Abstract
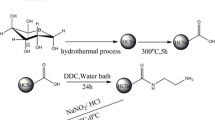
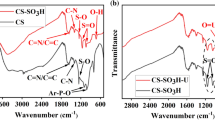
Hydrothermal carbon spheres (HCSs) functionalized with 4-aminoacetophenone oxime group (HCSs-oxime) were prepared by a grafting method and explored to adsorption of uranyl ions from aqueous solution. The results of FT-IR, elemental analysis and zeta potential indicate a successfully modification with oxime group. The adsorbent shows an excellent adsorption capacity (Langmuir, q m = 588.2 mg g−1) and quick adsorption kinetic (equilibrium time of approximately 60 min) at optimal pH of 6.0. The adsorptive selectivity for uranyl ions has been also great improved in present with various co-existing ions. Overall, HCSs-oxime is a potentially promising material for selective removal of uranium in the contaminated solution.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu J, Zhao C, Zhang Z et al (2016) Fluorine effects on U(VI) sorption by hydroxyapatite. Chem Eng J 288:505–515
Reinoso-Maset E, Ly J (2016) Study of uranium(VI) and radium(II) sorption at trace level on kaolinite using a multisite ion exchange model. J Environ Radioact 157:136–148
Shao L, Wang X, Ren Y et al (2016) Facile fabrication of magnetic cucurbit[6]uril/graphene oxide composite and application for uranium removal. Chem Eng J 286:311–319
Zhou L, Wang Y, Zou H et al (2016) Biosorption characteristics of uranium(VI) and thorium(IV) ions from aqueous solution using CaCl2-modified Giant Kelp biomass. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 307(1):635–644
Hoyer M, Zabelt D, Steudtner R et al (2014) Influence of speciation during membrane treatment of uranium contaminated water. Sep Purif Technol 132:413–421
Tan L, Zhang X, Liu Q et al (2015) Preparation of magnetic core–shell iron oxide@silica@nickel–ethylene glycol microspheres for highly efficient sorption of uranium(VI). Dalton Trans 44:6909–6917
Mishra S, Dwivedi J, Kumar A et al (2015) Studies on salophen anchored micro/meso porous activated carbon fibres for the removal and recovery of uranium. RSC Adv 5:33023–33036
Wang YL, Song LJ, Zhu L et al (2014) Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solution using iminodiacetic acid derivative functionalized SBA-15 as adsorbents. Dalton Trans 43:3739–3749
Zhang ZB, Yu XF, Cao XH et al (2014) Adsorption of U(VI) from aqueous solution by sulfonated ordered mesoporous carbon. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 301:821–830
Chen S, Hong J, Yang H et al (2013) Adsorption of uranium(VI) from aqueous solution using a novel graphene oxide-activated carbon felt composite. J Environ Radioact 126:253–258
Yan H, Bai J, Chen X et al (2013) High U(VI) adsorption capacity by mesoporous Mg(OH)2 deriving from MgO hydrolysis. RSC Adv 3:23278
Cao Q, Liu Y, Wang C et al (2013) Phosphorus-modified poly(styrene-co-divinylbenzene)-PAMAM chelating resin for the adsorption of uranium(VI) in aqueous. J Hazard Mater 263(Pt 2):311–321
Wang Z, Zachara JM, Shang J et al (2014) Investigation of U(VI) adsorption in quartz–chlorite mineral mixtures. Environ Sci Technol 48:7766–7773
Olivelli MS, Curutchet GA, Torres Sánchez RM (2013) Uranium uptake by montmorillonite–biomass complexes. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:2273–2279
Zhang ZB, Zhou ZW, Cao XH et al (2013) Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solutions by new phosphorus-containing carbon spheres synthesized via one-step hydrothermal carbonization of glucose in the presence of phosphoric acid. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299:1479–1487
Mi Y, Hu W, Dan Y et al (2008) Synthesis of carbon microspheres by a glucose hydrothermal method. Mater Lett 62:1194–1196
Yao C, Shin Y, Wang LQ et al (2007) Hydrothermal dehydration of aqueous fructose solutions in a closed system. J Phys Chem C 111:15141–15145
Zhang ZB, Nie WB, Li Q et al (2013) Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solutions by carboxyl-rich hydrothermal carbon spheres through low-temperature heat treatment in air. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 298:361–368
Yu XF, Liu YH, Zhou ZW et al (2014) Adsorptive removal of U(VI) from aqueous solution by hydrothermal carbon spheres with phosphate group. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 300:1235–1244
Geng J, Ma L, Wang H et al (2012) Amidoxime-grafted hydrothermal carbon microspheres for highly selective separation of uranium. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12:7354–7363
Zhao Y, Wang X, Li J et al (2015) Amidoxime functionalization of mesoporous silica and its high removal of U(VI). Polym Chem 6:5376–5384
Zhang Z, Dong Z, Dai Y et al (2016) Amidoxime-functionalized hydrothermal carbon materials for uranium removal from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 6:102462–102471
Zou YD, Cao XH, Luo XP et al (2015) Recycle of U(VI) from aqueous solution by situ phosphorylation mesoporous carbon. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 306:515–525
Song Q, Ma L, Liu J et al (2012) Preparation and adsorption performance of 5-azacytosine-functionalized hydrothermal carbon for selective solid-phase extraction of uranium. J Colloid Interface Sci 386:291–299
Aakeröy CB, Beatty AM, Leinen DS (2001) Syntheses and crystal structures of new extended building blocks for crystal engineering: (pyridylmethylene)aminoacetophenone oxime ligands. Cryst Growth Des 1:47–52
Nie BW, Zhang ZB, Cao XH et al (2013) Sorption study of uranium from aqueous solution on ordered mesoporous carbon CMK-3. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 295:663–670
Tripathi A, Melo JS, D’Souza SF (2013) Uranium(VI) recovery from aqueous medium using novel floating macroporous alginate–agarose–magnetite cryobeads. J Hazard Mater 246:87–95
Zare F, Ghaedi M, Daneshfar A et al (2015) Efficient removal of radioactive uranium from solvent phase using AgOH–MWCNTs nanoparticles: kinetic and thermodynamic study. Chem Eng J 273:296–306
Chen Z, Ma L, Li S et al (2011) Simple approach to carboxyl-rich materials through low-temperature heat treatment of hydrothermal carbon in air. Appl Surf Sci 257:8686–8691
Shen H, Pan S, Zhang Y et al (2012) A new insight on the adsorption mechanism of amino-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 magnetic polymers in Cu(II), Cr(VI) co-existing water system. Chem Eng J 183:180–191
He L, Dumée LF, Feng C et al (2015) Promoted water transport across graphene oxide–poly(amide) thin film composite membranes and their antibacterial activity. Desalination 365:126–135
Wang Y, Gu Z, Yang J et al (2014) Amidoxime-grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes by plasma techniques for efficient removal of uranium(VI). Appl Surf Sci 320:10–20
Tian G, Geng J, Jin Y et al (2011) Sorption of uranium(VI) using oxime-grafted ordered mesoporous carbon CMK-5. J Hazard Mater 190:442–450
Zhao Y, Li J, Zhang S et al (2014) Amidoxime-functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica for selective sorption of U(VI). RSC Adv 4:32710–32717
Li B, Ma L, Tian Y et al (2014) A catechol-like phenolic ligand-functionalized hydrothermal carbon: one-pot synthesis, characterization and sorption behavior toward uranium. J Hazard Mater 271:41–49
Yuan D, Chen L, Xiong X et al (2016) Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solution by amidoxime functionalized superparamagnetic polymer microspheres prepared by a controlled radical polymerization in the presence of DPE. Chem Eng J 285:358–367
Zhang S, Zhao X, Li B et al (2016) “Stereoscopic” 2D super-microporous phosphazene-based covalent organic framework: design, synthesis and selective sorption towards uranium at high acidic condition. J Hazard Mater 314:95–104
Boparai HK, Joseph M, O’Carroll DM (2011) Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zero valent iron particles. J Hazard Mater 186:458–465
Pillewan P, Mukherjee S, Roychowdhury T et al (2011) Removal of As(III) and As(V) from water by copper oxide incorporated mesoporous alumina. J Hazard Mater 186:367–375
Budnyak TM, Strizhak AV, Gładysz-Płaska A et al (2016) Silica with immobilized phosphinic acid-derivative for uranium extraction. J Hazard Mater 314:326–340
Zhang X, Jiao C, Wang J et al (2012) Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solutions by magnetic Schiff base: kinetic and thermodynamic investigation. Chem Eng J 198:412–419
Gunathilake C, Górka J, Dai S et al (2015) Amidoxime-modified mesoporous silica for uranium adsorption under seawater conditions. J Mater Chem A 3:11650–11659
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21561002, 21301028, 11475044, 41461070, 21401022), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (Grant No. IRT13054), the Science and Technology Support Program of Jiangxi Province (Grant Nos. 20141BBG70001, 20151BBG70010), the Advanced Science and Technology Innovation Team Program of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20142BCB24006), the Innovation Fund of Graduate Student (DHYC-2016010), and the Innovation Team Program of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Grant No. 2014BCB24006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Wang, Y., Zhao, W. et al. Adsorptive removal of uranyl ions in aqueous solution using hydrothermal carbon spheres functionalized with 4-aminoacetophenone oxime group. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 312, 187–198 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5209-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5209-y