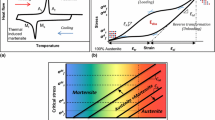
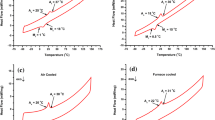
Abstract
In this study, the thermal stability and phase transformation of Ni50-xTi50Snx (x = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, and 3.5 at%) SMAs have been investigated. Some thermal, mechanical, and microstructural characteristics were measured using DSC, Vickers microhardness, XRD, and SEM–EDX devices. Calculations, such as grain size and entropy change, were also performed based on the DSC results. It is found that by increasing the amount of Sn in NiTiSn alloy, fragmentation has occurred in the alloy, which may be due to the high concentration of Sn and Ti in the grooves. Furthermore, the microhardness and grain size are in harmony, i.e., the microhardness of the alloys was influenced by the grain size. Additionally, martensite and austenite peaks were shifted to the lower temperature by increasing the cycling process, while the rate of shifting increased generally by adding more Sn element into the alloy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dagdelen F, Kok M, Qader I. Effects of Ta content on thermodynamic properties and transformation temperatures of shape memory NiTi alloy. Met Mater Int. 2019;25(6):1420–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00298-z.
Ercan E, Dagdelen F, Qader I. Effect of tantalum contents on transformation temperatures, thermal behaviors and microstructure of CuAlTa HTSMAs. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139(1):29–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08418-y.
Dagdelen F, Aldalawi M, Kok M, Qader I. Influence of Ni addition and heat treatment on phase transformation temperatures and microstructures of a ternary CuAlCr alloy. Eur Phys J Plus. 2019;134(2):66. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12479-3.
Duerig TW, Albrecht J, Gessinger GH. A shape-memory alloy for high-temperature applications. JOM. 1982;34(12):14–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03338156.
Qader IN, Kök M, Dağdelen F, Aydogdu Y. A review of smart materials: researches and applications. El-Cezerî J Sci Eng. 2019;6(3):755–88. https://doi.org/10.31202/ecjse.562177.
Frenzel J, George EP, Dlouhy A, Somsen C, Wagner M-X, Eggeler G. Influence of Ni on martensitic phase transformations in NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2010;58(9):3444–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.02.019.
Frenzel J, Zhang Z, Somsen C, Neuking K, Eggeler G. Influence of carbon on martensitic phase transformations in NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2007;55(4):1331–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.10.006.
Frenzel J, Wieczorek A, Opahle I, Maaß B, Drautz R, Eggeler G. On the effect of alloy composition on martensite start temperatures and latent heats in Ni–Ti–based shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2015;90:213–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.02.029.
Qader IN, Kök M, Dağdelen F. Effect of heat treatment on thermodynamics parameters, crystal and microstructure of (Cu–Al–Ni–Hf) shape memory alloy. Physica B. 2019;553:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.10.021.
Elahinia MH, Hashemi M, Tabesh M, Bhaduri SB. Manufacturing and processing of NiTi implants: a review. Prog Mater Sci. 2012;57(5):911–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2011.11.001.
Otsuka K, Ren X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog Mater Sci. 2005;50(5):511–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2004.10.001.
Miyazaki S, Igo Y, Otsuka K. Effect of thermal cycling on the transformation temperatures of Ti–Ni alloys. Acta Metall. 1986;34(10):2045–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(86)90263-4.
Tong Y, Gu H, James RD, Qi W, Shuitcev AV, Li L. Novel TiNiCuNb shape memory alloys with excellent thermal cycling stability. J Alloys Compd. 2019;782:343–7.
Tong Y, Guo B, Chen F, Tian B, Li L, Zheng Y, et al. Thermal cycling stability of ultrafine-grained TiNi shape memory alloys processed by equal channel angular pressing. Scr Mater. 2012;67(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2012.03.005.
Kockar B, Karaman I, Kim J, Chumlyakov YI, Sharp J, Yu C-JM. Thermomechanical cyclic response of an ultrafine-grained NiTi shape memory alloy. Acta Mater. 2008;56(14):3630–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2008.04.001.
Ma J, Karaman I, Noebe RD. High temperature shape memory alloys. Int Mater Rev. 2010;55(5):257–315. https://doi.org/10.1179/095066010X12646898728363.
Benafan O, Notardonato W, Meneghelli B, Vaidyanathan R. Design and development of a shape memory alloy activated heat pipe-based thermal switch. Smart Mater Struct. 2013;22(10):105017. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/22/10/105017.
Kim J-H, Choi H-J, Kim M-S, Miyazaki S, Kim Y-W, Chun BS, et al. Crystallization and martensitic transformation behavior of Ti–Ni–Sn alloy ribbons. Intermetallics. 2012;30:51–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2012.03.040.
Young AW, Torgerson T, Ley NA, Gomez K, Benafan O, Young ML. Effects of Sn addition on NiTi shape memory alloys. Shape Mem Superelast. 2019;5(1):125–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-018-00197-z.
Jang J-y, Chun S-j, Kim N-s, Cho J-w, Kim J-h, Yeom J-t, et al. Martensitic transformation behavior in Ti–Ni–X (Ag, In, Sn, Sb, Te, Tl, Pb, Bi) ternary alloys. Mater Res Bull. 2013;48(12):5064–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.05.004.
Singh N, Talapatra A, Junkaew A, Duong T, Gibbons S, Li S, et al. Effect of ternary additions to structural properties of NiTi alloys. Comput Mater Sci. 2016;112:347–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2015.10.029.
Bozzolo G, Noebe RD, Mosca HO. Site preference of ternary alloying additions to NiTi: Fe, Pt, Pd, Au, Al, Cu, Zr and Hf. J Alloys Compd. 2005;389(1–2):80–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.07.051.
Kim J-H, Jung K-T, Noh J-P, Cho G-B, Miyazaki S, Nam T-H. Martensitic transformation behavior of Ti–Ni–Sn alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2013;577:S200–4.
Choi H-J, Kim J-H, Noh J-P, Miyazaki S, Kim Y-W, Nam T-H. Crystallization behavior and microstructure of Ti–36Ni–7Sn (at.%) alloy ribbons. Scr Mater. 2011;65(7):611–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2011.06.039.
Eckelmeyer K. Effect of alloying on the shape memory phenomenon in nitinol. Scr Metall (United States). 1976. https://doi.org/10.1016/0036-9748(76)90339-2.
Uchil J, Kumara KG, Mahesh K. Effects of heat treatment temperature and thermal cycling on phase transformations in Ni–Ti–Cr alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2001;325(1–2):210–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(01)01274-9.
Zheng Y, Yang F, Meng X, Cai W, Zhao L. Microstructure and phase transformation of TiNi alloy with addition of third element Sn. Rare Metal Mater Eng. 2004;33(6):215–7.
Choe H-J, Kim J-H, Lee S-H, Noh J-P, Kim Y-W, Miyazaki S, et al. Microstructure and martensitic transformation behavior of crystallized Ti–36Ni–7Sn (at%) alloy ribbons. J Alloys Compd. 2013;577:S195–9.
Tong Y, Guo B, Chen F, Tian B, Li L, Zheng Y, et al. Two-way shape memory effect of TiNiSn alloys developed by martensitic deformation. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;550:434–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.04.052.
Kim J-H, Im Y-M, Noh J-P, Miyazaki S, Nam T-H. Microstructures and martensitic transformation behavior of Ti–Ni–Sn alloys. Scr Mater. 2011;65(7):608–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2011.06.040.
Wagner M-X, Dey S, Gugel H, Frenzel J, Somsen C, Eggeler G. Effect of low-temperature precipitation on the transformation characteristics of Ni-rich NiTi shape memory alloys during thermal cycling. Intermetallics. 2010;18(6):1172–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2010.02.048.
Uchil J, Kumara KG, Mahesh K. Effect of thermal cycling on R-phase stability in a NiTi shape memory alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2002;332(1–2):25–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(01)01711-7.
Tadaki T, Nakata Y, Ki Shimizu, Otsuka K. Crystal structure, composition and morphology of a precipitate in an aged Ti-51 at% Ni shape memory alloy. Trans Jpn Inst Met. 1986;27(10):731–40. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans1960.27.731.
Recarte V, Pérez-Landazábal J, Rodrıguez P, Bocanegra E, Nó M, San Juan J. Thermodynamics of thermally induced martensitic transformations in Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2004;52(13):3941–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2004.05.009.
Saud SN, Bakar TAA, Hamzah E, Ibrahim MK, Bahador A. Effect of quarterly element addition of cobalt on phase transformation characteristics of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloys. Metall Mater Trans A. 2015;46(8):3528–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2924-2.
Kök M, Zardawi HSA, Qader IN, Kanca MS. The effects of cobalt elements addition on Ti2Ni phases, thermodynamics parameters, crystal structure and transformation temperature of NiTi shape memory alloys. Eur Phys J Plus. 2019;134(5):197. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12570-9.
Dagdelen F, Kok M, Qader I. Effects of Ta content on thermodynamic properties and transformation temperatures of shape memory NiTi alloy. Met Mater Int. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00298-z.
Dagdelen F, Esra B, Qader IN, Ozen E, Kok M, Kanca MS, et al. Influence of the Nb content on the microstructure and phase transformation properties of NiTiNb shape memory alloys. JOM. 2020;72:1664–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04026-6.
Kök M, Qader IN, Mohammed SS, Öner E, Dağdelen F, Aydogdu Y. Thermal stability and some thermodynamics analysis of heat treated quaternary CuAlNiTa shape memory alloy. Mater Res Express. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab5bef.
Neves F, Fernandes FB, Martins I, Correia J, Oliveira M, Gaffet E, et al. The transformation behaviour of bulk nanostructured NiTi alloys. Smart Mater Struct. 2009;18(11):115003. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/18/11/115003.
Bassani P, Panseri S, Ruffini A, Montesi M, Ghetti M, Zanotti C, et al. Porous NiTi shape memory alloys produced by SHS: microstructure and biocompatibility in comparison with Ti2Ni and TiNi3. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(10):2277–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5253-x.
Lu B-C, Xu J. Glass formation of Ti–Ni–Sn ternary alloys correlated with TiNi–Ti3Sn pseudo binary eutectics. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2008;354(52–54):5425–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2008.09.016.
Hsieh S, Wu S. A study on a Ti52Ni47Al1 shape memory alloy. J Mater Sci. 1999;34(7):1659–65. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004593003848.
Xiaoyun S, Yan L, Fei Z, Shusuo L. NiTiAl intermetallic alloys strengthened by Mo replacement. Chin J Aeronaut. 2010;23(6):715–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1000-9361(09)60274-0.
Nishida M, Wayman CM, Honma T. Precipitation processes in near-equiatomic TiNi shape memory alloys. Metall Trans A. 1986;17(9):1505–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02650086.
Xiao F, Fukuda T, Kakeshita T. Inverse elastocaloric effect in a Ti–Ni alloy containing aligned coherent particles of Ti3Ni4. Scr Mater. 2016;124:133–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.07.016.
Elrasasi T, Dobróka M, Daróczi L, Beke D. Effect of thermal and mechanical cycling on the elastic and dissipative energy in CuAl (11.5 wt%) Ni (5.0 wt%) shape memory alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2013;577:S517–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.06.108.
Buytoz S, Dagdelen F, Qader I, Kok M, Tanyildizi B. Microstructure analysis and thermal characteristics of NiTiHf shape memory alloy with different composition. Met Mater Int. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00444-7.
Krishna BV, Bose S, Bandyopadhyay A. Laser processing of net-shape NiTi shape memory alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 2007;38(5):1096–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9127-4.
Xia M, Liu P, Sun Q. Grain size dependence of Young’s modulus and hardness for nanocrystalline NiTi shape memory alloy. Mater Lett. 2018;211:352–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.10.024.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Management Unit of the Scientific Research Projects of Firat University (FUBAP) (Project Number: FF.19.14). This article is a part of the current PhD study of I. N. Qader.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest in the printing of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qader, I.N., Kok, M. & Cirak, Z.D. The effects of substituting Sn for Ni on the thermal and some other characteristics of NiTiSn shape memory alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim 145, 279–288 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09758-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09758-w