Abstract
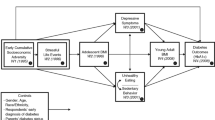
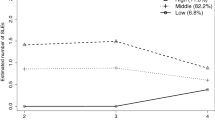
Research has primarily focused on additive (unique) associations between early stressful life experiences (specifically, socioeconomic adversity and maltreatment) and young adults’ cardiometabolic disease risk without considering multiplicative (synergistic) influences. Furthermore, research has not fully considered the varying patterns of health risk trajectories (e.g., substance use, obesogenic-related behaviors, depressive symptoms) across adolescence and the transition to young adulthood that may link earlier stressful experiences and later cardiometabolic disease risk. This study examined heterogeneity in conjoint health risk trajectories from adolescence to the transition to young adulthood and their additive and multiplicative (synergistic) influences with early stressful life experiences on cardiometabolic disease risk in young adulthood using data from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health (n = 9,421; 55.6% female) over a period of 13 years. Four distinct conjoint health risk trajectories were identified considering trajectories of substance use behaviors, obesogenic-related behaviors, and depressive symptoms: (a) overall high-risk, (b) behavioral risks, (c) psycho-obesogenic risks, and (d) overall low-risk. Socioeconomic adversity and maltreatment were additively and multiplicatively associated with cardiometabolic disease risk in young adulthood. Individuals with overall high-risk conjoint trajectories averaged higher cardiometabolic disease risk in young adulthood when they were exposed to early socioeconomic adversity. Implications for personalized interventions for individuals who have experienced multiple forms of health risks are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addington, J., & Duchak, V. (1997). Reasons for substance use in schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandivica, 96, 329–333. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.1997.tb09925.x.
Adkins, D. E., Daw, J. K., Mcclay, J. L., & Van den Oord, E. J. C. G. (2012). The influence of five monoamine genes on trajectories of depressive symptoms across adolescence and young adulthood. Development and Psychopathology, 24, 267–285. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579411000824.
Aiken, L. S., & West, S. G. (1991). Multiple regression: testing and interpreting interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications.
Arnett, J. J. (2000). Emerging adulthood: a theory of development from the late teens through the twenties. American Psychologist, 55, 469–480. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066x.55.5.469.
Audrain-McGovern, J., Rodríguez, D., & Moss, H. (2003). Smoking progression and physical activity. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention, 12, 1121–1129.
Barboza, G. E. (2018). Latent classes and cumulative impacts of adverse childhood experiences. Child Maltreatment, 23, 111–125. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077559517736628.
Benner, A. D., & Wang, Y. (2015). Adolescent substance use: the role of demographic marginalization and socioemotional distress. Developmental Psychology, 51, 1086–1097. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000026.
Berk, L. E. (2010). Exploring lifespan development. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Blain, S. D., Sasseen, T. A., Xi, M., Zhao, D., & DeYoung, C. C. (2020). Extraversion but not depression predicts reward sensitivity: Revisiting the measurement of anhedonic phenotypes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspp0000371.
Brody, G. H., Yu, T., Chen, Y., Kogan, S. M., Evans, G. W., & Beach, S. R. H., et al. (2013). Cumulative socioeconomic status risk, allostatic load, and adjustment: A prospective latent profile analysis with contextual and genetic protective factors. Developmental Psychology, 49, 913–927. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028847.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: experiments in nature and design. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Cicchetti, D. & & Toth, S. L. (1995). A developmental psychopathology perspective on child abuse and neglect. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 34(5), 541–565. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199505000-00008.
Cockerham, W. C. (2013). Bourdieu and an Update of Health Lifestyle Theory. In Cockerham W. (Ed). Medical Sociology on the Move (pp. 127-54). Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-6193-3_7.
Daw, J., Margolis, R., & Wright, L. (2017). Emerging adulthood, emergent health lifestyles: sociodemographic determinants of trajectories of smoking, binge drinking, obesity, and sedentary behavior. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 58, 181–197. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022146517702421.
Doom, J. R., Mason, S. M., Suglia, S. F., & Clark, C. J. (2017). Pathways between childhood /adolescent adversity, adolescent socioeconomic status, and long-term cardiovascular disease risk in young adulthood. Social Science & Medicine, 188, 166–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.06.044.
Enders, C. K., & Bandalos, D. L. (2001). The relative performance of full information maximum likelihood estimation for missing data in structural equation models. Structural Equation Modeling, 8, 430–457. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15328007sem0803_5.
Evan, G. W., Li, D., & Whipple, S. S. (2013). Cumulative risk and child development. Psychological Bulletin, 139, 1342–1396. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0031808.
Frech, A. (2012). Healthy behavior trajectories between adolescence and young adulthood. Advances in Life Course Research, 17(752), 59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcr.2012.01.003.
Grant, B. F., Stinson, F. S., Dawson, D. A., Chou, P., Dufour, M. C., Pickering, R. P., & Kaplan, K. (2004). Prevalence and co-occurrence of substance use disorders and independent mood and anxiety disorders. Archives of General Psychiatry Abbreviation, 61, 807–816. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.61.8.807.
Gearhardt, A. N., Harrison, E. L. R., & McKee, S. A. (2012). Does co-morbid depression alter the inverse relationship between obesity and substance use disorders? Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 124, 185–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.01.002.
Hentges, R. F., Shaw, D. S., & Wang, M. (2018). Early childhood parenting and child impulsivity as precursors to aggression, substance use, and risky sexual behavior in adolescence and early adulthood. Development and Psychopathology, 30, 1305–1319. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579417001596.
Hirshkowitz, M., Whiton, K., Albert, S. M., Alessi, C., Bruni, O., & DonCarlos, L., et al. (2015). The National Sleep Foundation’s sleep time duration recommendations: Methodology and results summary. Sleep Health, 1, 40–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2014.12.010.
Horan, J. M., & Widom, C. S. (2015). Cumulative childhood risk and adult functioning in abused and neglected children grown up. Development and Psychopathology, 27, 927–941. https://doi.org/10.1017/s095457941400090x.
Hostinar, C. E., Lachman, M. E., Mroczek, D. K., Seeman, T. E., & Miller, G. E. (2015). Additive contributions of childhood adversity and recent stressors to inflammation at midlife: findings from the MIDUS study. Developmental Psychology, 51, 1630–1644. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000049.
Howe, G. W. (2019). Preventive effect heterogeneity: causal inference in personalized prevention. Prevention Science, 20, 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-017-0826-9.
Hume, C., Timperio, A., Veitch, J., Salmon, J., Crawford, D., & Ball, K. (2011). Physical activity, sedentary behavior, and depressive symptoms among adolescents. Journal of Physical Activity & Health, 8, 152–156. https://doi.org/10.1123/jpah.8.2.152.
Isasi, C. R., Ostrovsky, N. W., & Wills, T. A. (2013). The association of emotion regulation with lifestyle behaviors in inner-city adolescents. Eating Behaviors, 14, 518–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2013.07.009.
Jones, N. L., Gilman, S. E., Cheng, T. L., Drury, S. S., Hill, C. V., & Geronimus, A. T. (2019). Life course approaches to the causes of health disparities. American Journal of Public Health, 109(Suppl 1), S48–S55. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.2018.304738.
Kinra, S., Nelder, R. P., & Lewendon, G. J. (2000). Deprivation and childhood obesity: a cross sectional study of 20973 children in Plymouth, United Kingdom. Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health, 54, 456–460. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.54.6.456.
Kuh, D., Ben-Shlomo, Y., Lynch, J., Hallqvist, J., & Power, C. (2003). Life course epidemiology. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 57, 778–783. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.57.10.778.
Laceulle, O. M., Veenstra, R., Vollebergh, W. A. M., & Ormel, J. (2019). Sequences of maladaptation: preadolescent self-regulation, adolescent negative social interactions, and young adult psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 31, 279–292. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579417001808.
Lawrence, E. M., Mollborn, S., & Hummer, R. A. (2017). Health lifestyles across the transition to adulthood: Implication for health. Social Science & Medicine, 193, 23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.09.041.
Lee, T. K., Wickrama, K. A. S., & O’Neal, C. W. (2019). Early socioeconomic adversity and cardiometabolic risk in young adults: Mediating roles of risky health lifestyle and depressive symptoms. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 42, 150–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-018-9952-5.
Lee, T. K., Wickrama, K. A. S., Kwon, J. A., Lorenz, F. O., & Oshri, A. (2017). Antecedents of transition patterns of depressive symptoms trajectories from adolescence to young adulthood. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 35, 498–515. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjdp.12189.
Leeb, R. T., Paulozzi, L. J.,Melanson, C., Simon, T. R., &Arias, I. (2008). Child maltreatment surveillance: Uniform definitions for public health and recommended data elements, version 1.0. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/pdf/cm_surveillance-a.pdfhttps://doi.org/10.1037/e587022010-001.
Little, R. J. A. (1988). A test of missing completely at random for multivariate data with missing values. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 83, 1198–1202. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1988.10478722.
Loxton, N. J. (2018). The role of reward sensitivity and impulsivity in overeating and food addiction. Current Addiction Reports, 5, 212–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40429-018-0206-y.
McLafferty, M., O’Neill, S., Murphy, S., Armour, C., Ferry, F., & Bunting, B. (2018). The moderating impact of childhood adversity profiles and conflict on psychological health and suicidal behavior in the Northern Ireland population. Psychiatry Research, 262, 213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2018.02.024.
McLaughlin, K. A., & Sheridan, M. A. (2016). Beyond cumulative risk: A dimensional approach to childhood adversity. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 25, 239–245. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721416655883.
Miller, G. E., Chen, E., & Parker, K. J. (2011). Psychological stress in childhood and susceptibility to the chronic disease of aging: Moving toward a model of behavioral and biological mechanisms. Psychological Bulletin, 137, 959–997. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0024768.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2017). Mplus User’s Guide. Eighth Edition Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén.
Nylund, K., Belmore, A., Nishina, A., & Graham, S. (2007). Subtypes, severity, and structural stability of peer victimization: What does latent class analysis say? Child Development, 78, 1706–1722. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2007.01097.x.
Oshri, A., Kogan, S., Kwon, J., Wickrama, K., Vanderbroek, L., Palmer, A., & MacKillop, J. (2018). Impulsivity as a mechanism linking child abuse and neglect with substance use in adolescence and adulthood. Development and Psychopathology, 30, 417–435. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579417000943.
Patrick, M. E., Wightman, P., Schoeni, R. F., & Schulenberg, J. E. (2012). Socioeconomic status and substance use among young adults: A comparison across constructs and drugs. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 73, 772–782. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsad.2012.73.772.
Pickering, R. P., Goldstein, R. B., Hasin, D. S., Blanco, C., Smith, S. M., & Grant, B. F. (2011). Temporal relationships between overweight and obesity and DSM-IV substance use, mood, and anxiety disorders: Results from a prospective study, the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 73, 1494–1502. https://doi.org/10.4088/jcp.10m06077gry.
Radloff, L. S. (1977). The CES-D: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement, 3, 385–401. https://doi.org/10.1177/014662167700100306.
Rodriguez, V. J., Chahine, A., Parrish, M. S., Alcaide, M. L., Lee, T. K., Hurwitz, B., Sawhney, M., Weiss, S. M., Jones, D. L., & Kumar, M. (2020). The contribution of syndemic conditions to cardiovascular disease risk. AIDS Care, 13, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2020.1761518.
Saydah, S., Bullard, K. M., Imperatore, G., Geiss, L., & Gregg, E. W. (2013). Cardiometabolic risk factors among US adolescents and young adults and risk of early mortality. Pediatrics, 31, e679–e686. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-2583.
Scheidell, J. D., Quinn, K., McGorray, S. P., Frueh, B. C., Beharie, N. N., & Cottler, L. B., et al. (2018). Childhood traumatic experiences and the association with marijuana and cocaine use in adolescence through adulthood. Addiction, 113, 44–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.13921.
Sittner, K. J. (2016). Trajectories of substance use: onset and adverse outcomes among North American Indigenous adolescents. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 26, 830–844. https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.12233.
Spence, C. (2017). Breakfast: The most important meal of the day? International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science, 8, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgfs.2017.01.003.
Tsai, A. C., Mendenhall, E., Trostle, J. A., & Kawachi, I. (2017). Co-occurring epidemics, syndemics, and population health. The Lancet, 389, 978–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(17)30403-8.
UNICEF. (2011). The state of the world’s children 2011. Retrieved from https://www.unicef.org/sowc2011/pdfs/SOWC-2011-Executive-Summary-LoRes_EN_12132010.pdf
Wickrama, K. A. S., Bae, D., & O’Neal, C. W. (2017). Explaining the association between early adversity and young adults’ diabetes outcomes: Physiological, psychological, and behavioral mechanisms. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 46, 2407–2420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-017-0639-y.
Wickrama, K., Lee, T., & O’Neal, C. (2018). Genetic moderation of multiple pathways linking early cumulative socioeconomic adversity and young adults’ cardiometabolic disease risk. Development and Psychopathology, 30, 165–177. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579417000542.
Wickrama, K. A. S., Lee, T. K., O’Neal, C. W., & Lorenz, F. O. (2016). Higher-order growth curves and mixture modeling with Mplus: a practical guide. New York, NY: Routledge. 10.4324/9781315642741.
Wickrama, K. A. S., O’Neal, C. W., Lee, T. K., & Wickrama, T. (2015). Early socioeconomic adversity, youth positive development, and young adults’ cardio-metabolic disease risk. Health Psychology, 34, 905–914. https://doi.org/10.1037/hea0000208.
Acknowledgements
This research uses data from Add Health, a program project directed by Kathleen Mullan Harris and designed by J. Richard Udry, Peter S. Bearman, and Kathleen Mullan Harris at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and funded by grant P01- HD31921 from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, with cooperative funding from 23 other federal agencies and foundations. Special acknowledgment is due Ronald R. Rindfuss and Barbara Entwisle for assistance in the original design. Information on how to obtain the Add Health data files is available on the Add Health website (http://www.cpc.unc.edu/addhealth). No direct support was received from Grant P01-HD31921 for this analysis.
Authors’ Contributions
T.K.L. conceived of the study design, performed statistical analysis and interpretation of the data, and drafted the manuscript; K. A. S. W. contributed to the study design, interpretation of the data, and helped to draft the manuscript; C.W.O. participated in the interpretation of the data and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Data Sharing and Declaration
This research uses data from Add Health, a program project directed by Kathleen Mullan Harris and designed by J. Richard Udry, Peter S. Bearman, and Kathleen Mullan Harris at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Information on how to obtain the Add Health data files is available at http://www.cpc.unc.edu/addhealth.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, T.K., Wickrama, K.A.S. & O’Neal, C.W. How Early Stressful Life Experiences Combine With Adolescents’ Conjoint Health Risk Trajectories to Influence Cardiometabolic Disease Risk in Young Adulthood. J Youth Adolescence 50, 1234–1253 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-021-01440-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-021-01440-0