Abstract
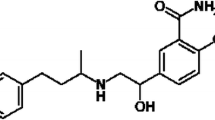
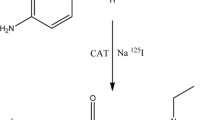
The objective of this work was to develop a potential selective radiotracer for the non-invasive assessment of heart imaging. [125I]iododobutamine was obtained via direct electrophilic substitution reaction with a high labeling yield of 96.79 ± 0.86%. The in vivo biodistribution of iodinated dobutamine showed high heart uptake of 31.49 ± 1.3%ID/g at 2 min after injection with low lungs and liver consumption which alleviate rapid myocardial imaging with significant minimum radiation hazards risk to the patients. Receptor blocking study showed reduction of heart uptake to 0.9 ± 0.01% which confirm the selectivity and specificity of [125I]iododobutamine for beta-adrenoceptors.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tuttle RR, Mills J (1975) Dobutamine: development of a new catecholamine to selectively increase cardiac contractility. Circ Res 36:185–196
Tibayan FA, Chesnutt AN, Folkesson HG, Eandi J, Matthay MA (1997) Dobutamine increases alveolar liquid clearance in ventilated rats by beta-2 receptor stimulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:438–444
Cleland JG (2002) Contemporary management of heart failure in clinical practice. Heart 88(S2):5–8
Ibrahim IT, El-Kolaly MT, Aboumanei MH, Abdelbary A (2016) 125I labeling of clomiphene and biodistribution studies for possible use as a model in breast cancer imaging. Appl Radiat Isotopes 115:37–44
Motaleb MA (2009) Synthesis, radioiodination and biological evaluation of a novel phthalimide derivative. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 307:363–372
Budoff MJ et al (2005) American College of Cardiology Foundation; American Heart Association; American College of Physicians Task Force on Clinical Competence and Training; American Society of Echocardiography; American Society of Nuclear Cardiology; Society of Atherosclerosis Imaging; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions. J Am Coll Cardiol. 46: 383–402
Bateman T, Dilsizian V, Beanlands R, DePuey EG, Heller G, Wolinsky D (2016) ASNC/SNMMI position statement on the clinical indications for myocardial perfusion PET. J Nucl Med 57:1654–1657
Baggish AL, Boucher CA (2008) Radiopharmaceutical agents for myocardial perfusion imaging. Circulation 118:1668–1674
Taillefer R, Harel F (2018) Radiopharmaceuticals for cardiac imaging: current status and future trends. J Nucl Cardiol 25(4):1242–1246
Strauss HW, Harrison K, Langan JK, Lebowitz E, Pitt B (1975) Thallium-201 for myocardial imaging. Relation of thallium-201 to regional myocardial perfusion. Circulation 51:641–645
Nakajima K, Taki J, Bunko H, Matsudaira M, Muramori A, Matsunari I, Hisada K, Ichihara T (1991) Dynamic acquisition with a three-headed SPECT system: application to technetium 99 m-SQ30217 myocardial imaging. J Nucl Med 32(6):1273–1277
Wei K, Le E, Bin JP, Coggins M, Jayawera AR, Kaul S (2001) Mechanism of reversible 99mTc-sestamibi perfusion defects during pharmacologically induced vasodilatation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280:H1896–H1904
Arthur J, Scholte HA (2016) The future of cardiac 123I MIBG imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2016(43):2381–2382
Saha GB, Saha GB (2004) Fundamentals of nuclear pharmacy, vol 6. Springer, New York, pp 96–100
Bayoumi NA, Amin AM, Ismail NS, Abouzid KA, El-Kolaly MT (2015) Radioiodination and biological evaluation of Cladribine as potential agent for tumor imaging and therapy. Radiochim Acta 103:777–787
Aboumanei MH, Abdelbary AA, Ibrahim IT, Tadros MI, El-Kolaly MT (2018) Design and development of microemulsion systems of a new antineoplaston A10 analog for enhanced intravenous antitumor activity: in vitro characterization, molecular docking, 125I-radiolabeling and in vivo biodistribution studies. Int J Pharm 545(1–2):240–253
Motaleb MA, Ibrahim IT, Abo Rizq RS, Elzanfaly ES (2017) Preparation, chromatographic evaluation and biodistribution of 99mTc-procainamide as a radiopharmaceutical for heart imaging. Radiochim Acta 105:2015–2023
Rhodes BA (1974) Considerations in the radiolabeling of albumin. In: Seminars in nuclear medicine, vol 4, no 3, pp 281–293. WB Saunders
Aboumanei MH, Abdelbary AA, Ibrahim IT, Tadros MI, El-Kolaly MT (2018) Improved targeting and tumor retention of a newly synthesized antineoplaston A10 derivative by intratumoral administration: molecular docking, technetium 99m radiolabeling, and in vivo biodistribution studies. Cancer Biotherapy Radiopharmaceuticals 33(6):221–232
Clanton J, Sandler MP (2010) Molecular imaging: radiopharmaceuticals for PET and SPECT. J Nucl Med 51(4):660–661
Lee YS (2010) Radiopharmaceuticals for molecular imaging. Open Nucl Med J 2(1):178–185
Montelaro RC, Rueckert RR (1977) A mechanism and an evaluation of surface specific iodination by the chloramine-T procedure. Arch Biochem Biophys 178(2):555–564
Tashtoush BM, Traboulsi AA, Dittert L, Hussain AA (2001) Chloramine-T in radiolabeling techniques: IV. Penta-O-acetyl-N-chloro-N-methylglucamine as an oxidizing agent in radiolabeling techniques. Anal Biochem 288(1): 16–21
Cotton FA, Wilkinson G, Murillo CA, Bochmann M, Grimes R (1998) Advanced inorganic chemistry, 5th edn. Wiley, New York
Turgut B, Unlu M, Temiz NH, Kitapci MT, Alkan ML (2003) Dobutamine Tc-99m furifosmin SPECT in detection of coronary artery disease: evaluation of same day, rest-stress protocol. Ann Nucl Med 17(7):531–539
Cavina L, van der Born D, Klaren PH, Feiters MC, Boerman OC, Rutjes FP (2017) Design of radioiodinated pharmaceuticals: structural features affecting metabolic stability towards in vivo deiodination. Eur J Org Chem 2017(24):3387–3414
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almalki, F.A., Motaleb, M.A., Ibrahim, I.T. et al. Radiosynthesis, chromatographic evaluation and biodistribution of [125I]iododobutamine as a radiotracer for myocardial perfusion imaging. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 324, 459–466 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07120-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07120-w