Abstract
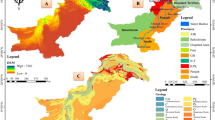
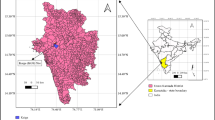
The measurements of radon concentrations in drinking water sources in and around the Main Central Thrust (MCT) region in Garhwal Himalaya, India, were carried out using the scintillation detector-based SMART RnDuo technique for radiation protection purposes. Radon values in the analyzed samples were observed between 1.1 and 183.9 Bq L−1 (AM = 19.7 Bq L−1). Radon values in 94% of the samples were found well below the World Health Organization (WHO) reference limit. The estimated radiation doses for different age groups were found higher than the WHO safe limit of 100 µSv y−1 (from all sources including radon) except for the age groups of 0–12 months infants and 1–3 years children. The results of this study may be useful for future studies on epidemiology, examining hidden faults, uranium exploration etc.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, volume 1: World Health Organization, 3rd edn. WHO Library Cataloguing, Geneva
Risk assessment (1999) Risk Assessment of Radon in drinking Water. National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Yu KN, Guan ZJ, Stokes MJ, Young ECM (1994) A Preliminary Study on the Radon Concentrations in Water in Hong Kong and the Associated Health Effects
World Health Organization (2017) WHO guidelines for the drinking water. World health Statistics 1–116
Tanner AB (1980) Radon migration in the ground: a supplementary review. Nat Radiation Environ III 5–56
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans., International Agency for Research on Cancer, National Cancer Institute (U.S.) (1988) Man-made mineral fibres and radon. World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer
Prasad G, Prasad Y, Gusain GS, Ramola RC (2008) Measurement of radon and thoron levels in soil, water and indoor atmosphere of Budhakedar in Garhwal Himalaya, India. Radiat Meas. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2008.04.050
Ishimori Y, Lange K, Martin P et al (2013) Measurement and calculation of Radon releases from NORM residues. International Atomic Energy Agency Vienna International Centre, Austria, pp 1–103
Feng S, Li C, Cui Y et al (2021) Novel method for measuring temperature-dependent diffusion coefficient of radon in porous media. Appl Radiat Isot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2020.109506
UNSCEAR SOURCES, EFFECTS AND RISKS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation 1988 Report to the General Assembly, with annexes UNITED NATIONS. New York
Sethy NK, Jha V, Tripathi RM (2015) Causes of emissions from agricultural residue burning in north-west India: evaluation of a technology policy response. Ann Geophys Atmos Hydros Space Sci 109:367–379. https://doi.org/10.18520/v109/i10/1855-1859
Srilatha MC, Sannappa J, Rangaswami DR (2014) Studies on concentration of Radon and Physicochemical parameters in ground water around Ramanagara and Tumkur districts, Karnataka, India. Int J Adv Sci Tech Res 2:641–660
Yadav M, Jindal MK, Ramola RC (2023) Study of Radionuclides in Rocks samples from Ukhimath Area and its correlation with soil and Water Data. Chemistry Africa. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-023-00635-1
Gusain GS, Badoni M, Prasad G et al (2009) Studies of natural radionuclides and dose estimation from soil samples of Kumaun Himalaya, India. Indian J Phys 83:1215–1220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-009-0104-1
Gusain GS, Rautela BS, Sahoo SK et al (2012) Distribution of terrestrial gamma radiation dose rate in the eastern coastal area of Odisha, India. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 152:42–45. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncs148
Ramola RC, Prasad M, Rawat M et al (2015) Comparative study of various techniques for environmental radon, thoron and progeny measurements. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 167:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncv215
Prasad M, Rawat M, Dangwal A et al (2015) Measurements of radon and thoron progeny concentrations in dwellings of Tehri Garhwal, India, using LR-115 deposition-based DTPS/DRPS technique. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 167:102–106. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncv224
Prasad M, Rawat M, Dangwal A et al (2016) Variability of radon and thoron equilibrium factors in indoor environment of Garhwal Himalaya. J Environ Radioact. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2015.10.017
Ramola RC, Prasad M, Kandari T et al (2016) Dose estimation derived from the exposure to radon, thoron and their progeny in the indoor environment. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31061
Kandari T, Aswal S, Prasad M et al (2016) Estimation of annual effective dose from radon concentration along Main Boundary Thrust (MBT) in Garhwal Himalaya. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 9:228–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.10.005
Kandari T, Aswal S, Prasad M et al (2016) Study of radiation exposure due to radon, thoron and their progeny in the indoor environment of Rajpur region of Uttarakhand Himalaya. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncw059
Pant P, Kandari T, Prasad M, Ramola RC (2016) A comparative study of diurnal variation of radon and thoron concentrations in indoor environment. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 171:212–216. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncw061
Prasad M, Rawat M, Dangwal A et al (2016) Study of radiation exposure due to radon, thoron and progeny in the indoor environment of Yamuna and tons valleys of Garhwal Himalaya. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 171:187–191. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncw055
Prasad M, Bossew P, Anil Kumar G et al (2018) Dose assessment from the exposure to attached and unattached progeny of radon and thoron in indoor environment. Acta Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0111-8
Pant P, Kandari T, Prasad M et al (2018) Continuous measurement of equilibrium equivalent radon/thoron concentration using time-integrated flow-mode grab sampler. Acta Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0163-9
Ramola RC, Prasad M (2020) Significance of thoron measurements in indoor environment. J Environ Radioact. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2020.106453
Bourai AA, Aswal S, Dangwal A et al (2013) Measurements of radon flux and soil-gas radon concentration along the Main Central Thrust, Garhwal Himalaya, using SRM and RAD7 detectors. Acta Geophys 61:950–957. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-013-0132-2
Yadav M, Prasad M, Joshi V et al (2016) A comparative study of radium content and radon exhalation rate from soil samples using active and passive techniques. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 171:254–256. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncw069
Kandari T, Prasad M, Pant P et al (2018) Study of radon flux and natural radionuclides (226Ra, 232Th and 40K) in the Main Boundary Thrust region of Garhwal Himalaya. Acta Geophys 66:1243–1248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0158-6
Kumar A, Singh P, Semwal P et al (2021) Study of primordial radionuclides and radon/thoron exhalation rates in Bageshwar region of Kumaun Himalaya, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 328:1361–1367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07582-y
Panwar P, Prasad M, Ramola RC (2021) Study of soil-gas and indoor radon concentration in a test village at Tehri Garhwal, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07901-x
Ramola RC, Gusain GS, Badoni M et al (2008) 226Ra, 232Th and 40K contents in soil samples from Garhwal Himalaya, India, and its radiological implications. J Radiol Prot 28:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1088/0952-4746/28/3/008
Ramola RC, Prasad G, Prasad Y (2007) Radon emanation from soil and groundwater and surface gamma dose rate in Budhakedar, Garhwal Himalayas, India. Indoor and Built Environment 16:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X06074668
Ramola RC, Prasad G (2004) A Survey of Surface γ-Dose Rate in Relation to Radon Concentrations in Soil and Spring Water at Budhakedar, Tehri Garhwal (Uttaranchal). National Symposium On Environment
Yadav M, Rawat M, Dangwal A et al (2014) Levels and effects of natural radionuclides in soil samples of Garhwal Himalaya. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 302:869–873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3277-9
Yadav M, Rawat M, Dangwal A et al (2015) Analysis of natural radionuclides in soil samples of Purola area of Garhwal Himalaya, India. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 167:215–218. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncv247
Prasad M, Ranga V, Kumar GA, Ramola RC (2020) Radiological impact assessment of soil and groundwater of himalayan regions in Uttarakhand, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 323:1269–1282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-019-06827-9
Yadav M, Prasad M, Dutt S, Ramola RC (2022) Variation of natural radioactivity in soil and water samples of Garhwal Himalaya, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08147-3
Rautela BS, Yadav M, Bourai AA et al (2012) Study of natural radionuclide and absorbed gamma dose in ukhimath area of garhwal Himalaya, India. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 152:58–61. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncs187
Choubey VM, Ramola RC (1997) Correlation between geology and radon levels in groundwater, soil and indoor air in Bhilangana Valley, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Environ Geol 32:258–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050215
Sezgin Z, Yüksel N, Baykara T (2006) Preparation and characterization of polymeric micelles for solubilization of poorly soluble anticancer drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 64:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2006.06.003
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Thilagavathi R et al (2015) Occurrence of high uranium and radon in hard rock aquifers of South India - evaluating the temporal and spatial trends. Groundw Sustain Dev 1:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2016.01.003
Prasad M, Kumar GA, Sahoo BK, Ramola RC (2018) A comprehensive study of radon levels and associated radiation doses in Himalayan groundwater. Acta Geophys 66:1223–1231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0135-0
Prasad M, Semwal P, Panwar P et al (2022) Uranium contamination in drinking water as a health concern in Uttarakhand, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08128-6
Ravikumar P, Somashekar RK (2014) Determination of the radiation dose due to radon ingestion and inhalation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:493–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0252-x
Uttarkashi D, Uttarakhand Govt., Geology and mining unit (2020) District Survey Report, Silica Sand, Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand. Uttarkashi
Bilham roger (2004) Earthquakes in India and Himalaya: tectonics, geodesy and history. Ann Geophys 47:839–858
Jade S, Mukul M, Bhattacharyya AK et al (2007) Estimates of interseismic deformation in Northeast India from GPS measurements. Earth Planet Sci Lett 263:221–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2007.08.031
Jade S, Bhatt BC, Yang Z et al (2004) GPS measurements from the Ladakh Himalaya, India: preliminary tests of plate-like or continuous deformation in Tibet. Bull Geol Soc Am 116:1385–1391. https://doi.org/10.1130/B25357.1
Ramola RC, Prasad Y, Prasad G et al (2008) Soil-gas radon as seismotectonic indicator in Garhwal Himalaya. Appl Radiat Isot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2008.04.006
Ramola RC (2014) A study of radon exhalation rates from water samples by using Liquid Scintillation Counter
Operational M (2015) Portable Radon Monitor-Smart RnDuo operational manual of Portable Radon Monitor-Smart RnDuo. Portable Radon Monitor-Smart RnDuo CONTENT
UNSCEAR Sources and effects of ionizing radiation : United Nations Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation : UNSCEAR 1993 report to the General Assembly, with scientific annexes. United Nations, New York
SOURCES AND EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (2000) UNSCEAR 2000 Report to the General Assembly. SOURCES UNITED NATIONS, with Scientific Annexes VOLUME I
Ramola RC (1955) Assessment of health risk due to radon and its daughter product in the lower atmosphere. Curr Sci 73:8–9
Prasad M, Kumar GA, Sahoo SK, Ramola RC (2019) Health risks associated with the exposure to uranium and heavy metals through potable groundwater in Uttarakhand state of India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 319:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6281-7
United Nations. Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (2010) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation : United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation : UNSCEAR 2008 report to the General Assembly, with scientific annexes. United Nations
Eckerman K, Harrison J, Menzel GH, Clement HC (2012) Annals of the ICRP Compendium of Dose Coefficients based on ICRP Publication 60
Institute of Medicine (2005) Dietary reference intakes for water, potassium, sodium, chloride, and sulfate. Washington, DC. The National Academies Press
Li WB, Karpas Z, Salonen L et al (2009) A compartmental model of Uranium in Human hair for protracted ingestion of natural uranium in drinking Water. Health Phys 96:636–645
Mehra R, Kaur S, Chand S et al (2021) Dosimetric assessment of primordial radionuclides in soil and groundwater of Sikar district, Rajasthan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 330:1605–1620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07998-0
UNSCEAR SOURCES AND EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation UNSCEAR 2000 Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes VOLUME I: SOURCES UNITED NATIONS. New York
Taskin H, Karavus M, Ay P et al (2009) Radionuclide concentrations in soil and lifetime cancer risk due to gamma radioactivity in Kirklareli, Turkey. J Environ Radioact 100:49–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2008.10.012
Wu YY, Ma YZ, Cui HX et al (2014) Radon concentrations in drinking water in Beijing city, China and contribution to radiation dose. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11:11121–11131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph111111121
Marques AL, Dos Santos W, Geraldo LP (2004) Direct measurements of radon activity in water from various natural sources using nuclear track detectors. Appl Radiat Isot 60:801–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2004.01.015
Akar Tarim U, Gurler O, Akkaya G et al (2012) Evaluation of radon concentration in well and tap waters in Bursa, Turkey. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 150:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncr394
Cho JS, Ahn JK, Kim HC, Lee DW (2004) Radon concentrations in groundwater in Busan measured with a liquid scintillation counter method. J Environ Radioact 75:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2003.06.002
Sarrou I, Pashalidis I (2003) Radon levels in Cyprus. J Environ Radioact 68:269–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0265-931X(03)00066-3
Nikolopoulos D, Louizi A (2008) Study of indoor radon and radon in drinking water in Greece and Cyprus: implications to exposure and dose. Radiat Meas 43:1305–1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2008.03.043
Otwoma D, Mustaphai A (1998) 0 Note MEASUREMENT OF 222Rn CONCENTRATION IN KENYAN GROUNDWATER
Abdallah SM, Habib RR, Nuwayhid RY et al (2007) Radon measurements in well and spring water in Lebanon. Radiat Meas 42:298–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2006.11.004
Amin RM (2014) IPA-Under Creative Commons license 3.0 evaluation of radon gas concentration in the drinking water and dwellings of south-west Libya, using CR-39 detectors. Int J Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.6088/ijes.20140400005
Nasir T, Shah M (2012) Measurement of Annual effective doses of Radon from drinking Water and Dwellings by CR-39 track detectors in Kulachi City of Pakistan. J Basic Appl Sci 8:528–536
Rani A, Mehra R, Duggal V (2013) Radon monitoring in groundwater samples from some areas of northern Rajasthan, India, using a RAD7 detector. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 153:496–501. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncs130
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges the Uttarakhand State Council for Science and Technology (UCOST), Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India for financial support in the form of a research project. The author also extends their thanks to Nuclear Research Laboratory, H.N.B. Garhwal University, BadshahiThaul Campus, Tehri Garhwal, Uttarakhand, India extending their laboratory facilities for conducting the experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they don’t have any conflict of interest regarding this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, K.P., Chandra, S., Prasad, M. et al. Estimation of radiation dose due to ingestion of radon in water samples of Garhwal Himalaya, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09002-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09002-3