Abstract
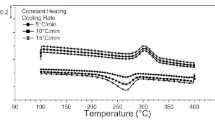
In this study, the effects of heating and cooling rate on the thermal properties of high nickel-rich Ni55Ti45 shape memory alloy were investigated. Transformation temperatures and enthalpies were determined by differential scanning calorimetry. R-phase was observed with two-stage phase transformation during cooling. Transformation finish temperatures were affected, while the transformation start temperatures were not changed by heating–cooling rate. Kissinger, Takhor, and Ozawa methods were applied to find activation energy that is needed for phase transformation. The average activation energy value of 200.5 kJ mol−1 was calculated for Ni55Ti45 alloy. The calculated activation energy was found lower than the ones reported in the literature.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otsuka K, Ren X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog Mater Sci. 2005;50(5):511–678.
Aboutalebi MR, Karimzadeh M, Salehi MT, Abbasi SM, Morakabati M. Influences of aging and thermomechanical treatments on the martensitic transformation and superelasticity of highly Ni-rich Ti-51.5 at.% Ni shape memory alloy. Thermochimica Acta. 2015;616:14–9.
Otsuka K, Sawamura T, Shimizu K. Crystal structure and internal defects of equiatomic TiNi martensite. Phys Status Solidi (a). 1971;5(2):457–70.
Oshida Y, Miyazaki S. Corrosion and biocompatibility of shape memory alloys. Zairyo-to-Kankyo. 1991;40(12):834–44.
Shida Y, Sugimoto Y. Water jet erosion behaviour of Ti–Ni binary alloys. Wear. 1991;146(2):219–28.
Li DY. Wear behavior of TiNi shape memory alloys. Scr Mater. 1996;34(2):195–200.
Lin HC, He JL, Chen KC, Liao HM, Lin KM. Wear characteristics of TiNi shape memory alloys. Metallur Mater Trans A. 1997;28(9):1871–7.
Hartl DJ, Lagoudas DC. Aerospace applications of shape memory alloys. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part G J Aerosp Eng. 2007;221(4):535–52.
Deberg L, Taheri Andani M, Hosseinipour M, Elahinia M. An SMA passive ankle foot orthosis: design, modeling, and experimental evaluation. Smart Mater Res. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/572094.
El Feninat F, Laroche G, Fiset M, Mantovani D. Shape memory materials for biomedical applications. Adv Eng Mater. 2002;4(3):91–104.
Chau ETF, Friend CM, Allen DM, Hora J, Webster JR. A technical and economic appraisal of shape memory alloys for aerospace applications. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2006;438–440:589–92.
Brantley WA, Iijima M, Grentzer TH. Temperature-modulated DSC study of phase transformations in nickel–titanium orthodontic wires. Thermochim Acta. 2002;392–393:329–37.
Florian G, Gabor AR, Nicolae CA, Iacobescu G, Stănică N, Mărăşescu P, et al. Physical properties (thermal, thermomechanical, magnetic, and adhesive) of some smart orthodontic wires. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;134(1):189–208.
Frenzel J, George EP, Dlouhy A, Somsen C, Wagner MF-X, Eggeler G. Influence of Ni on martensitic phase transformations in NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2010;58(9):3444–58.
Karaca HE, Kaya I, Tobe H, Basaran B, Nagasako M, Kainuma R, et al. Shape memory behavior of high strength Ni54Ti46 alloys. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2013;580:66–70.
Padula S, Qiu S, Gaydosh D, Noebe R, Bigelow G, Garg A, et al. Effect of upper-cycle temperature on the load-biased, strain-temperature response of NiTi. Metallur Mater Trans A. 2012;43(12):4610–21.
Nishida M, Wayman CM, Honma T. Precipitation processes in near-equiatomic TiNi shape memory alloys. Metall Trans A. 1986;17(9):1505–15.
Kaya I, Tobe H, Karaca HE, Basaran B, Nagasako M, Kainuma R, et al. Effects of aging on the shape memory and superelasticity behavior of ultra-high strength Ni54Ti46 alloys under compression. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2016;678:93–100.
Motemani Y, Nili-Ahmadabadi M, Tan MJ, Bornapour M, Rayagan S. Effect of cooling rate on the phase transformation behavior and mechanical properties of Ni-rich NiTi shape memory alloy. J Alloy Compd. 2009;469(1–2):164–8.
Kim JI, Liu Y, Miyazaki S. Ageing-induced two-stage R-phase transformation in Ti–50.9 at.% Ni. Acta Mater. 2004;52(2):487–99.
Dlouhy A, Khalil-Allafi J, Eggeler G. Multiple-step martensitic transformations in Ni-rich NiTi alloys—an in situ transmission electron microscopy investigation. Phil Mag. 2003;83(3):339–63.
Antonucci V, Faiella G, Giordano M, Mennella F, Nicolais L. Electrical resistivity study and characterization during NiTi phase transformations. Thermochim Acta. 2007;462(1–2):64–9.
Kök M, Yakinci ZD, Aydogdu A, Aydogdu Y. Thermal and magnetic properties of Ni51Mn28. 5Ga19. 5B magnetic-shape-memory alloy. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115(1):555–9.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;29(11):1702–6.
Takhor RL. Advances in nucleation and crystallization of glasses. Columbus: American Ceramics Society; 1971. p. 166.
Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1965;38(11):1881–6.
Salzbrenner RJ, Cohen M. On the thermodynamics of thermoelastic martensitic transformations. Acta Metall. 1979;27(5):739–48.
Tong HC, Wayman CM. Thermodynamics of thermoelastic martensitic transformations. Acta Metall. 1975;23(2):209–15.
Dlouhý A, Bojda O, Somsen C, Eggeler G. Conventional and in situ transmission electron microscopy investigations into multistage martensitic transformations in Ni-rich NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2008;481–482:409–13.
Hamilton RF, Sehitoglu H, Chumlyakov Y, Maier HJ. Stress dependence of the hysteresis in single crystal NiTi alloys. Acta Mater. 2004;52(11):3383–402.
Paryab M, Nasr A, Bayat O, Abouei V, Eshraghi A. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructural and superelastic behavior of NiTi alloy with wt% Ni. Metal. 2010;16(2):123–31.
Acar E. The determination of the phase transformations and the activation energies in TiNi smart alloys. Gazi Univ Sci J Part C Des Technol. 2016;4(3):165–71.
Dağdelen F, Buytoz S, Akbaş İ. The effects on thermal and microstructure properties of Cu addition in NiTi SMAs. Fırat Univ J Eng Sci. 2017;29(1):269–75.
Dagdelen F, Aydogdu Y. Transformation behavior in NiTi–20Ta and NiTi–20Nb SMAs. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136(2):637–42.
Natalia R, Sergey B. Entropy change in the B2 → B19′ martensitic transformation in TiNi alloy. Thermochim Acta. 2015;602:30–5.
Wang ZG, Zu XT, Huo Y. Effect of heating/cooling rate on the transformation temperatures in TiNiCu shape memory alloys. Thermochim Acta. 2005;436(1–2):153–5.
Acknowledgements
First author acknowledges the support from Eskisehir Technical University (Grant No. BAP-1706F382).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaya, I., Özdemir, Y., Kaya, E. et al. The heating–cooling rate effect on thermal properties of high nickel-rich NiTi shape memory alloy. J Therm Anal Calorim 139, 817–822 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08511-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08511-2