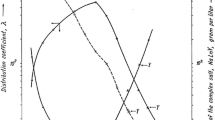
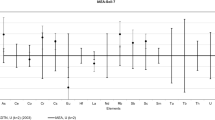
Abstract
In the light of the values recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry for the isotopic composition of the elements, the feasibility of using low abundant isotopes to determine some elements by reactor neutron activation analysis is discussed. The characteristics of the tables informing the pertinent data are described. In particular, the possibilities of determining sulphur, calcium, iron, nickel, selenium, strontium, tin, barium, gadolinium, ytterbium, mercury and uranium are revised. Some reflections on the situation of the analyst, as user of the literature data, are formulated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robouch P, Arana G, Eguskiza M, Pommé S, Etxebarria N (2000) Uncertainty budget for k0-NAA. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 245:195–197
De Bièvre P, De Corte F, Moens L, Simonits A, Hoste J (1983) The need for accurate minor isotope abundance values in reactor neutron activation analysis. Int J Mass Spectrom 51:31–38
Holden NE, Martin RL, Barnes IL (1984) Isotopic compositions of the elements 1983. Pure Appl Chem 56:675–694
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (1991) Isotopic compositions of the elements 1989. Pure Appl Chem 63:991–10026
Rosman KJR, Taylor PDP (1998) Isotopic compositions of the elements 1997. Pure Appl Chem 70:217–235
De Laeter JR, Böhlke JK, De Bièvre P, Hidaka H, Peiser HS, Rosman KJR, Taylor PDP (2003) Atomic weights of the elements: review 2000. Pure Appl Chem 75:683–800
Berglund M, Wieser ME (2011) Isotopic compositions of the elements 2009 (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 83:397–410
National Nuclear Data Center (2016) NuDat 2.6. http://www.nndc.bnl.gov/nudat2/. December 2016
Moore LJ, Machlan LA (1972) High accuracy determination of calcium in blood serum by isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 44:2291–2296
Mckown DM, Morris JS (1978) Rapid measurement of selenium in biological samples using instrumental neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Chem 43:411–420
Blotcky AJ, Ebrahim A, Rack EP (1988) Determination of selenium metabolites in biological fluids using instrumental and molecular neutron activation analysis. Anal Chem 60:2734–2737
Lavi N, Alfassi B (1990) Determination of trace amounts of cadmium, cobalt, chromium, iron, molybdenum, nickel, selenium, titanium, vanadium and zinc in blood and milk by neutron activation analysis. Analyst 115:817–822
Navarrete M, Cabrera L, Deschamps N, Boscher N, Revel G, Meyer JP, Stampfler A (1990) Activation analysis of Se in biological samples through 75Se and 77mSe. J Radioanal Nucl Chem Letters 145:445–452
Sun YC, Yang JY (1999) Simultaneous determination of arsenic (III, V), selenium (IV, VI), and antimony (III, V) in natural water by coprecipitation and neutron activation analysis. Anal Chim Acta 395:293–300
Kim IJ, Watson RP, Lindstrom RM (2011) Accurate and precise measurement of selenium by instrumental neutron activation analysis. Anal Chem 83:3493–3498
Pors Nielsen S (2004) The biological role of strontium. Bone 35:583–588
Hoffman EL (1992) Instrumental neutron activation in geoanalysis. J Geochem Explor 44:297–319
Vermaercke P, Farina F, Sneyers L, Bruggeman M, Bouças JG (2009) Validation of the determination of tin by k0-instrumental neutron activation analysis in foodstuff. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 281:35–39
Devillers C, Lecomte T, Hagemann R (1983) Absolute isotope abundances of tin Int. J. Mass Spectrom Ion Phys 50:205–217
Geisler M, Nguyen TT, Taskaev E (1985) Instrumental neutron activation analysis of six Bulgarian geostandards. Geostandard Newslett 9:19–23
D’Angelo JA, Martinez LD, Resnizky S, Perino E, Marchevsky EJ (2001) Determination of eight lanthanides in apatites by ICP-AES, XRF, and NAA. J Trace Microprobe Tech 19:79–90
Wasim M, Iqbal S, Ali M (2015) Radiological and elemental analysis of soils from Hunza in Central Karakoram using gamma-ray spectrometry and k0-instrumental neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-015-4220-4
Mackey EA, Becker DA, Spatz RO, Paul RL, Greenberg RR, Lindstrom RM, Yu LL, Wood LJ,. Long SE, Kelly WR, Mann JL, MacDonald BS, Wilson SA, Brown ZA, Briggs PH, Budhan J (2004) Certification of NIST Standard Reference Material 1575a Pine Needles and Results of an International Laboratory Comparison. NIST Special Publication 260-156. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, USA
Mackey EA, Christopher SJ, Lindstrom RM, Long SE, Marlow AF, Murphy KE, Paul RL, Popelka-Filcoff RS, Rabb SA, Sieber JR, Spatz RO, Tomlin BE, Wood LJ, Yen JH, Yu LL, Zeisler R, Wilson SA, Adams MG, Brown ZA, Lamothe PL, Taggart JE, Jones C, Nebelsic J (2010) Certification of Three NIST Renewal Soil Standard Reference Materials for Element Content: SRM 2709a San Joaquin Soil, SRM 2710a Montana Soil I, and SRM 2711a Montana Soil II. NIST Special Publication 260-172. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, USA
Heydorn K (2006) Radiochemical neutron activation analysis, in encyclopedia of analytical chemistry. Wiley. doi:10.1002/9780470027318.a621
Furnari JC, Cohen IM (1998) Application of the concept of traceability to the management of nuclear data. Appl Radiat Isot 49:1523–1527
Acknowledgement
The author wishes to thank Eduardo Montoya for his valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, I.M. Use of low-abundant isotopes in reactor neutron activation analysis: implications, questions, and tentative answers. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 312, 29–36 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5189-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5189-y