–301.
Perwez A, Kumar R. Thermal performance invesigation of the flat and spherical dimple absorber plate solar air heaters. Sol Energy. 2019;193:309–23.
Bhushan A, Kumar R, Perwez A. Experimental investigations of thermal performance for flat and dimpled plate solar air heater under turbulent flow conditions. Sol Energy. 2022;231:664–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2021.11.060.
Bezbaruah PJ, Das RS, Sarkar BK. Experimental and numerical analysis of solar air heater accoutered with modified conical vortex generators in a staggered fashion. Renew Energy. 2021;180:109–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.08.046.
Quaschning V. Understanding renewable energy systems. Underst. Renew. Energy Syst. 2014.
Vejen NK, Furbo S, Shah LJ. Development of 12.5 m2 solar collector panel for solar heating plants. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2004;84:205–23.
Gao W, Lin W, Liu T, Xia C. Analytical and experimental studies on the thermal performance of cross-corrugated and flat-plate solar air heaters. Appl Energy. 2007;84:425–41.
Abdullah AS, Amro MI, Younes MM, Omara ZM, Kabeel AE, Essa FA. Experimental investigation of single pass solar air heater with reflectors and turbulators. Alexandria Eng J. 2020;59:579–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2020.02.004.
Peng D, Zhang X, Dong H, Lv K. Performance study of a novel solar air collector. Appl Therm Eng. 2010;30:2594–601.
Koyuncu T. Performance of various design of solar air heaters for crop drying applications. Renew Energy. 2006;31:1073–88.
Rao Y, Li B, Feng Y. Heat transfer of turbulent flow over surfaces with spherical dimples and teardrop dimples. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2015;61:201–9.
Rao Y, Feng Y, Li B, Weigand B. Experimental and numerical study of heat transfer and flow friction in channels with dimples of different shapes. J Heat Transf. 2015;137:031901.
Shin S, Lee KS, Park SD, Kwak JS. Measurement of the heat transfer coefficient in the dimpled channel: effects of dimple arrangement and channel height. J Mech Sci Technol. 2009;23:624–30.
Park D, Silva CA, Marotta E, Fletcher L. Study of laminar forced convection heat transfer for dimpled heat sinks. J Thermophys Heat Transf. 2008;22:262–70.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization contributed by SP, RK; data curation contributed by SP; formal analysis contributed by SP; investigation contributed by SP; methodology contributed by SP, RK; roles/writing—original draft contributed by SP; writing—review & editing contributed by SP, RK; supervision contributed by RK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Panda, S., Kumar, R. Experimental investigation on the characteristics of inline dimple-based SAH with dimple pitch variation. J Therm Anal Calorim (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13088-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13088-6