Abstract
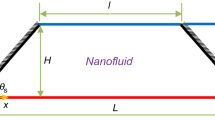
A numerical investigation has been performed to analyze heat convection through a micropolar nanofluid in an open rectangular enclosure filled with a porous medium. The enclosure is embedded with a heated object and having a heated non-planar bottom wall. Three different shapes of the embedded heated object, diamond-shaped, L-shaped, and triangular-shaped, are considered, and their effects are compared numerically. Successive over-relaxation method coupled with Gauss–Seidel iteration technique are employed in order to numerically tackle the nonlinear model momentum and energy equations. The outcomes are discussed in terms of streamlines, isotherms, and isolines of microrotation, averaged Nusselt number on the heated wall for different values of intricated parameters. The calibrated parameters Darcy number, vortex viscosity, Rayleigh number, and volume fraction of nanoparticles, respectively, are taken in the range 0.0001 ≤ Da ≤ 0.1, 0.5 ≤ K ≤ 5.0, 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, and 0 ≤ φ ≤ 0.04. It reveals that in the absence of heated object, the non-planarity of the wall lessens the heat transfer rate by 12.95% (when compared to the planar wall). The impact of the shape of the embedded heated object on the heat transfer rate is estimated and found an enhancement of 15.34%, 11.63%, 13.51% for diamond-shaped, L-shaped, and triangular-shaped objects, respectively. Increasing the Darcy number boosts the heat transfer rate while an upsurge in the vortex viscosity parameter lessens the heat transfer rate. The Nusselt number in the enclosure with and without a heated object (depending on the volume fraction of nanoparticles) is also computed numerically.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(c_{\text{p}}\) :
-
Specific heat capacity (J kg−1 K−1)
- Da:
-
Darcy number (–)
- H :
-
Height of the enclosure (m)
- j :
-
Micro-inertia density (m−2)
- k :
-
Coefficient of thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- K :
-
Dimensionless vortex viscosity (–)
- N* :
-
Angular velocity (s−1)
- N :
-
Dimensionless angular velocity vector normal to the x–y plane (–)
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number (–)
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number (–)
- Ra:
-
Rayleigh number (–)
- \(T^{*}\) :
-
Dimensional temperature (K)
- \(u^{*}\), \(v^{*}\) :
-
Dimensional velocity component along x and y-axis (m s−1)
- u, v :
-
Dimensionless velocity component along x and y-axis (–)
- \(u_{\text{in}}\) :
-
Inlet velocity (m s−1)
- \(x^{*} ,y^{*}\) :
-
Dimensional Cartesian coordinates (m)
- x, y :
-
Dimensionless Cartesian coordinates (–)
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity (m2 s−1)
- \(\beta\) :
-
Coefficient of volumetric thermal expansion (K−1)
- \(\xi ,\eta\) :
-
Coordinates of the computational domain in the dimensionless form (–)
- \(\theta\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature (–)
- κ :
-
Vortex viscosity (m−1 s−1)
- \(\mu\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- \(\upsilon\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity (m2 s−1)
- \(\varphi\) :
-
Volume fraction of nanoparticle (–)
- \(\chi\) :
-
Material parameter (–)
- \(\omega\) :
-
Dimensionless vorticity (–)
- ave:
-
Average
- f:
-
Base fluid
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- p:
-
Particle, pressure
References
Nield DA, Bejan A. Convection in porous media. 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer; 2006.
Alhashash A, Saleh H. Natural convection induced by undulated surfaces in a porous enclosure filled with nanoliquid. Adv Mech Eng. 2019;11(9):1–9.
Biswal P, Basak T. Heatlines visualization of convective heat flow during differential heating of porous enclosures with concave/convex side walls. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2018;28:1506–38.
Cheong HT, Sivasankaran S, Bhuvaneswari M. Natural convection in a wavy porous cavity with sinusoidal heating and internal heat generation. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2017;27(2):287–309.
Rashed ZZ, Ahmed SE, Aly AM. Heat transfer enhancement in the complex geometries filled with porous media. Therm Sci. 2019. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI181218166R.
Sharma MK, Manjeet C. Nanofluid flow and heat convection in a channel filled with porous medium. J Int Acta Phys Sci. 2017;21:167–88.
Mehryan SAM, Izadi M, Sheremet MA. Analysis of conjugate natural convection within a porous square enclosure occupied with micro polar nanofluid using local thermal non-equilibrium model. J Mol Liq. 2018;250:353–68.
Biswas N, Manna NK, Datta P, Mahapatra PS. Analysis of heat transfer and pumping power for bottom-heated porous cavity saturated with Cu–water nanofluid. Powder Technol. 2018;326:356–69.
Torki M, Etesami N. Experimental investigation of natural convection heat transfer of SiO2/water nanofluid inside inclined enclosure. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139:1565–74.
Dutta S, Goswami N, Pati S, Biswas AK. Natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation in a porous rhombic enclosure: influence of non-uniform heating. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09634-7.
Dogonchi AS, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ, Ganji DD. Numerical analysis of natural convection of Cu–water nanofuid filling triangular cavity with semi-circular bottom wall. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135(6):3485–97.
Dutta S, Biswas AK, Pati S. Natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation inside porous quadrantal enclosure with non-isothermal heating at the bottom wall. Numer Heat Transf. 2018;73(4):222–40.
Dutta S, Biswas AK, Pati S. Numerical analysis of natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation in a porous quadrantal cavity. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2019;29(12):4826–49.
Dutta S, Biswas AK. Entropy generation due to natural convection with non-uniform heating of porous quadrantal enclosure—a numerical study. Front Heat Mass Transf. 2018;10(8):1–12.
Astanina MS, Sheremet MA, Oztop HF, Hamdeh NA. MHD natural convection and entropy generation of ferro fluid in an open trapezoidal cavity partially filled with a porous medium. Int J Mech Sci. 2018;136:493–502.
Rundora L, Makinde OD. Effects of suction/injection on unsteady reactive variable viscosity non-Newtonian fluid flow in a channel filled with porous medium. J Petrol Sci Eng. 2013;108:328–35.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. Simulation of water based nanofluid convective flow inside a porous enclosure via non-equilibrium model. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;120:1200–12.
Choi SUS. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Fluids Eng Div. 1995;231:99–105.
Qiu L, Zhu N, Feng Y, Michaelides EE, Żyła G, Jing D, Zhang X, Norris PM, Markides CN, Mahian O. A review of recent advances in thermophysical properties at the nanoscale: from solid state to colloids. Phys Rep. 2020;843:1–81.
Molana M, Zarrinderafsh V, Chamkha AJ, Izadi S, Rafizadeh S. Magnetohydrodynamics convection in nanofluids filled cavities: a review. Heat Transf Asian Res. 2020;49(23):1418–43.
Bourantas GC, Skouras ED, Loukopoulos VC, Burganos VN. Heat transfer and natural convection of nanofluids in porous media. Eur J Mech B Fluids. 2014;43:45–56.
Sharma MK, Manjeet C, Makinde OD. Flow and heat transfer in nanofluid flow through a cylinder filled with foam porous medium under radial injection. Defect Diffus Forum. 2018;387:166–81.
Mansour MA, Ahmed SE. A Numerical study on natural convection in porous media filled an inclined triangular enclosure with heat source using nanofluid in the presence of heat generation effect. Eng Sci Technol Int J. 2015;18(3):485–95.
Yirga Y, Shankar B. MHD Flow and heat transfer of nanofluids through a porous media due to a stretching sheet with viscous dissipation and chemical reaction effects. Int J Comput Methods Eng Sci Mech. 2015;16(5):275–84.
Izadi M, Sinaei S, Mehryan SAM, Oztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. Natural convection of a nanofluid between two eccentric cylinders saturated by porous material: Buongiorno’s two phase model. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;127:67–75.
House JM, Beckermann C, Smith TF. Effect of a centered conducting body on natural convection heat transfer in an enclosure. Numer Heat Transf. 1990;18(2):213–25.
Mahmoodi M, Sebdani SM. Natural convection in a square cavity containing a nanofluid and an adiabatic square block at the centre. Superlattices Microstruct. 2012;52(2):261–75.
Tayebi T, Chamkha AJ. MHD Natural convection heat transfer of hybrid nanofluid in a square enclosure in the presence of a wavy circular conductive cylinder. J Therm Sci Eng Appl. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4044857.
Bendaraa A, Charafi MM, Hasnaoui A. Numerical study of natural convection in a differentially heated square cavity filled with nanofluid in the presence of fins attached to walls in different locations. Phys Fluids. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5091709.
Roy NC. Flow and heat transfer characteristics of a nanofluid between a square enclosure and a wavy wall obstacle. Phys Fluids. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5111517.
Akar S, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Second law of thermodynamic analysis for nanofluid turbulent flow around a rotating cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:1189–200.
Rashidi S, Akbarzadeh M, Karimi N, Masoodi R. Combined effects of nanofluid and transverse twisted-baffles on the flow structures, heat transfer and irreversibilities inside a square duct—a numerical study. Appl Therm Eng. 2018;130:135–48.
Laein RP, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Experimental investigation of nanofluid free convection over the vertical and horizontal flat plates with uniform heat flux by PIV. Adv Powder Technol. 2016;27(2):312–22.
Giwa SO, Sharifpur M, Ahmadi MH, Meyer JP. A review of magnetic field influence on natural convection heat transfer performance of nanofluids in square cavities. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09832-3.
Bovand M, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Optimum interaction between magnetohydrodynamics and nanofluid for thermal and drag management. J Thermophys Heat Transf. 2016;31:218–29.
Rashidi S, Bovand M, Esfahani JA, Ahmadi G. Discrete particle model for convective AL2O3-water nanofluid around a triangular obstacle. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;100:39–54.
Maskaniyan M, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. A two-way couple of Eulerian–Lagrangian model for particle transport with different sizes in an obstructed channel. Powder Technol. 2017;312(1):260–9.
Rashidi S, Bovand M, Esfahan JA. Structural optimization of nanofluid flow around an equilateral triangular obstacle. Energy. 2015;88(1):385–98.
Bovand M, Rashidi S, Ahmadi G, Esfahani JA. Effects of trap and reflect particle boundary conditions on particle transport and convective heat transfer for duct flow—a two-way coupling of Eulerian–Lagrangian model. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;108:368–77.
Sheremet M, Pop I, Öztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. Natural convection of nanofluid inside a wavy cavity with a non-uniform heating entropy generation analysis. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2017;27(4):958–80.
Oztop HF, Abu-Nada E. Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2008;29(5):1326–36.
Selimefendigil F, Öztop HF. Mixed convection of nanofluids in a three-dimensional cavity with two adiabatic inner rotating cylinders. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;117:331–43.
Bondareva NS, Sheremet MA, Oztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. Entropy generation due to natural convection of a nanofluid in a partially open triangular cavity. Adv Powder Technol. 2017;28(1):244–55.
Eringen AC. Simple microfluids. Int J Eng Sci. 1964;2:205–17.
Eringen AC. Theory of micropolar fluids. J Math Mech. 1966;16:1–18.
Papautsky I, Brazzle J, Ameel T, Frazier AB. Laminar fluid behavior in micro-channel using micropolar fluid theory. Sens Actuators. 1999;73:101–8.
Aydin O, Pop I. Natural convection from a discrete heater in enclosures filled with a micropolar fluid. Int J Eng Sci. 2005;43(19–20):1409–18.
Rashad AM, Mansour MA, Gorla RSR. Mixed convection from a discrete heater in lid-driven enclosures filled with non-Newtonian nanofluids. J Nanomater Nanoeng Nanosyst. 2017;231(1):3–16.
Reddy CS, Prasad VR, Jayalakshmi K. Numerical simulation of natural convection of micropolar fluid in a rectangular porous enclosure. IJITEE. 2019;8(4S):329–39.
Maripala S, Kishan N. Micropolar nanofluid over a MHD heat transfer porous shrinking sheet. Int J Math Appl. 2017;9(4-B):211–7.
Pordanjani AH, Jahanbakhshi A, Nadooshan AA, Afrand M. Effect of two isothermal obstacles on the natural convection of nanofluid in the presence of magnetic field inside an enclosure with sinusoidal wall temperature distribution. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;121:565–78.
Maxwell JC. A treatise on electricity and magnetism. 2nd ed. London: Oxford University Press; 1904.
Brinkman HC. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J Chem Phys. 1952;20:571–81.
Seyyedi SM, Dayyan M, Soleimani S, Ghasemi E. Natural convection heat transfer under constant heat flux wall in a nanofluid filled annulus enclosure. Ain Shams Eng J. 2015;6(1):267–80.
Saleem M, Hossain MA, Saha SC. Mixed convection flow of micropolar fluid in an open-ended arc-shape cavity. J Fluids Eng Trans ASME. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4007268.
Bakar NA, Karimipour A, Roslan R. Effect of magnetic field on mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven square cavity. J Thermodyn. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3487182.
Jani S, Mahmoodi M, Amini M. Magnetohydrodynamic free convection in a square cavity heated from below and cooled from other walls. Int J Mech Aero Ind Mech Manuf Eng. 2013;7(4):329–34.
Morshed KN, Sharif MAR, Islam AW. Laminar mixed convection in a lid-driven square cavity with two isothermally heated square internal blockages. Chem Eng Commun. 2015;202(9):1176–90.
Feng S, Graham AL, Abbott JR, Brenner H. Antisymmetric stresses in suspensions: vortex viscosity and energy dissipation. J Fluids Mech. 2006;563:97–122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ushachew, E.G., Sharma, M.K. & Makinde, O.D. Heat convection in micropolar nanofluid through porous medium-filled rectangular open enclosure: effect of an embedded heated object with different geometries. J Therm Anal Calorim 146, 1865–1881 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10118-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10118-x