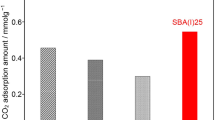
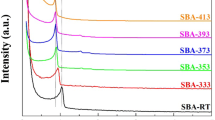
Abstract
In this study, the preparation by grafting of amino-functionalized SBA-15 molecular sieves was carried out. Amino-functionalized molecular sieves were synthesized using a silane coupling agent and different types of amination reagents which react with modified SBA-15. These composites were characterized by FT-IR spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction at low angles, nitrogen physisorption at 77 K, and evaluated by the adsorption of CO2 and its temperature-programmed desorption—TPD. Thermal stability was investigated by TGA and DTA methods. In the view of a possible use of these amino-functionalized molecular sieves as sorbents for CO2 removal, their adsorption–desorption properties towards CO2 were also investigated by the TPD method. The mass loss of amino-functionalized molecular sieves above 215 °C was due to the oxidation and decomposition of amino propyl functional groups. This means that these composites could be used for adsorption of CO2 at temperatures below 215 °C. The adsorption of CO2 and its temperature programmed desorption using thermogravimetry were studied for amino-functionalized molecular sieves at 60 °C. The evolved gases during the adsorption–desorption of CO2 on amino-functionalized molecular sieves were identified by online mass spectrometry coupled with thermogravimetry. CO2 adsorption isotherms of functionalized samples at 60 °C showed that both the adsorption capacity (mg CO2/g adsorbent) and the efficiency of amino groups (mol CO2/mol NH2) depend on the type of amination reagents and the amount of organic compound used.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Samanta A, Zhao A, Shimizu GKH, Sarkar P, Gupta R. Post-combustion CO2 capture using solid sorbents: a review. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2012;51(4):1438–63.
Leung DYC, Caramanna G, Maroto-Valer MM. An overview of current status of carbon dioxide capture and storage technologies. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2014;39:426–43.
Fauth DJ, Gray ML, Pennline HW, Krutka HM, Sjostrom S, Ault AM. Investigation of porous silica supported mixed-amine sorbents for post-combustion CO2 capture. Energy Fuels. 2012;26(4):2483–96.
Bhown AS, Freeman BC. Analysis and status of post-combustion carbon dioxide capture technologies. Environ Sci Technol. 2011;45(20):8624–32.
Mason JA, McDonald TM, Bae T-H, Bachman JE, Sumida K, Dutton JJ, Steven SK, Long JR. Application of a high-throughput analyzer in evaluating solid adsorbents for post-combustion carbon capture via multicomponent adsorption of CO2, N2, and H2O. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137(14):4787–803.
Rezaei F, Lively RP, Labreche Y, Chen G, Fan Y, Koros WJ, Jones CW. Aminosilane-grafted polymer/silica hollow fiber adsorbents for CO2 capture from flue gas. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(9):3921–31.
Bhagiyalakshmi M, Hemalatha P, Ganesh M, Peng MM, Jang HT. Synthesis of copper exchanged heteropolyacids supported on MCM-48 and its application for CO2 adsorption. J Ind Eng Chem. 2011;17:628–32.
Belmabkhout Y, Serna-Guerrero R, Sayari A. Adsorption of CO2-containing gas mixtures over amine-bearing pore-expanded MCM-41 silica: application for gas purification. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2010;49:359–65.
Ma B, Zhuang L, Chen S. Rapid synthesis of tunable-structured short-pore SBA-15 and its application on CO2 capture. J Porous Mater. 2016;23:529–37.
Cao L, Man T, Kruk M. Synthesis of ultra-large-pore SBA-15 silica with two-dimensional hexagonal structure using triisopropylbenzene as micelle expander. Chem Mater. 2009;21:1144–53.
Fan J, Yu C, Wang L, Tu B, Zhao D, Sakamoto Y, Terasaki O. Mesotunnels on the silica wall of ordered SBA-15 to generate three-dimensional large-pore mesoporous networks. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:12113–4.
Kruk M, Cao L. Pore size tailoring in large-pore SBA-15 silica synthesized in the presence of hexane. Langmuir. 2007;23:7247–54.
Sun J, Zhang H, Ma D, Chen Y, Bao X, Klein-Hoffmann A, Pfanderb N, Su DS. Alkanes-assisted low temperature formation of highly ordered SBA-15 with large cylindrical mesopores. Chem Commun. 2005;42:5343–5.
Zholobenko VL, Khodakov AY, Impéror-Clerc M, Durand D, Grillo I. Initial stages of SBA-15 synthesis: an overview. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2008;142:67–74.
Popa A, Sasca V, Verdes O, Ianasi C, Banica R. Heteropolyacids anchored on amino-functionalized MCM-41 and SBA-15 and its application to the ethanol conversion reaction. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127:319–34.
Heydari-Gorji A, Belmabkhout Y, Sayari A. Polyethylenimine-impregnated mesoporous silica: effect of amine loading and surface alkyl chains on CO2 adsorption. Langmuir. 2011;27:12411–6.
Heydari-Gorji A, Yang Y, Sayari A. Effect of the pore length on CO2 adsorption over amine-modified mesoporous silicas. Energy Fuels. 2011;25:4206–10.
Sheng X, Kong J, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhou S. Direct synthesis, characterization and catalytic application of SBA-15 mesoporous silica with heteropolyacid incorporated into their framework. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014;187:7–13.
Popa A, Sasca V, Holclajtner-Antunovic I. The influence of surface coverage on textural, structural and catalytic properties of cesium salts of 12-molybdophosphoric acid supported on SBA-15 mesoporous silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012;156:127–37.
Ivanova R, Genova I, Kovacheva D, Atanasova G, Tsoncheva T. Effect of porous structure on the formation of active sites in manganese hosted in ordered mesoporous silica catalysts for environmental protection. J Porous Mater. 2016;23:1005–13.
Martin A, Garcia RA, Karaman DS, Rosenholm JM. Polyethyleneimine-functionalized large pore ordered silica materials for poorly water-soluble drug delivery. J Mater Sci. 2014;49:1437–47.
Manzano M, Vallet-Regí M. New developments in ordered mesoporous materials for drug delivery. J Mater Chem. 2010;20:5593–604.
Kumar P, Guliants VV. Periodic mesoporous organic–inorganic hybrid materials: applications in membrane separations and adsorption. Micropor Mesopor Mater. 2010;132:1–14.
Kim DH, Celedonio J, Ko YS. A study on grafting efficiency of amine and CO2 sorption behavior inside amorphous silica. Top Catal. 2017;60:706–13.
Li W, Choi S, Drese JH, Hornbostel M, Krishnan G, Eisenberger PM, Jones CW. Steam-stripping for regeneration of supported amine-based CO2 adsorbents. Chemsuschem. 2010;3:899–903.
Jones CW. CO2 capture from dilute gases as a component of modern global carbon management. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2011;2:31–52.
Zhao D, Huo Q, Feng J, Chmelka BF, Stucky GD. Nonionic triblock and star diblock copolymer and oligomeric surfactant syntheses of highly ordered, hydrothermally stable, mesoporous silica structures. J Am Chem Soc. 1998;120:6024–36.
Rocchiccioli-Deltcheff C, Amirouche M, Fournier M, Frank R. Structure and catalytic properties of silica-supported polyoxomolybdates III. 12-molybdosilicic acid catalysts: vibrational study of the dispersion effect and nature of the Mo species in interaction with the silica support. J Catal. 1992;138:445–56.
Sydorchuk V, Zazhigalov V, Khalameida S, Skubiszewska-Zieba J, Charmas B, Leboda R. Deposition of tungsten heteropolycompounds on activated silica surface. Colloids Surf A. 2009;341(1–3):53–9.
Khalameida SV, Sydorchuk VV, Skubiszewska-Zieba J, Leboda R, Zazhigalov VA. Sol–gel synthesis and properties of compositions containing heteropoly compounds in porous silica matrix. Glass Phys Chem. 2014;40(1):8–16.
Hiyoshi N, Yogo K, Yashima T. Adsorption characteristics of carbon dioxide on organically functionalized SBA-15. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005;84:357–65.
Acknowledgements
These investigations were partially financed by Romanian Academy Project No. 4.3 and through the Partnerships in priority areas—PN II Romania program, developed with the support of The Ministry of National Education—UEFISCDI, Project No. PN-II-PT-PCCA-2013-4-1708.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popa, A., Sasca, V., Verdes, O. et al. Effect of the amine type on thermal stability of modified mesoporous silica used for CO2 adsorption. J Therm Anal Calorim 134, 269–279 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7457-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7457-7