Abstract
Neutron Activation Analysis is an analytical technique to assay the chemical elemental composition in samples of various matrices. It has been applied by the Laboratory for Neutron Activation Analysis, located at Nuclear Technology Development Centre/Brazilian Commission for Nuclear Energy, CDTN/CNEN, since the starting up of the TRIGA Mark I IPR-R1 reactor in 1960. Among the methods of this technique, the k0-method, which was established at CDTN in 1995 and re-established and improved in 2003 as k0-standardized method, is the most efficient multielemental concentration determination. The results of participation in proficiency testings indicated which unsatisfactory data produced by k0-method should be improved over the years. This paper is about the history of the development of k0-method at the laboratory and the main achievements.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tófani P C, Paiano M (1989) Uses of a small research reactor in Brazil, NUCLEBRÁS, CDTN, CNEN/CDTN-611, Belo Horizonte
Simonits A, De Corte F, Hoste J (1975) Single-comparator methods in reactor neutron-activation analysis. J Radioanal Chem 24:31–46
Smodiš B, Jaćimović R, Jovanović S, Stegnar P (1990) Determination of trace elements in standard reference materials by the k0-standardization method. Biol Trace Elem Res 26:43–51
De Corte F (1987) The k0-standardisation method; a move to the optimisation of neutron activation analysis, Habilitation thesis, Ryksuniversiteit Gent, Gent, Belgium. http://www.kayzero.com/k0naa/k0naaorg/Links_files/The%20ko-Standardization%20Method.pdf Accessed 20 May 2022
De Corte F (2001) The standardization of standardless NAA. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 248:13–20
Jaćimović R, Stibilj V, Benedik L, Smodiš B (2003) Characterization of the neutron flux gradients in typical irradiation channels of a TRIGA Mark II reactor. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 257:545–549
Yavar AR, Sarmani S, Wood AK, Fadzil SM, Masood Z, Khoo KS (2011) Neutron flux parameters for k0-NAA method at the Malaysian Nuclear Agency Research Reactor after core reconfiguration. Radiat Meas 46:219–223
Jaćimović R, De Corte F, Kennedy G, Vermaercke P, Revay Z (2014) The 2012 recommended k0 database. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 300:589–592
Tupinambá GAC (1969) Análise de rotina de urânio e tório pelo método dos nêutrons retardados (Routine analysis of uranium and thorium by the delayed neutron method) M.Sc. dissertation, UFMG, Belo Horizonte (in Portuguese)
Menezes MABC, Sabino CVS (1999) Thorium: determination by CDTN. Czech J Phys 49:359–365
Montoya E, Bedregal P, Mendoza P, Ubillús M, Torres B, Cohen IM (2010) The development of the k0 method in Peru: past, present and future perspectives. Nucl Instr Meth A 622:381–384
Sabino CVS, Rossi HM, Kastner GF, Franco MB, Tests to establish the k0-method at CDTN/CNEN using the reactor TRIGA MARK I IPR-RI, CDTN-805/95, Belo Horizonte, 1995 (in Portuguese)
Franco MB, Sabino CVS (2002) Determinação dos parâmetros nucleares α, f e temperatura de nêutrons no reator TRIGA Mark I IPR-R1 (Determination of nuclear parameters α, f and temperature of neutrons in the TRIGA Mark I IPR-R1 reactor) INAC/ENAN 2002, Conferência Internacional Nuclear do Atlântico/Encontro de Aplicações Nucleares Nucleares (In Portuguese) https://www.ipen.br/biblioteca/cd/inac/2002/ENAN/E02/E02_365.PDF Accessed 23 May 2022
Franco MB (2006) Levantamento de parâmetros nucleares do reator TRIGA Mark I IPR RI com configuração concêntrica visando a aplicação da técnica de ativação neutrônica paramétrica k0 (Survey of nuclear parameters of the TRIGA Mark I IPR RI reactor with concentric configuration aiming at the application of the neutron activation technique k0) Ph.D. thesis, UNICAMP, São Paulo (in Portuguese)
Menezes MÂBC, Sabino CVS, Franco MB, Kastner GF, Rossi EHM (2003) k0 - Instrumental neutron activation establishment at CDTN, Brazil: a successful story. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 257:627–632
Menezes MABC, Jacimovic R (2011) k0-INAA quality assessment by analysis of soil reference material GBW07401 using the comparator and neutron flux monitor approaches. Appl Radiat Isot 69:1057–1063
Menezes MABC, Sabino CVS, Maria AA, Mattos SVM, Santos Filho S (2000) k0-NAA applied to certified reference materials and hair samples: evaluation of exposure level in a galvanising industry. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 245:173–178
Menezes MABC, Sabino CVS, Franco MB, Maia ECP, Albinati CCB (2004) Assessment of workers` contamination caused by air pollution exposure in industry using biomonitors. J Atmos Chem 49:403–414
Leal A, Menezes MABC, Vermaercke P, Sneyers L, Jensen C (2006) Investigation of chemical impurities in formulations, phytotherapics and polyvitaminic medicines by k0-instrumental neutron activation analysis. Nucl Instr Meth A 564:729–732
HYPERLAB-PC V5.0, User’s Manual, Institute of Isotopes, Budapest, Hungary, 2002.
KAYZERO/SOLCOI, User’s Manual, for reactor neutron activation analysis (NAA) using the k0 standardisation method, Ver. 5a, February, 2003.
Menezes MABC, Jaćimović R (2006) Optimised k0-instrumental neutron activation method using the TRIGA Mark I IPR-R1 Reactor at CDTN/CNEN, Belo Horizonte, Brazil. Nucl Instr Meth A 564:707–715
Avelar AC, Ferreira WM, Menezes MABC (2015) Dietary phosphate contribution to uranium deposition in rabbit shinbones. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 304:1071–1076
Salles PMB, Menezes MABC, Jaćimović R, Campos TPR (2015) Inorganic elements in sugar samples consumed in several countries. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 308:485–493
Salles PMB, Menezes MABC, Sathler MM, Moura RR, Campos TPR (2017) Elemental composition of dietary supplements most consumed in Belo Horizonte, Brazil, analysed by k0-INAA. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 312:421–431
Sathler MM, Salles PMB, Menezes MÂBC (2019) Trace elements detection in whole food samples by neutron activation analysis, k0-method. Brazilian J Radiation Sci 7:1–13
Beinner MA, Menezes MÂBC, Silva JBB, Amorim FR, Jansen AK, Lamounier JA (2010) Plasma zinc and hair zinc levels, anthropometric status and food intake of children in a rural area of Brazil. Rev Nutr 23:75–83
Menezes MÂBC, Maia ECP, Albinati CCB, Amaral AM (2007) Assessment of gold exposure and contamination in galvanising workplace applying neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 271:119–123
Leal AS, Menezes MÂBC, Jaćimović R, Sepe FP, Gomes TCB (2014) Investigation of the quality of the drug Enalapril commercialized by pharmacies of manipulation in Belo Horizonte Brazil. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 300:645–651
Silveira JN, Menezes MÂBC, Lara PCP, Beinner MA, Silva JBB (2015) Determination of Al Ca, Cl, Cr, K, Mg, Sb and Ti in industrialized and formulated antihypertensive drugs using neutron activation analysis. J Pharm Biol Sci 10:40–45
Barbosa NPU, Fernandes GW, Uemura G, Menezes MÂBC, Matos LVS, Silva MA, Menezes RSC, Almeida-Cortez JS (2013) Calotropis procera: um levantamento preliminar sobre as suas capacidades de fitoextração no Brasil. Neotropical Biol Conserv 8:150–155
Jaćimović R, Menezes MÂBC, Kennedy G, Vermaercke P (2017) Losses of Cr content in plant samples using digestion procedures with acids. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 1:1–4
Oliveira KAP, Menezes MÂBC, Jacomino VMF, Sperling EV (2013) Use of nuclear technique in samples for agricultural purposes. Engenharia Agrícola 33:46–54
Silva WF, Menezes MÂBC, Marques DJ (2019) Corn cultivation for silage: evaluation of elemental composition in the soil and plants by neutron activation analysis. J Exp Agric Int 32:1–9
Menezes MÂBC, Falnoga I, Slejkovec Z, Jaćimović R, Couto N, Deschamps E, Faganeli J (2020) Arsenic in sediments, soil and plants in a remediated area of the Iron Quadrangle, Brazil, and its accumulation and biotransformation in Eleocharis geniculata. Acta Chim Slov 67:985–991
Passos RG, Cota SDS, Menezes MÂBC, Palmieri HEL, Auler LMLA (2021) Effect of partial lockdown due to Covid-19 pandemic on PM10 concentration in Belo Horizonte Brazil. Desenvolvimento e Meio Ambiente 58:351–362
Viana CO, Menezes MÂBC, Pereira-Maia EC (2011) Epiphytic lichens on air biomonitoring in Belo Horizonte City, Brazil: a preliminary assessment. Int J Environ Health 5:324–336
Moura IFS, Barreto AA, Cesar HS, Cruz AB, Menezes MÂBC (2018) Use of statistical multivariate analysis to identify sources emitting particulate matter in Belo Horizonte, Brazil. Revista Ambiente e Agua 13(1–12):e2202
Moura IFS, Cruz AB, Cesar HS, Oliveira AF, Barreto AA, Menezes MÂBC (2019) Use of the neutron activation analysis, k0-standardized method, in the evaluation of the air quality in critical points of Belo Horizonte. Brazilian J Radiation Sci 7:1–14
Menezes MÂBC, Pereira-Maia EC, Filho S, Albinati C, Sabino CVS (2004) Assessment of workers’ contamination caused by air pollution exposure in industry using biomonitors. J Atmos Chem 49:403–414
Menezes MABC, Maia EC, Albinati CC, Sabino CVS, Batista JR (2004) How suitable are scalp hair toenail as biomonitors. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 259:81–86
Menezes MÂBC, Jaćimović R, Pereira C (2015) Spatial distribution of neutron flux in geological larger sample analysis at CDTN/CNEN Brazil. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 306:611–616
Menezes MÂBC, Jaćimović R (2014) Implementation of a methodology to analyse cylindrical 5-g sample by neutron activation technique, k0 method, at CDTN/CNEN Belo Horizonte, Brazil. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 300:523–531
Dutra Neto A, Menezes MÂBC, Pelaes OAC, Jaćimović R (2018) Automatic sample changer for neutron activation analysis at CDTN Brazil. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 1:1–6
Menezes MÂBC, Jaćimović R, Ribeiro L (2018) Contribution of analytical nuclear techniques in the reconstruction of the Brazilian prehistory analyzing archaeological ceramics of Tupiguarani Tradition. IAEA-TECDOC 1838:4–22
Silva BC, Cury LA, Leal AS, Menezes MÂBC, Nagorny S, St N, Saiki M, Jaćimović R, Krambrock K (2021) Neutron-induced point defects and luminescence properties of enriched Zn Se crystals. J Appl Phys 130:054502
Ferreira MP, Da Nova MW, Dutra PR, Menezes MÂBC, Pedrosa TA (2021) Physical-chemical exfoliation of pristine graphite flakes. Radiat Phys Chem 188:109652
Moura RR, Menezes MÂBC, Pujoni DGF, Salles PMB (2022) Evaluation of uranium and thorium in environmental monitoring program using NAA, k0 method: case study at the Nuclear Technology Development Centre. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 331:4437–4450
HyperLab 2002 System (2002) Installation and Quick Start Guide, HyperLabs software, Budapest, Hungary. http://www.hlabsoft.com/web/support/hl2002_2003-02.php. Accessed 20 Jul 2022
Kayzero for Windows® (2011) User’s Manual, for reactor neutron activation analysis (NAA) using the k0 standardisation method, Ver. 2.46. k0-Ware, Heerlen, The Netherlands
Kayzero for Windows® (KayWin), (2017) User's Manual for reactor neutron activation analysis (NAA) using the k0 standardization method Version 3.37
ISO/IEC 17025:2017, General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. International Organization for Standardization, Dec 2017
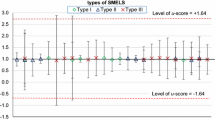
Menezes MÂBC, Jaćimović R (2008) Validation of the k0_IAEA software using SMELS material at CDTN/CNEN. Brazil, J Radioanal Nucl Chem 278:607–611
Fajon V, Horvat M, Kotnik J, Jaćimović R, Heath D (2019) Report on the Interlaboratory Comparisons, Trace elements in mushroom PT Mushroom, ISO-FOOD, Era Chair for Isotope Techniques in Food Quality, Safety and Traceability
ISO 13528:2015, Statistical methods for use in proficiency testing by interlaboratory comparisons, second edition 2015–08–01, issued by ISO-Geneva (CH), International Organization for Standardization
Bode P (2013) Evaluation of results of an Interlaboratory Comparison in 2013 by participants in IAEA/AFRA project RAF 4/022, IAEA ARCAL RLA 0037 and IAEA RER 4/032– 1/007, reference CSA-RAF4022–29–01
WEPAL, Wageningen University, Environmental Sciences (2015) Quarterly Report 2015.1, January–March. Wageningen Evaluating Program for Analytical Laboratories, International Plant-Analytical Exchange – IPE, 104p
WEPAL, Wageningen University, Environmental Sciences (2015) Quarterly Report 2015.1, January–March. Wageningen Evaluating Program for Analytical Laboratories, International Soil-Analytical Exchange–ISE, 214p
WEPAL, Wageningen University, Environmental Sciences (2015) Quarterly Report 2015.2, April – June. Wageningen Evaluating Program for Analytical Laboratories, International Plant-Analytical Exchange – IPE, 94p.
WEPAL, Wageningen University, Environmental Sciences (2015) Quarterly Report 2015.2, April – June. Wageningen Evaluating Program for Analytical Laboratories, International Soil-Analytical Exchange – ISE, 206p.
WEPAL, Wageningen University, Environmental Sciences (2017) Quarterly Report 2017.3, July – September. Wageningen Evaluating Program for Analytical Laboratories, International Plant-Analytical Exchange – IPE, 224p.
WEPAL, Wageningen University, Environmental Sciences (2017) Quarterly Report 2017.3, July – September. Wageningen Evaluating Program for Analytical Laboratories, International Plant-Analytical Exchange – ISE, 703p.
Worldwide Open Proficiency Test for Neutron Activation Analysis Laboratories PTNAAIAEA15 Determination of Major, Minor and Trace Elements in a Marine Sediment and in an Animal Tissue. http://www.pt-nsil.com/ Accessed 20 Jul 2022
Worldwide Open Proficiency Test for Nuclear and Related Analytical Techniques Laboratories PTNATIAEA16 Determination of Major, Minor and Trace Elements in a Cereal Grain http://www.pt-nsil.com/ Accessed 20 Jul 2022
Worldwide Open Proficiency Test for Neutron Activation Analysis Laboratories PTNAAIAEA17 Determination of Major, Minor and Trace Elements in a Land-plant material and a Siliceous material http://www.pt-nsil.com/ Accessed 20 Jul 2022
PTNATIAEA19 Worldwide Open Proficiency Test for Nuclear and Related Analytical Techniques Laboratories. Determination of Major, Minor and Trace Elements in a Clay Sample and in a Plant Sample PTNATIAEA19 – 4 March 2022 http://www.pt-nsil.com/ Accessed 20 Jul 2022
Jaćimović R, Menezes MABC (2022) Reevaluation of spectral parameters and neutron fluxes in IC-7 Irradiation channel of TRIGA MARK I IPR-R1 research nuclear reactor. J Nuclear Eng Radiation Sci 8:041504-1–041504-6
Acknowledgements
The authors thank to CAPES, FAPEMIG, CNPq, and CDTN/CNEN by financial, material and technical-scientific support for the development of this method along the years. We are also thankful to the International Atomic Energy Agency for supporting the Experts’ Missions of Dr. Radojko Jaćimović and acquirement of first version of software HyperLab and Kayzero/Solcoi, and also to Slovenian Research Agency (ARRS) through programme P1-0143 and the Metrology Institute of the Republic of Slovenia (MIRS) under contract No. C3212-10-000071 (6401-5/2009/27) for activities and obligations performed as a Designate Institute. The authors also thank to Fausto Maretti Júnior (retired), Dante Zamgirolami (retired), Luiz Claudio Andrade and Daniel Almeida Magalhães Campolina, Supervisors of the TRIGA Mark I IPR-R1 reactor, and Paulo Fernando Oliveira (retired) and Luiz Otávio Ivanenko Sette Câmara, Marlucio Antonio da Silva, José Augusto Ribeiro da Silva, Reactor Operators, for providing assistance and operating the reactor during the analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menezes, M.A.d.B.C., Sabino, C.d.V.S. & Jaćimović, R. k0-Neutron Activation Analysis at CDTN, Brazil: 27 years of history, development and main achievements. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 332, 3457–3468 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-08804-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-08804-9