Abstract
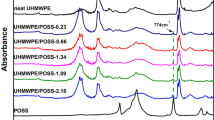
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE)/disilanolisobutyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocomposites in a disentangled state were synthesized by in situ ethylene polymerization. This is the first report of a detailed study on the phase structure and mechanical properties of disentangled UHMWPE/ POSS nanocomposites in a solid state. The phase structure and chain dynamics of UHMWPE nanocomposites were characterized using wide-line proton NMR and 13C cross-polarization/magic-angle spinning (CP/MAS) solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The results showed that a strong interaction between the POSS and nascent UHMWPE matrix occurred in a solid state, especially in the intermediate and monoclinic crystalline phases. This strong interaction between POSS particles and UHMWPE chains may result in improved melt recovery properties. Mechanical testing indicated that the lowest friction coefficients and highest breaking strength were achieved when 1 wt% loading of POSS was incorporated. The influence of the microstructure on lubrication and mechanical properties was also studied.

Probable mechanism of polymer growth during ethylene polymerization









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones RL, Armoush M (2009) Catalysts for UHMWPE. Macromol Symp 88:283–284
Sun YS, Duan YR, Chen XY, Zhang Q, Jin XF, Li JX, Ma Y, Sun L, Wang QR (2006) Research on the molecular entanglement and disentanglement in the dry spinning process of UHMWPE/decalin solution. J Appl Polym Sci 102:864–875
Jauffres D, Lame O, Vigier G, Dore F (2008) How Nascent Structure of Semicrystalline Polymer Powders Enhances Bulk Mechanical Properties. Macromolecules 41:9793–9801
Sharma KG (2005) Easily Processable Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene with Narrow Molecular Weight Distribution.Ph.D. Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology
Rizwan M, Mcgarry FJ (2004) Processing of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene by hot isostatic pressing, and the effect of processing parameters on its microstructure. Polym Eng Sci 44:1848–1857
Park K, Mishra S, Lewis G, Losby J, Fan ZB, Park JB (2004) Biomaterials Quasi-static and dynamic nanoindentation studies on highly crosslinked ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. 25:2427–2436
Deng M, Shalaby SW (1997) Validation of a small punch testing technique to characterize the mechanical behaviour of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. Biomaterials 18:1659–1663
Wright TM, Astion DJ, Bansal M, Rimnac CM, Green T, Insall JN, Robinson RP (1988) Failure of carbon fiber-reinforced polyethylene total knee-replacement components. A report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 70:926–932
Lewis G (2001) Properties of crosslinked ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. Biomaterials 22:371–401
Tang W, Santare MH, Advani SG (2003) Melt processing and mechanical property characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotube/high density polyethylene (MWNT/HDPE) composite films. Carbon 41:2779–2785
Bahuleyan BK, Atieh MA, De SK, Khan MJ, Al-Harthi MA (2012) Easy one-pot method to control the morphology of polyethylene/carbon nanotube nanocomposites using metallocene catalysts. J Polym Res 19:9744–9752
Hu Z, Liu CB (2013) Polyethylene/graphite oxide nanocomposites obtained by in situ polymerization using modified graphite oxide–supported metallocene catalysts. J Polym Res 20:39–47
Stürzel M, Kempe F, Thomann Y, Mark S, Enders M, Mülhaupt R (2012) Novel Graphene UHMWPE Nanocomposites Prepared by Polymerization Filling Using Single-Site Catalysts Supported on Functionalized Graphene Nanosheet Dispersions. Macromolecules 45:6878–6887
Ronca S, Forte G, Tjaden H, Yao YF, Rastogi S (2012) Tailoring molecular structure via nanoparticles for solvent-free processing of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composites. Polymer 53:2897–2907
Li W, Guan C, Xu J, Mu JS, Gong DR, Chen ZR, Zhou Q (2014) Disentangled UHMWPE/POSS nanocomposites prepared by ethylene in situ polymerization. Polymer 55:1792–1798
Blümich B (2000) NMR Imaging of Materials. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Yao YF, Jiang SZ, Rastogi S (2014) 13C Solid State NMR Characterization of Structure and Orientation Development in the Narrow and Broad Molar Mass Disentangled UHMWPE. Macromolecules 47:1371–1382
Li W, Adams A, Wang JD, Blümich B, Yang YR (2010) Polyethylene/palygorskite nanocomposites: Preparation by in situ polymerization and their characterization. Polymer 51:4686–4697
Li W, Jiang BB, Buda A, Wang JD, Blümich B, Yang YR, Zheng J (2010) An NMR investigation on the phase structure and molecular mobility of the novel exfoliated polyethylene/palygorskite nanocomposites. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phy 48:1363–1371
Massiot D, Fayon F, Capron M, King I, Le Calve S, Alonso B, Durand JQ, Bujoli B, Gan ZH, Hoatson G (2002) Modelling one- and two-dimensional solid-state NMR spectra. Magn Reson Chem 40:70–76
Earl WL, Vanderhart DL (1979) Observations in Solid Polyethylenes by Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance with Magic Angle Sample Spinning. Macromolecules 12:762–767
Tzou DL, Schmidt-Rohr K, Spiess HW (1994) Solid-state n.m.r. studies of crystalline phases in gel-spun ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. Polymer 35:4728–4733
Hillebrand L, Schmidt A, Bolz A, Hess M, Meier WVR, Velden G (1998) Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Detection of Two Distinctly Different Chains in the Orthorhombic Crystalline Phase of Polyethylenes. Macromolecules 31:5010–5021
Milliman HW, Ishida H, Schiraldi DA (2012) Structure property relationships and the role of processing in the reinforcement of nylon 6-poss blends. Macromolecules 45:4650–4657
Seguela R (2005) Critical review of the molecular topology of semicrystalline polymers: The origin and assessment of intercrystalline tie molecules and chain entanglements. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys 43:1729–1748
Soares JBP, Abbott RF, Kim JD (2000) Environmental stress cracking resistance of polyethylene: The use of CRYSTAF and SEC to establish structure–property relationships. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys 38:1267–1275
Han J, Ding SY, Zheng WG, Li WY, Li H (2013) Microstructure and anti- wear and corrosion performances of novel UHMWPE/graphene-nanosheet composite coatings deposited by flame spraying. Polym Adv Tech 24:888–894
Shan CLP, Soares JBP, Penlidis A (2003) HDPE/LLDPE reactor blends with bimodal microstructures— Part II: rheological properties. Polymer 44:177–185
Zhang QH, Lippits DR, Rastogi S (2006) Dispersion and Rheological Aspects of SWNTs in Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene. Macromolecules 39:658–666
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding from the Natural Science Foundation of China Project (No. 21206078), the Key Innovation Team of Zhejiang Province (2011R50001-5, -11), sponsored by the K.C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1998 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Yang, H. & Li, W. Phase structure and mechanical properties of disentangled ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposites in a solid state. J Polym Res 22, 223 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0867-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0867-3